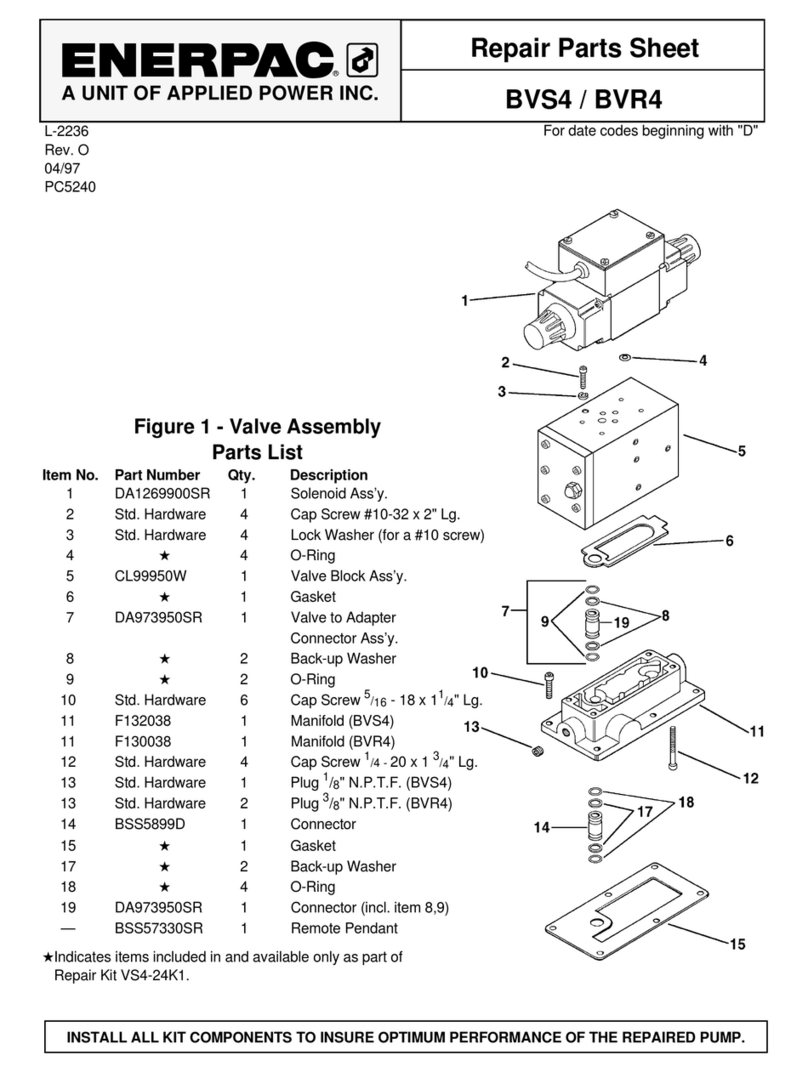
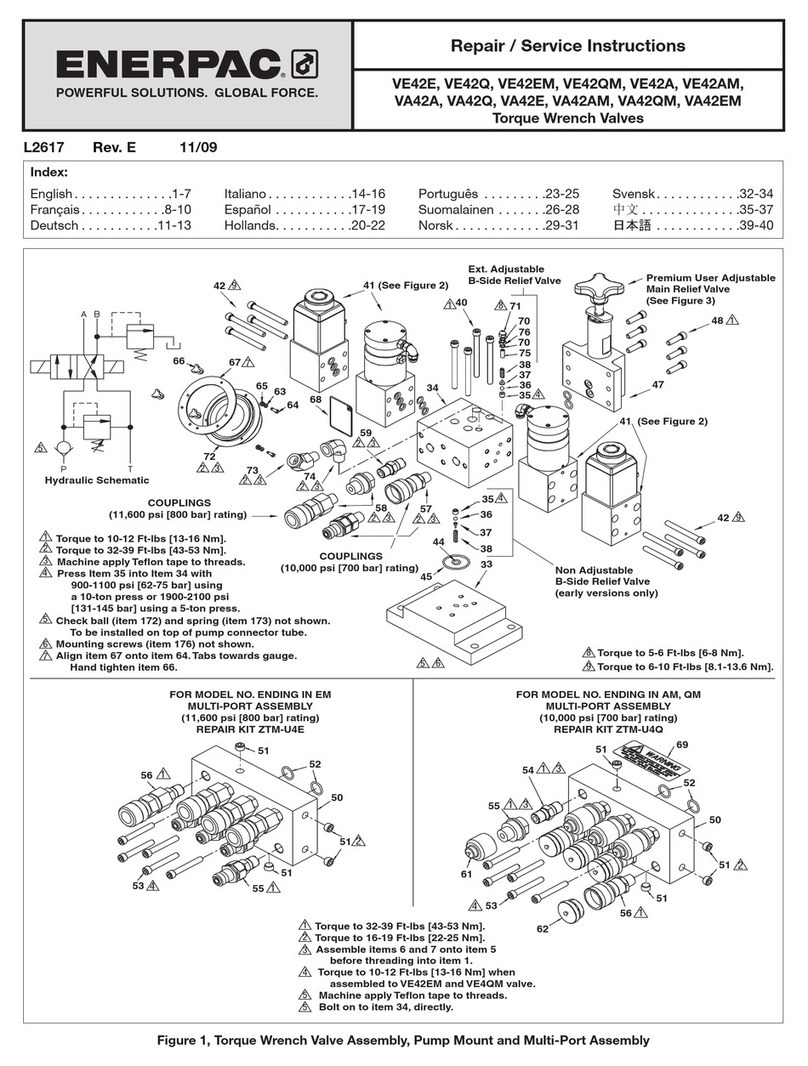
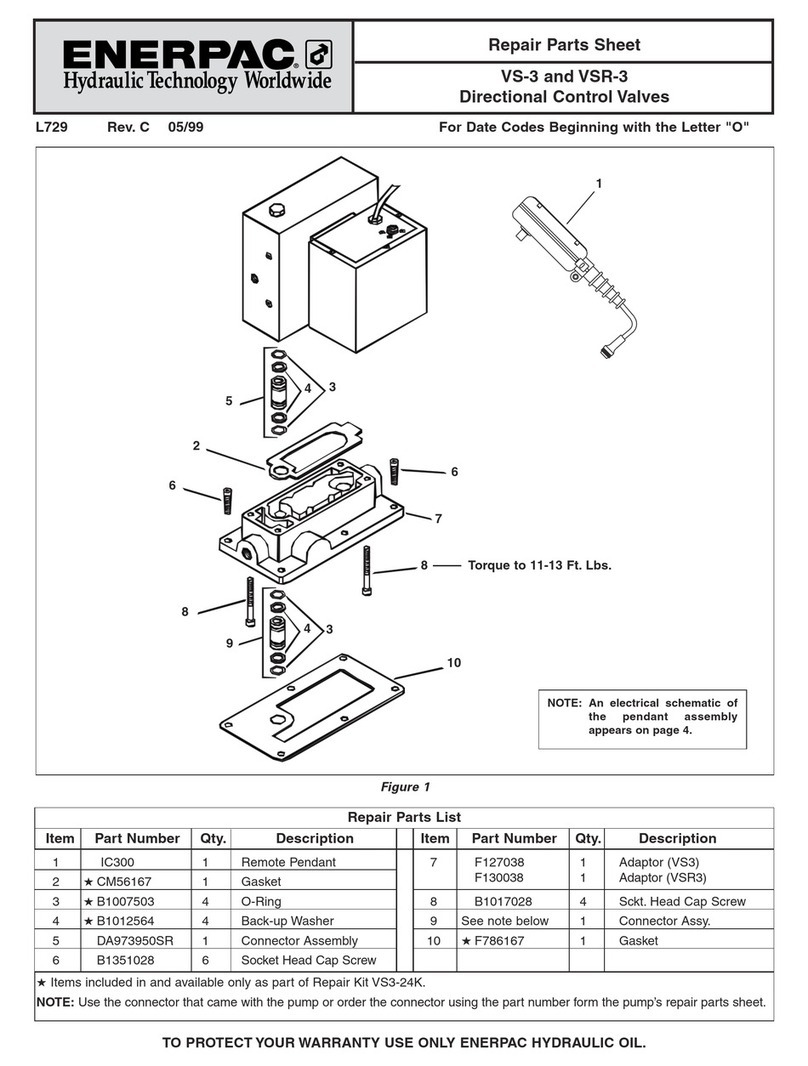
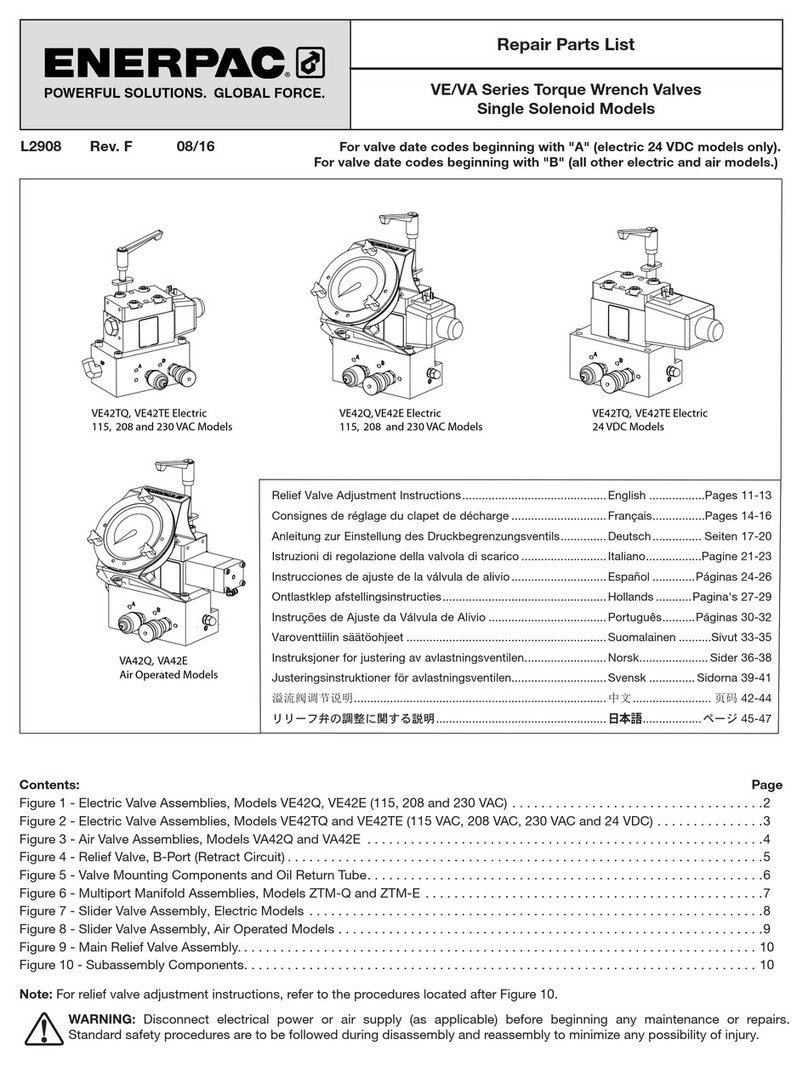
4L4523_a
• Verify that all appropriate safety measures have
been taken to avoid the risk of injury and property
damage from your application or system.
• Be sure that all personnel involved with operating
or servicing the workholding devices read and
understand the information contained in the
manuals included with these devices. Observe
and follow all safety instructions and precautions
contained in the manuals.
• Design the control units of power operated
clamping systems to avoid inadvertent or
unauthorized activation.
