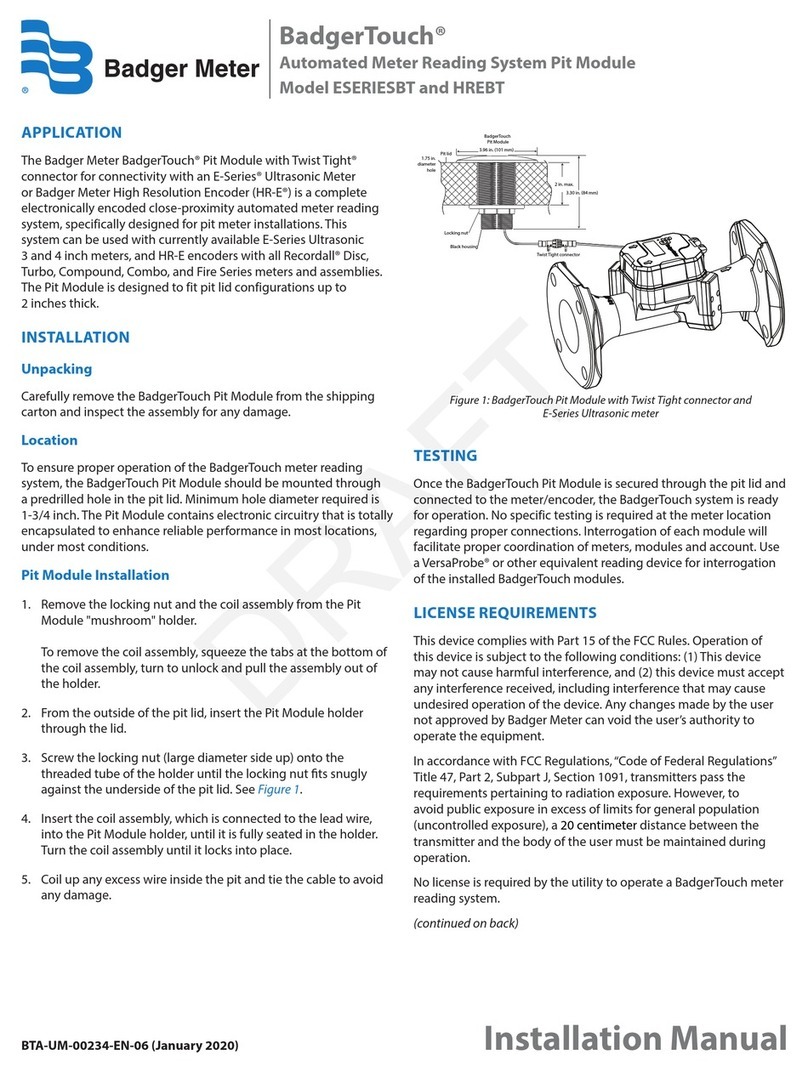
ELTRA CS-580A User manual

© Eltra GmbH, 42781 Haan, Retsch-Allee 1-5, Germany 02.07.2014 0001
Operating Manual
Carbon and Sulfur Analyzer CS-580A (Helios)
Original

