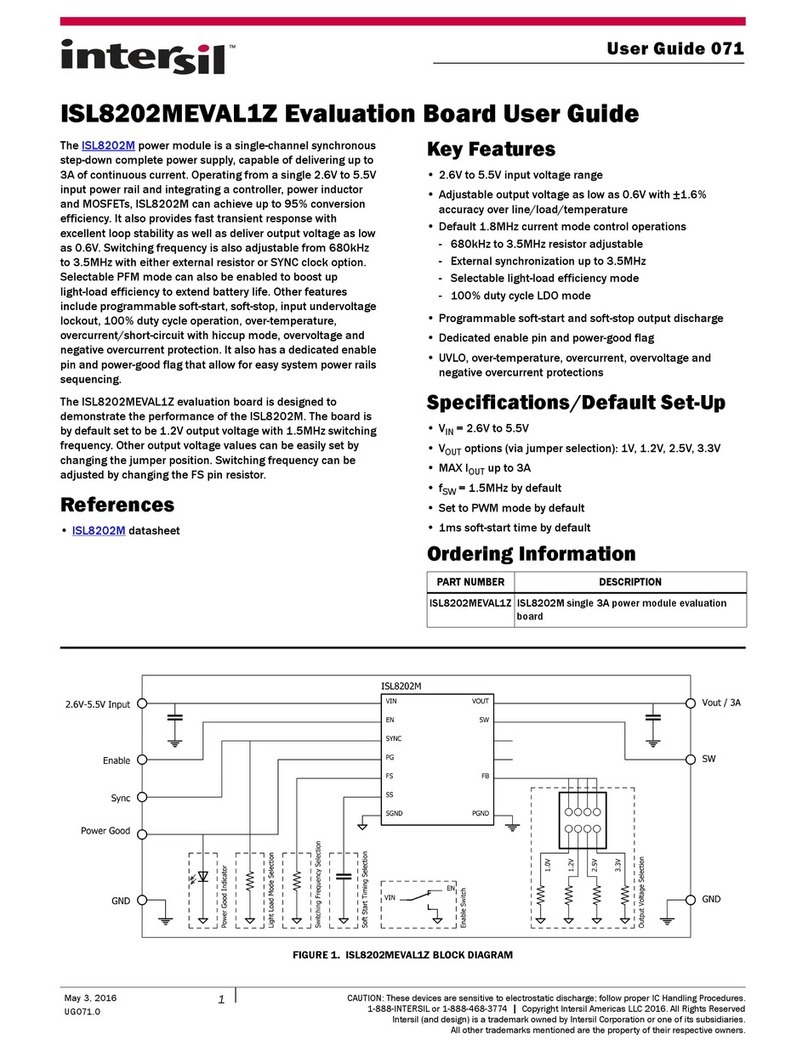
5AN1471.0
June 4, 2009
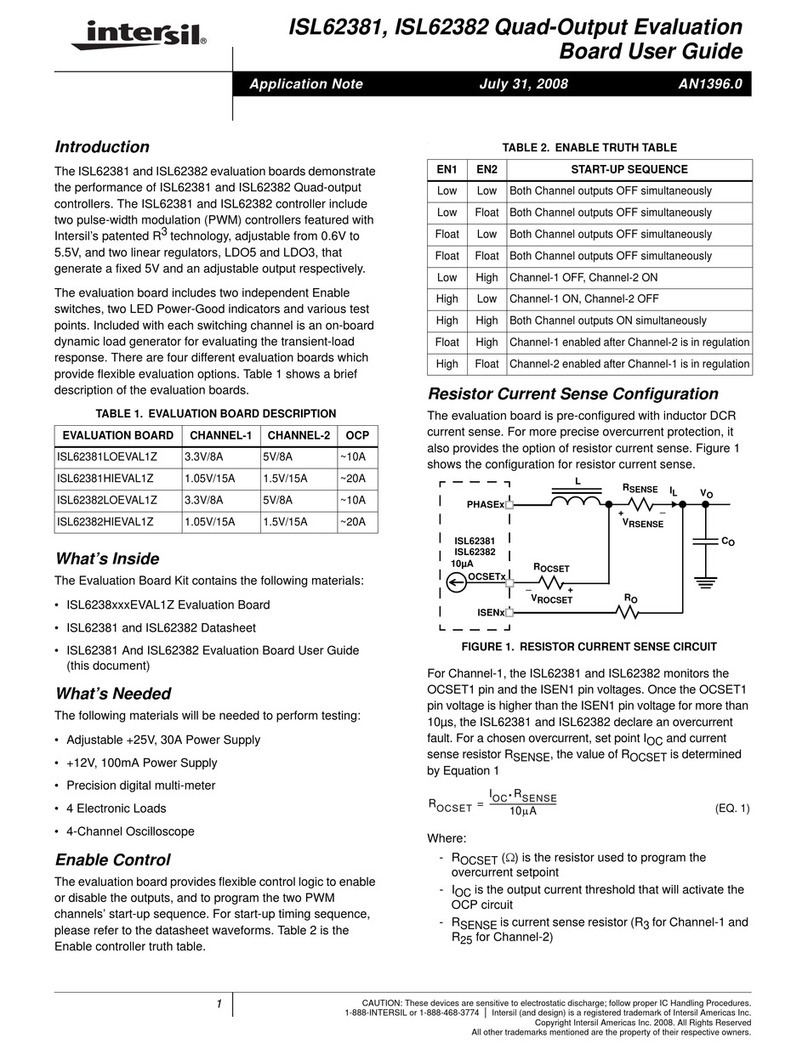
the Rx input voltages, in case the user wants to evaluate the
Rx switching points.