• Be sure that clamping cylinders and other similar
workholding devices are properly positioned
before clamping forces are applied.
• Maintain a safe distance from clamping elements
and workpiece to avoid personal injury. Stay clear
of pinch points. Keep your hands, feet and body
away from the clamping area.
• Use mechanical devices and not fingers to hold
a part in place until the clamping hydraulics are
activated. Do not remove or disable the pressure
relief valve.
Hydraulic equipment must only be serviced
by a qualified hydraulic technician. For repair service,
contact the Enerpac authorized service center in your
area.
1.1.2 Hydraulic Intensifier Safety
Precautions (All PID Series Models)
Failure to observe and comply with the
following precautions could result in death or serious
personal injury. Property damage could also occur.
• Be sure that the hydraulic pump or system hydraulic
power unit is turned off and disconnected from
power source before beginning any work. Lockout
and tag controls to prevent accidental startup as
installation is being performed.
• Be sure that any hydraulic pressure in the circuit is
completely relieved before loosening any hydraulic
fittings or removing any hoses or components. All
gauges must indicate zero (0) psi/bar. Be certain
that no hydraulic hoses are stiff and that there are
no other indications of trapped pressure within the
system.
• Work with clean tools in clean surroundings, free
of dust or dirt.
• Ensure that the intensifier installation is performed
only by trained and qualified personnel, familiar with
the setup and installation of hydraulic equipment.
• If unsure about safety, installation or adjustment
procedures described in this manual, consult
an experienced hydraulic systems engineer or
technician, and if needed, the Enerpac Technical
Service Department.
• Never exceed the maximum rated operating
pressure of the intensifier. Never exceed the
maximum pressure rating of other devices in
the circuit. Refer to the tables in Section 2.0 of
this manual for intensifier maximum operating
pressures.
1.0 SAFETY
Read all instructions carefully. Follow all recommended
safety precautions to avoid personal injury as well as
damage to the product and/or damage to other property.
Enerpac cannot be responsible for any damage or injury
from unsafe use, lack of maintenance, or incorrect
operation. Do not remove warning labels, tags, or
decals. In the event that any questions or concerns
arise, contact Enerpac or a local Enerpac distributor for
clarification.
Save these instructions for future use.
Appropriate training in the safe use of workholding
hydraulic systems and components is required prior to
the installation and operation of the intensifier. If training
is needed, contact your local Enerpac distributor or
authorized service center for information about an
Enerpac hydraulic safety training course.
This manual follows a system of safety alert symbols,
signals, words, and safety messages to warn the user of
specific hazards. Failure to comply with these warnings
could result in death or serious personal injury, as well
as damage to the equipment or other property.
The Safety Alert Symbol appears throughout
this manual. It is used to alert you to potential
physical injury hazards. Pay close attention
to Safety Alert Symbols and obey all safety
messages that follow this symbol to avoid the possibility
of death or serious injury.
Safety Alert Symbols are used in conjunction with certain
Signal Words that call attention to safety messages or
property damage messages and designate a degree or
level of hazard seriousness. The Signal Words used in
this manual are WARNING, CAUTION and NOTICE.
Indicates a hazardous situation that, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious personal injury.
Indicates a hazardous situation that, if not
avoided, could result in minor or moderate personal
injury.
Indicates information considered important,
but not hazard related (e.g. messages related to property
damage). Please note that the Safety Alert Symbol will
not be used with the signal word.
1.1 Hydraulic Safety Precautions
1.1.1 General Workholding Safety
Precautions
Failure to observe and comply with the
following precautions could result in death or serious
personal injury. Property damage could also occur.
• Although hydraulic operation moves the control of
the clamping fixture to an area of greater safety,
operators must still remain alert and use common
sense practises during their work.
• Use care when selecting components for the
workholding application so that safe operation
is ensured. Be certain that all components and
devices are of adequate rated capacity to perform
their intended functions. Do not exceed equipment
ratings.