2
Copyright
© Copyright by
Eltra GmbH
Haan, Retsch-Allee 1-5
D-42781 Haan
Federal Republic of Germany

3

4
1Notes on the Service Manual ................................................................................................................6
1.1 Explanations of the safety warnings .................................................................................................. 6
2Installation...............................................................................................................................................8
2.1 Setting check up ................................................................................................................................ 8
2.2 Front panel illustration ....................................................................................................................... 9
2.3 Mains power connections ................................................................................................................ 10
2.4 Data Interface .................................................................................................................................. 11
2.5 Oxygen connection .......................................................................................................................... 12
2.6 Operation modes ............................................................................................................................. 12
2.7 Adjusting the gas flow...................................................................................................................... 14
2.8 Temperature adjustment.................................................................................................................. 15
2.9 Preheating the furnace .................................................................................................................... 15
2.9.1 Configuration of preheating ......................................................................................................... 15
2.9.2 BIOS-configuration ...................................................................................................................... 16
3Analysis.................................................................................................................................................17
3.1 Working procedure .......................................................................................................................... 17
3.1.1 Procedure of carrying out analyses with autoloader.................................................................... 17
3.1.2 Procedure of carrying out analyses with manual loading of the sample ..................................... 18
3.2 TIC-determination ............................................................................................................................ 19
3.2.1 TIC-module .................................................................................................................................. 19
3.2.2 TIC analysis ................................................................................................................................. 19
3.2.3 TIC-module installation ................................................................................................................ 20
3.2.4 TIC-module Operation procedure ................................................................................................ 21
3.3 Applications...................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.1 Coal.............................................................................................................................................. 22
3.3.2 Calcium Carbonate ...................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.3 Graphite ....................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.4 Limestone .................................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.5 Oil, Asphalt and Rubber............................................................................................................... 22
3.3.6 Wood............................................................................................................................................ 22
4Maintenance..........................................................................................................................................24
4.1 General information ......................................................................................................................... 24
4.2 Reagent tubes filling ........................................................................................................................ 26
4.2.1 Reagent tube replacing................................................................................................................ 26
4.2.2 Filling quantities ........................................................................................................................... 27
4.3 Moisture trap replacing (furnace)..................................................................................................... 29
4.4 O-rings replacing ............................................................................................................................. 29
4.5 Dust filter cartridge replacing ........................................................................................................... 30
4.6 Combustion tube replacing .............................................................................................................. 31
4.7 Lance replacing ............................................................................................................................... 32
4.8 Heating elements replacing ............................................................................................................. 33
5Function description ............................................................................................................................35
5.1 Measuring principle.......................................................................................................................... 35
5.2 Gas flow system .............................................................................................................................. 36
5.3 Infrared cell ...................................................................................................................................... 39
5.4 Micro-controller unit and PC Software............................................................................................. 40

5
6Ordering numbers ................................................................................................................................41
6.1 Analyszer front view......................................................................................................................... 41
6.2 Rear side (outside view) .................................................................................................................. 42
6.3 Bottom (outside view) ...................................................................................................................... 43
6.4 Left side view (inside) ...................................................................................................................... 44
6.5 Furnace side (inside view) ............................................................................................................... 46
6.6 TIC-module ...................................................................................................................................... 48
6.7 Packaging ........................................................................................................................................ 50
7Pre-installation guide ...........................................................................................................................51
8Approved methodologies to which Eltra instruments conform ......................................................52
8.1 Inorganic materials (Metals) ............................................................................................................ 52
8.2 Organic materials (Oil, Coal, foodstuffs).......................................................................................... 53
9Disposal.................................................................................................................................................54
10 Index ......................................................................................................................................................55
Appendix .................................................................................................................................. following page

Notes on the Service Manual
6
1 Notes on the Service Manual
1.1 Explanations of the safety warnings
In this Operating Manual we give you the following safety warnings
Mortal injury may result from failing to heed these safety warnings. We give you
the following warnings and corresponding content.
DANGER
Type of danger / personal injury
Source of danger
–Possible consequences if the dangers are not observed.
•Instructions on how the dangers are to be avoided.
We also use the following signal word box in the text or in the instructions on action
to be taken:
DANGER
Serious injury may result from failing to heed these safety warnings. We give you
the following warnings and corresponding content.
WARNING
Type of danger / personal injury
Source of danger
–Possible consequences if the dangers are not observed.
•Instructions on how the dangers are to be avoided.
We also use the following signal word box in the text or in the instructions on action
to be taken:
WARNING
Moderate or mild injury may result from failing to heed these safety warnings.
We give you the following warnings and corresponding content.
CAUTION
Type of danger / personal injury
Source of danger
–Possible consequences if the dangers are not observed.
•Instructions on how the dangers are to be avoided.
We also use the following signal word box in the text or in the instructions on action
to be taken:
CAUTION
In the event of possible property damage we inform you with the word
“Instructions” and the corresponding content.

Notes on the Service Manual
7
NOTICE
Nature of the property damage
Source of property damage
–Possible consequences if the instructions are not observed.
•Instructions on how the dangers are to be avoided.
We also use the following signal word in the text or in the instructions on action to
be taken:
NOTICE