To disable the Rx outputs via the active high RXEN pin,
remove “J10” (2) and “J9” (3), and switch the “(RXEN)” (11)
jumper to the “LOW” position (make sure the “RXEN1” (10)
jumper is in the “VH” position). To disable the Rx outputs via
the active low RXEN1 pin, move jumper “RXEN1” to the
“VH” position (make sure the “(RXEN)” jumper is in the
“LOW” position).
Return the “RXEN1” and “(RXEN)” jumpers to the “VH”
position, remove the “RXBIAS” power supply, and reinstall
the “RXBIAS-VCC” (15) jumper.
DRIVER TESTS
The RS-232 Tx outputs, Y and Z, are high (≈6.2V) and low
(≈-5.7V), respectively, in the default configuration. To switch
the output states, simply switch the “DY1 (DZ/SLEW)” (13)
and “DZ1/DE1 (DY)” (14) jumpers to the opposite states. To
evaluate the loaded driver output voltages, configure the port
for “external loopback”, as described previously (i.e., install
jumpers (5) and (6)). Each driver output is now loaded by an
Rx input resistor (≈5kΩ), and the output voltages still exceed
±5.5V.
The driver outputs can be disabled by moving the
“(DEN)” (8) jumper to the “LOW” position.
Remove the “external loopback” jumpers when finished,
switch the “DY1(DZ/SLEW)” and “(DEN)” jumpers to the
“VH” position, and move the “DZ1/DE1 (DY)” jumper back to
the “LOW” position.
INTERNAL LOOPBACK
To configure the ISL3331 for internal loopback mode, simply
move the “(ON)” (12) jumper to the “LOW” position, while
ensuring that the “(DEN)” (8) and “(RXEN)” (11) jumpers are
set to “VH”. Note that ICC increases due to the enabling of
the loopback receivers. RA is now low due to Tx output Y
feeding back to Rx A, while RB is high due to Z feeding back
to Rx B. You can repeat the previous Rx switching tests to
confirm that the external Rx input pins now have no affect on
RA nor RB.
LOW POWER SHDN
The ISL3331 enters the SHDN mode when
“(ON)” (12) = “LOW”, and the Tx and Rx are disabled
(“(DEN)” (8) = “LOW”, “(RXEN)” (11) = “LOW”, and
“RXEN1 (10) = “VH”), and the already low supply current
drops to as low as 10µA. SHDN disables the Tx and Rx
outputs, and disables the charge pumps, so V+ collapses to
VCC, and V- collapses to GND.
All but 10µA of SHDN ICC current is due to the on-chip SPB
pull-up resistor (~10µA/resistor), so SHDN ICC varies
depending on the ISL333x configuration. To evaluate the
lowest SHDN ICC, ensure that the “SPB” (9) jumper is in the
“VH” position.
SINGLE TX AND SINGLE TRANSCEIVER MODES
RS-232 mode also offers the options of selecting a single Tx
mode, or a single Tx/Rx pair mode. To evaluate the single Tx
mode, set the “(ON)” (12) and “(RXEN)” (11) jumpers “LOW”
and “(DEN)” (8) and “RXEN1” (10) jumpers to “VH”. To
evaluate the single Tx/Rx mode, set the “(ON)” and “(DEN)”
jumpers “LOW” and either the “RXEN1” jumper to “LOW” or
the “(RXEN)” jumper to “VH”.
Basic AC Evaluation
Before starting, ensure that the jumpers are back in the
default RS-232 positions. Note that the RS-232 data rate is
fixed, so the speed select pins have no effect.
RECEIVER TESTS
Add jumper “A1” (1) to engage the 50Ωterm, connect a
generator to the “A1” BNC, and set it for at least a 0V to 3V
swing. Monitoring test points “TP6” (input), and “RB1(RA)”
(output) with a scope allows the Rx prop delays and skews
to be measured. If desired, you can load the Rx output with a
1kΩresistor by adding jumper “J6” (not numbered), located
below test point “RB1 (RA)”. This resistor terminates to the
“VLOAD” banana jack (upper left hand corner), allowing the
resistor to be terminated to GND by shorting “VLOAD” to
GND, or terminated to any voltage by connecting “VLOAD”
to an external supply.
To measure the Rx enable/disable time to/from a high output
state via the active high RXEN pin, start from the previous
jumper configuration, leave the “J6” jumper installed, and
connect the “VLOAD” banana jack to GND. Remove the “A1”
jumper (Rx input is pulled low by its on-chip pull-down),
switch the “(RXEN)” (11) jumper to the low position to
engage the 50Ωterm, set the generator to swing from 0V to
3V, and move the generator to the “DEN2 (RXEN)” BNC.
Monitoring test points “TP12” (input), and “RB1 (RA)”
(output) with a scope allows the Rx enable and disable times
to be measured. To evaluate the Rx enable/disable time
to/from a low output state, install the A1 Rx bias jumper,
“J10” (2).
To evaluate the Rx enable/disable times using the active low
RXEN pin, repeat the previous test but leave the “(RXEN)”
jumper in the “LOW” position, move the “RXEN1” (10)
jumper to the “LOW” position to connect the 50Ωterm, and
connect the generator to the “RXEN1” BNC.
DRIVER TESTS
Ensure that the “DZ1/DE1 (DY)” (14) jumper is in the “LOW”
position to engage the 50Ωterm resistor, connect the
generator to the “DZ1/DE1 (DY)” BNC, and set the swing for
0V to 3V. Monitoring test points “TP18” (input) and “TP5”
(output) with a scope, allows the Tx prop delays, skews, and
transition times to be measured.
To measure the “loaded” driver performance, simply remove
the “J10” (2) jumper, and connect the “A1/Y1_LB” (5) jumper,
Application Note 1471