SECTION
3 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
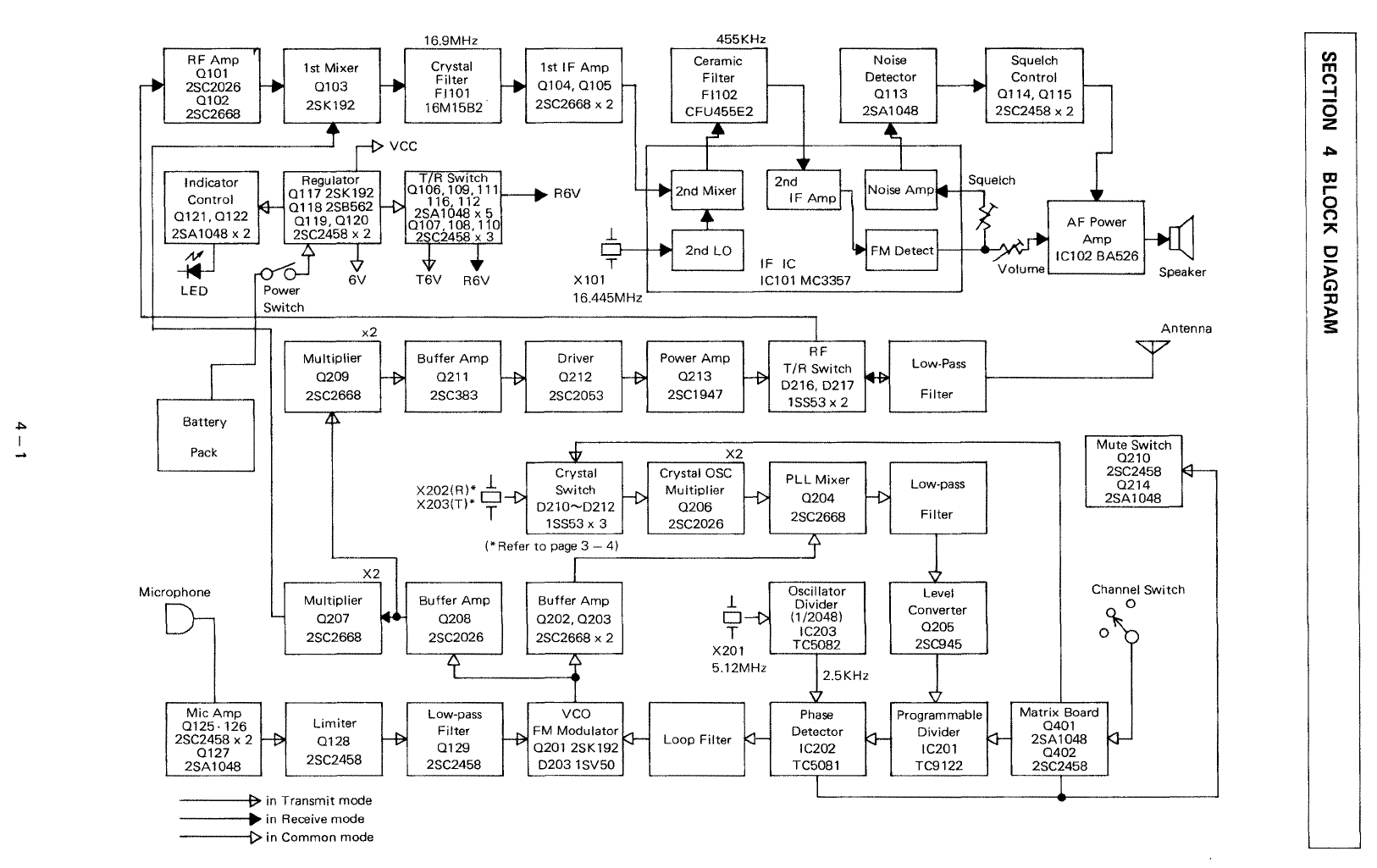
3 - 1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
3 - 1 - 1 ANTENNA SWITCHING CIRCUIT
Signals from the antenna connector are fed
to
the antenna switching circuit through Chebyshev low-pass
filter consisting
of
L229, L230, C295, C297 and C298 in the PLL board.
The antenna switching circuit employs a quater wave switching circuit.
In
the
receive mode, switching diodes,
0216
and
0217
are turned OFF, and
they
make isolation against
the transmitter circuit and matching circuit, and the incoming signals are fed
to
the
RF
amplifier.
3 - 1 • 2
RF
AMPLIFIER
AND
FIRST MIXER
The signals from the switching circuit are fed
to
the
cascode amplifier
0101
and
0102.
The amplified signals are fed
to
the gate of the first mixer
0103
through the band-pass filter L102 -
L104, which reduces interference and intermodulation from
out
of the band signals.
To the source of
0103,
a 140MHz signal*
is
supplied from the PLL circuit
to
convert the RF signals into
16.9MHz first
IF
signals. (*This frequency differs depending on the version, and it can
be
calculated by
formula; "Receive frequency" -16.9MHz.)
The first
IF
signals are taken from the drain
of
0103
and fed
to
the
IF
circuit.
3 -
1·3
IF
CIRCUIT
The first
IF
signals from
0103
are fed
to
the
matched pair crystal filter F1101, then
IF
amplifiers
0104
and
0105.
The amplified signals are fed
to
IC101. IC101
is
composed
of
the second localoscillator, second mixer,
limiter amplifier, quadrature detector and active filter circuits.
The second local oscillator oscillates 16.445MHz with X101, and
is
fed
to
the second mixer with thefirst
IF
signals
to
convert into 455KHz second
IF
signals. The second
IF
signals are put
out
from
Pin
3, and
fed
to
external ceramic filter F1102 which has excellent selectivity, then fed
to
IC101
(Pin
5) again
to
amplify and detect.
The detected AF signals are put
out
from
Pin
9.
3 - 1 - 4
AF
AND
SQUELCH CIRCUITS
The detected AF signals are
put
6dB/Octave de-emphasis by integral circuit consisting of R117 and Cl26,
and fed
to
AF power amplifier IC102 through
the
VOLUME control R1,
to
obtain enough power
to
drive
the
speaker.
Noise components put
out
from
Pin
9 of
IC101
are fed
to
IC101
(Pin
10) again through the SQUELCH
control R2, which controls the squelch threshold level, filtered about 20KHz signal {noise) and
put
out
from Pin 11.
This signal (noise)
is
rectified by
0113,
integrated by R135, R136 and C136, and turns
0114
ON
and
turns OFF
the
regulator for AF power amplifier consisting of
0103,
0115
and
0116.
This reduces the current drain of the set,
in
the standby condition.
When
a signal
is
received, noise
is
suppressed by
the
signal and turns
0114
OFF and
the
regulator
is
turned
ON
and supplies regulated
voltage
to
the AF power amplifier, and incoming signal can be heard from
the
speaker.
In
the transmit mode, a voltage
is
applied
to
0114
and turns it ON, and turns the regulator OFF
the
same
as
in
the standby condition.
3-1