Installation
8
2 Installation
2.1 Setting check up
Since the analyser weighs about 90 kg it should be placed on a suitably stable
surface. Due to the balance, the platform should be as free of vibration as possible.
The loader is attached to the right side of the analyser. There are no strong
recommendations where to place the balance, PC, display and printer. Generally,
placing them on the right is recommended. The size of a desktop (approx. 200 cm
80 cm for the analyzer with 130-crucibles autoloader) is sufficient for the entire set-
up.
Below is an example of installation:
Fig. 1:Arrangement Suggestion
The environment of the device does not have to necessarily be air-conditioned,
although it is best if the room temperature remains between 18°C and 30°C.
NOTICE
Under no conditions the device should be placed in direct sunshine!
Avoid places exposed to the wind of air conditioners or to the wind blowing through
open windows or doors.
01
2
3
C / S - A n a l y s e r
A u t o s a m p l e r
Air
Powe r
Inlet
Gas
Pr e c l e a n i n g
MAXDATA
Magic
T A R E
C FI / O F
T A R E
sart oriu s
C A L
C a r ri e r
Mois t u r e t r a p
H E L I O S
80
20
120
Air 2 0 ° C 101 3 2 5 P a l / h
200
50
300
Air 2 0 ° C 101 3 2 5 P a l / h
200
100
50
300
Air 2 0 ° C 101 3 2 5 P a l / h
I n le t
Lance
100
40
Fi l t e r

Installation
9
2.2 Front panel illustration
Fig. 1: Illustration front panel
1
Moisture trap
2
Carrier gas purification
3
Mains power switch
4
Compressed air gauge
5
Oxygen pressure gauge
6
Furnace inlet flow adjustment
7
Furnace inlet flow meter
8
Carrier gas flow meter
9
Lance flow meter
10
Lance flow adjustment
11
Furnace low inlet
12
Dust filter cartridge
01
2
3
C / S - A n a l y s e r
A u t o s a m p l e r
A i r
Po w e r
I n l e t
G a s
P r e c l e a n i n g
C a r r i e r
M o i s t u r e t r a p
H E L I O S
80
20
12 0
Ai r 20 ° C 10 1 3 2 5 P a l/ h
20 0
50
30 0
Ai r 20 ° C 10 1 3 2 5 P a l/ h
20 0
10 0
50
30 0
Ai r 20 ° C 10 1 3 2 5 P a l / h
I n l e t
La n c e
10 0
40
F i l t e r
1
2
3
4
5
8
6
9
10
11
13

Installation
10
2.3 Mains power connections
Since the infrared cell requires about 1 hour for reaching a stable operating
temperature, it is advisable to first connect the analyzer to the mains power and to
set the mains power switch to position 1 before further installation work is carried
out.
This waiting time is only necessary when the analyzer was completely switched off
(position 0). It is recommended to keep the analyzer at standby (position 1) during
working breaks, to keep the IR-cell operating temperature stable.
The furnace temperature is software controlled.
Fig. 2:Rearview –Mains power connections
1
Analyzer
2
Computer
3
Monitor
4
Printer
5
Balance
6
Quad power socket
At first, only the analyzer (1) is plugged in and switched on. Turn the mains power
switch to position 1 (stand-by condition). The switch is on the front panel of the
analyzer. See chapter front panel illustration
The mains power cable of the analyzer is mounted inside the analyzer.
35434
1
2
2
3
4
51
6
Pass the cables
through the
provided hole
between the two fans
of the bottom panel.

Installation
11
All power cables of peripheral devices [computer (2), the printer (4) and the
balance (5)] should be connected to the quad mains power socket (6) as shown in
the figure.
Remark
Before placing balance, PC, display and printer on the desk for connecting their
power cables, the loader should be attached to the analyzer and aligned. Please,
refer to “LOADER installation, service and operation manual” for the instructions on
installation, connection and alignment of the loader.
2.4 Data Interface
Fig. 3: Microcontroller board
1
PC USB connector
2
Power and temperature control interface
3
Analog input/output signals
4
Pump control
5
24V connector
6
Digital input/output signals
7
Autoloader connection
8
Regulating valve (not relevant for CS-580A)
When all units are connected to the mains power, then interface connections can
be made. The required interface cables are included in the scope of supply. The
supplied additional devices have been already adapted to the interfaces when the
analyzers are taken into operation in our company. The plugs are all different from
each other, so that they cannot be interchanged. The computer is already provided
with operation system and with software for controlling the analyzer.

Installation
12
Please note: As the balance transfers the weight to the PC, its serial interface must
be programmed. This is important, if you use a balance, which was not ordered
with the analyzer.
NOTICE
For all instructions for using the PC software refer to the Help-function of the
software.
2.5 Oxygen connection
The analyzer requires two gas connections: oxygen and compressed air. The
necessary tubes for connecting the analyser to the oxygen and compressed air
supplies are shipped with the analyzer.
Fig. 4: Oxygen and air connection s–rear side of device
Tube (1) connects the oxygen supply to the analyzer on the fitting of a pressure
regulator. This connection must be very secure, considering that the incoming
oxygen pressure in the tube is 2 to 4 bar (30 to 60 psi). Do not tighten the nut too
much in order to avoid damaging of the tube. Drive the cup nut manually. Don’t use
any tool.
Fig. 2: Compressed air connection
The tube (2) connects the device through a connector with the compressor or
compressed air supply. For connecting the tube, simply push it into the connector.
This connection must be also very secure, considering that the pressure in the
compressed air is 4 to 6 bar (60 to 90 psi).
2.6 Operation modes
There are 4 different positions of the mains power switch possible:
2
1
2

Installation
13
0
Off.
The analyzer is completely switched off.
1
Standby.
The thermostatic control of the IR-cell is
switched on. The furnace is switched off
and the gas flow is disabled.
Communication with the PC is possible.
2
Furnace on.
Furnace is switched on, but the gas flow
remains disabled.
3
Gas flow.
All functions of the analyzer are in
operation mode.
In case the analyzer was switched off (pos. 0) for long, it should be set to pos. 1 for
at least 1 hour, in order for the IR-cell to reach the stable operating temperature.
The furnace heating-up time depends on the set temperature. In order to power the
furnace, the analyzer has to be switched to position 2. At this position the gas flow
is still disabled so that there is no gas consumption.
For running analyses set the power switch to position 3. At this position, the pump
is enabled so that air and any moisture which has entered the gas flow system can
be purged by the oxygen flow. Keep it there for about 10-15 minutes before starting
the first analysis. To save time, the purging can be started before the set
temperature has been reached. The slight influence of the oxygen flow on the
temperature of the infrared cell is compensated.
At short working breaks (like lunch breaks) the mains switch remains on position 2
(furnace on) to save gas and to keep the set temperature.
During longer breaks, e.g. after finishing the work for the day, the mains switch is
set to position 1 (standby). The thermostatic control of the infrared cell is then
working, so that no long warm-up time is needed, when re-starting the analyzer.
Energy consumption and wear are negligible on standby. The analyzer is designed
for long term use, so that no damage results.
Switch off the analyzer (position 0) is only useful, when working break takes
several days or weeks.
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3
01
2
3

Installation
14
2.7 Adjusting the gas flow
Fig. 3: Illustration front panel
1
Moisture trap
2
Carrier gas purification
3
Mains power switch
4
Compressed air gauge
5
Oxygen pressure gauge
6
Furnace inlet flow adjustment
7
Furnace inlet flow meter
8
Carrier gas flow meter
9
Lance flow meter
10
Lance flow adjustment
11
Furnace low inlet
12
Dust filter cartridge
01
2
3
C / S - A n a l y s e r
A u t o s a m p l e r
A i r
Po w e r
I n l e t
G a s
P r e c l e a n i n g
C a r r i e r
M o i s t u r e t r a p
H E L I O S
80
20
12 0
Ai r 20 ° C 10 1 3 2 5 P a l/ h
20 0
50
30 0
Ai r 20 ° C 10 1 3 2 5 P a l/ h
20 0
10 0
50
30 0
Ai r 20 ° C 10 1 3 2 5 P a l / h
I n l e t
La n c e
10 0
40
F i l t e r
1
2
3
4
5
8
6
9
10
11
13

Installation
15
2.8 Temperature adjustment
The furnace temperature is PC-controlled.
The CS-580A is delivered with 1350°C set temperature saved in a software profile.
After switching on the instrument at position 2 and starting of the UNI-software, the
heating up to the set temperature is started automatically. (The cable connection
between instrument and PC is in the scope of supply).
The actual furnace temperature and the set temperature are visible in the window
Heater.
You can change the set temperature in the window Configuration.
Fig. 4: Window Configuration –Heater –Temperature
2.9 Preheating the furnace
NOTICE
For heating up, the mains power switch of the analyzer has to be at position 2 and
the PC has to be switched on. The configuration of the BIOS has to be done by the
customer as needed.
During heating up to the set temperature, the ceramic combustion tube is under
high thermic stress. This stress is increased with increasing speed of the heating
up process.
For maximum service life of the combustion tube, the furnace can be heated up
slowly with a heating rate of 10°C/min. In order to avoid long waiting time until the
furnace heats up, the heating up of the furnace can be started automatically long
before the work begins. See chapter Bios Configuration
Please note that the automatic preheating can only be started when the analyzer
temperature is below 100°C.
NOTICE
The analyzer is delivered with a default heating rate of 10°C/min. Much higher
heating rates are possible; however with respect to the service life of the
combustion tube, higher rates should only be used when necessary.
2.9.1 Configuration of preheating
1. Open the window Default and choose Configuration.
Fig. 5: window Default
2. In the chapter Furnace you find Preheat.

Installation
16
Fig. 6: Window Configuration –Heater - Preheating
The value shows the chosen heating rate in °C/min. (The preheating function is
switched off by entering 0 in this place. Then, the heating occurs with maximum
speed after start of the UNI-software.)
3. Save your entry with Enter.
4. The preheating starts automatically with the next start of the software, if the
furnace temperature is lower than 100°C and the analyzer switch is at
position 2.
NOTICE
When the preheating function is activated (by any other value except 0) the
software automatically creates a shortcut at the startup menu of Windows. This
enables the start of the UNI-software with every start of the PC. The shortcut is
deleted automatically when the preheating is deactivated.
2.9.2 BIOS-configuration
In order to start the preheating before the work begins, the BIOS has to be
configured to start the PC automatically at the selected time. (The preheating starts
automatically by starting the UNI-software.)
1. Switch on your PC and enter the BIOS by pressing the corresponding key
(e.g. F2). The normal booting process is interrupted and the BIOS menu
appears.
2. Choose Power Management Setup
3. Activate "Resume by Alarm" (enabled).
4. Enter the required days and times when the heating up of the analyzer
should be started.
5. Save your entries at Save/Exit with Yes.
6. The booting process will be sustained.

Analysis
17
3 Analysis
3.1 Working procedure
With the CS-580A (Helios), a wide variety of materials can be analyzed. The
analysis methods are therefore diverse. As different materials burn differently, the
chosen sample weight, the possible accelerators and the sensitivity of the infrared
cells will all be different. The user of the device can receive from us free advice
regarding the different methods involved for different materials. The sensitivities of
the infrared cells are optimized, free of charge, for each individual purpose.
In the following, the procedures are described for the analysis of coal samples.
Before starting making analyses ensure the following:
–The temperature of the analyzer is stable (at least one to two hours on
setting 1).
–The moisture traps are checked and, if necessary, the magnesium
perchlorate is replaced. See chapter “Moisture trap replacing furnace“.
–The incoming oxygen supply has a pressure of 2-4 bar (30 to 60 psi).
–The furnace has reached its operating temperature. See chapter
“Temperature adjustment“.
–The mains switch is set to position 3 for at least 10 to 15 minutes.
–The software is started on the connected PC.
3.1.1 Procedure of carrying out analyses with autoloader
1. Place an empty crucible on the balance.
2. Tare the balance using the “Tare” button, located on the balance, or
“F6-Tare” button in the “Analysis control” window of the software (F6
on the PC-keyboard).
3. Put about 250 mg coal sample into the crucible.
4. Press the “F4-Balance” button in the ”Analysis control” window of the
software (or F4 on the PC-keyboard) to transfer the weight value from
the balance to the PC. The transfer function is performed regardless
how often the button is pressed. This enables a correction of any
falsely entered weight.
5. Enter the sample ID into the corresponding input field of the “Analysis
control” window of the software. This step is optional. If no sample ID
is required, the entry may be omitted.
6. Press the “F7-Add” button in the “Loader” window. The sample weight
and sample ID are transferred to the loader stack and memorized
there.
7. Take the crucible from the balance and put it on the loader, on the first
tray before the pick-up position.
8. Mark the “F8-Run/Stop” checkbox to start the analysis.
The analysis procedure begins. From now on, no operator intervention is required.
The furnace is opened automatically, the crucible of the previous analysis is picked
up from the pedestal and disposed, and the crucible is taken from the loader and
put on the pedestal for analysis. The furnace closes. At the end of analysis, the
results are displayed on the PC-screen and saved in the database of the software.
A series of analyses can be run with the CS-580A (Helios) analyzer. To do this,
repeat steps 1 to 7 for every sample in the series, while each crucible is placed as
next after the last one placed on the loader. This can be done at any time, with or
without running analyses.
When putting the samples on the loader, the order of positioning the crucibles on
the trays must be respected, i.e. the crucibles must be placed on the loader exactly

Analysis
18
in the same order in which they are weighed and memorized in the loader stack. It
is allowed to leave one or more empty trays on the loader, for example in order to
separate groups of crucibles carrying the same sample material or a calibration
standard etc.
3.1.2 Procedure of carrying out analyses with manual loading of the sample
Although the CS-580A (Helios) is equipped with an autoloader and normally
analyses are carried out using this autoloader, it is possible to load the sample
manually for analysis.
•Place an empty crucible on the balance.
•Tare the balance using the “F6-Tare” button located on the balance,
or the “Tare” button in the “Analysis control” window of the software
(F6 on the PC-keyboard).
•Put around 250 mg of coal sample into the crucible.
•Press the “F4-Balance” button in the ”Analysis control” window of the
software (F4 on the PC-keyboard) to transfer the weight value from
the balance to the PC. The transfer function is performed regardless
of how often the button is pressed. This enables a correction of any
falsely entered weight.
•Enter the sample ID into the corresponding input field of the “Analysis
control” window of the software. This step is optional. If no sample ID
is required, the entry may be omitted.
•Press the “F2-Furnace” button to open the furnace (if it is closed).
•Take the crucible from the balance and put it on the pedestal.
•Press the “F5-Start” button to begin the analysis.
From now on, no further operator intervention is required. The furnace closes and
the analysis is carried out automatically. At the end of each analysis, the results
are displayed on the PC-display and saved in the database of the software.
Remarks
The sulfur range should be deactivated when only carbon is required. This avoids
undue delays of the analysis caused by sulfur compounds which are difficult to
burn, like it is in case of cement analysis. Accelerators are also not necessary.
The sample weights are valid when the detectors have appropriate sensitivities and
the right path lengths of the IR-cells. If not, the analysis condition can be improved
by sample weight variation.
Generally, the weight has an optimum size when the peaks on the screen reach
the middle of the range, i.e. the peak maximum go up to 4 to 6 volts.
The sample weight should be reduced when the IR-cell is saturated. However,
when the weight is lower than 100 mg, the accuracy will be reduced due to the
samples being not homogeneous and due to lower weighing accuracy.

Analysis
19
3.2 TIC-determination
3.2.1 TIC-module
Due to the modular design of the CS-580 (Helios), the analyzer can be upgraded
by a module for Total Inorganic Carbon (TIC) without further modification. For the
TIC determination, the sample is treated with acid in the TIC module.
3.2.2 TIC analysis
The sample is treated with acid in an Erlenmeyer flask inside the TIC-module. The
acid decomposes the carbonates in the sample, creating CO2. The oxygen flow
purges the CO2 out of the flask through the gas flow system to the infrared
detector.
Fig. 7: Installation of TIC-module
Fig. 5: TIC-module
1
TIC module

Analysis
20
2
CO2 outlet
3
Glass distributor
4
Connection to the furnace
5
Acid supply
6
50 ml glass flask
7
Heater with magnetic stirrer
8
Elevator with variable height
9
Acid
10
Furnace
11
Analyzer
12
Moisture trap
13
TIC/TC toggle
3.2.3 TIC-module installation
1. The TIC module is placed next to the analyzer.
2. Connect the mains power plug to a power socket.
3. Connect the TIC module and the analyzer with the provided tubes. The
connectors are located at the backside of the analyzer and of the TIC-
module.
4. The outlet of the furnace is connected via the H2O trap to the connection (2)
and finally to the inlet (1) of the TIC module.
5. Inside the TIC module, this tube is connected to the input of the glass
distributor (3) (connection on top tube 4).
6. The bottle of acid with dispenser (9) is placed to the right of the platform (8)
and it is connected to the connection (5) of the glass distributor.
7. The glass distributor (3) with the glass flask (6) is adjusted properly when the
whole surface of the bottom of the glass flask (6) touches the surface of the
heater (7).
8. The heater (7) is switched on and the temperature is set to 75°C.
9. The stirrer is set to 400.
Other manuals for CS-580A
1
Table of contents
Other ELTRA Measuring Instrument manuals

ELTRA
ELTRA CS-580A User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA CSi/d User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA CS-800 User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA Thermostep TGA User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA CS-800 User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA ELEMENTRAC CS-i User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA ON-900 User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA CS-i User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA CS-2000 User manual

ELTRA
ELTRA ON-900 User manual
Popular Measuring Instrument manuals by other brands

XS Instruments
XS Instruments OXY 7 Vio instruction manual

Southwest Microwave
Southwest Microwave INTREPID MicroTrack II Installation and operation manual

Forward
Forward SM-8800 user manual

In-situ
In-situ Level TROLL 500 Operator's manual

geo-FENNEL
geo-FENNEL S-Digit multi user manual

Megger
Megger DLRO-H200 user guide