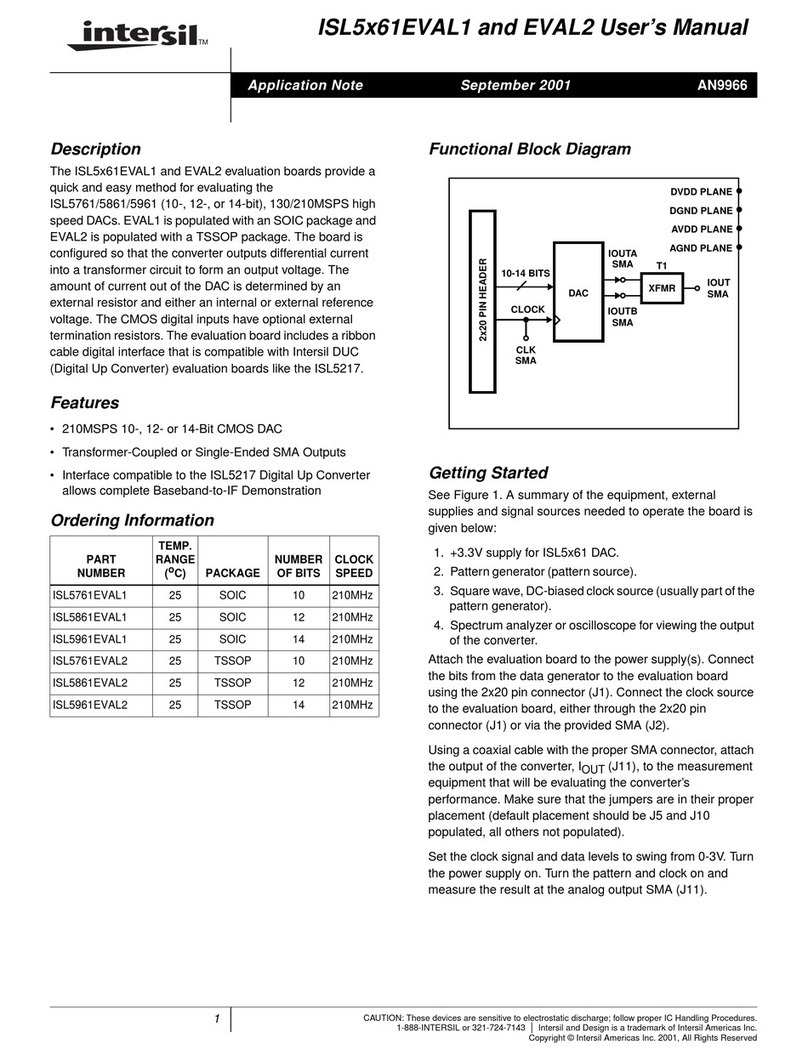
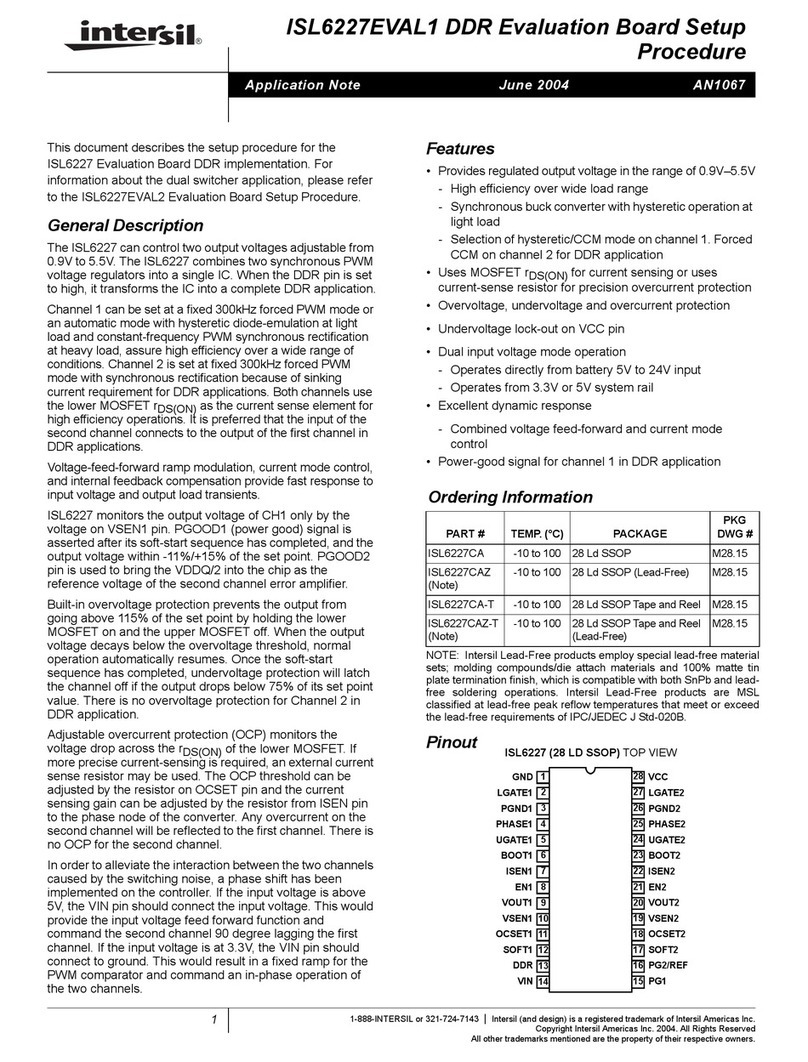
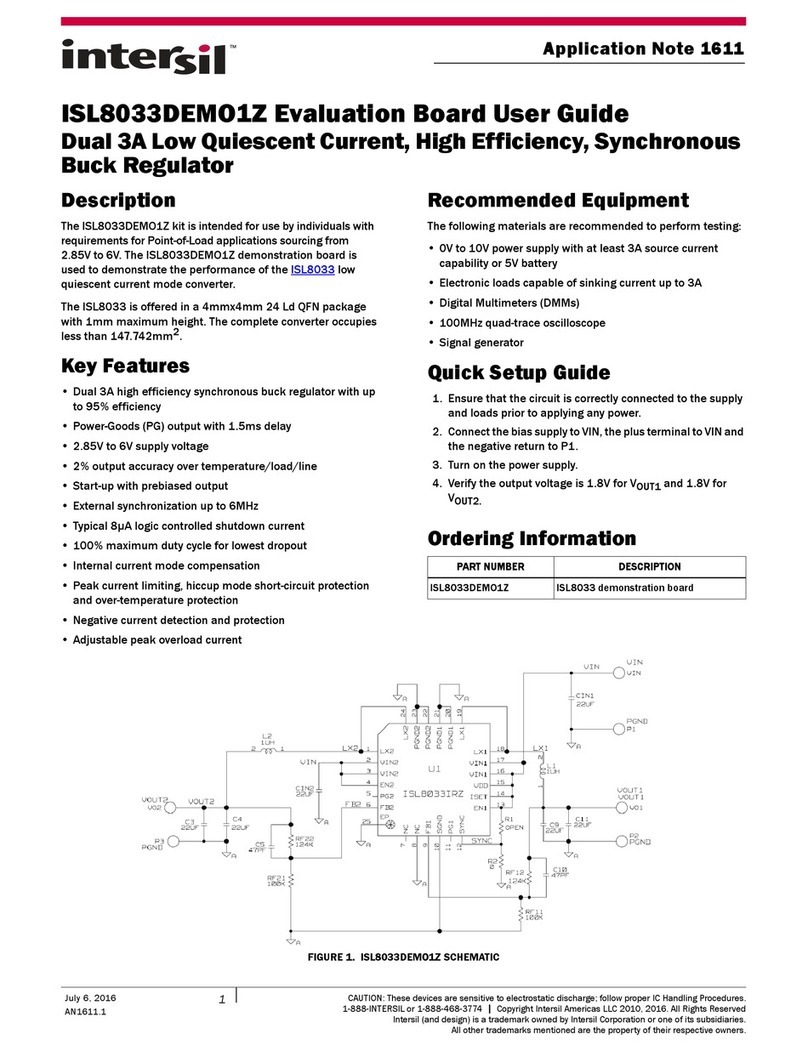
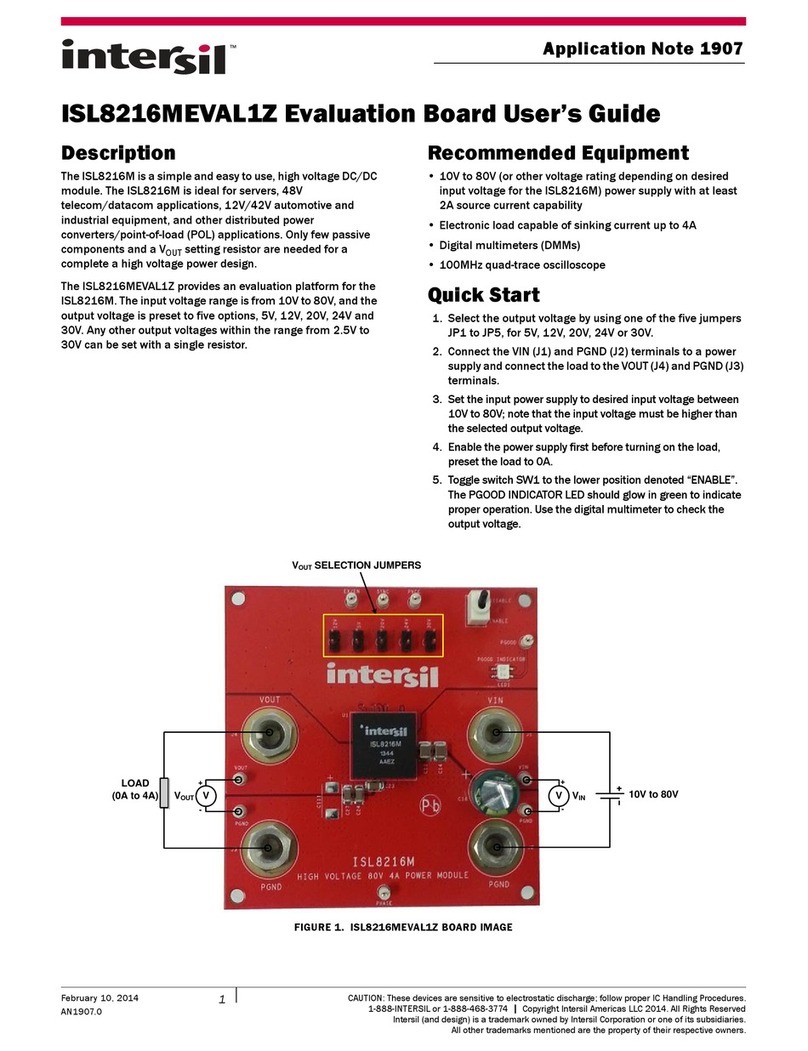
ISL71040MEV1Z 2. General PCB Layout Guidelines
R12UZ0042EU0200 Rev.2.0 Page 5
Feb.9.21
2. General PCB Layout Guidelines
The AC performance of the ISL71040M depends significantly on the design of the Printed Circuit Board (PCB).
The following layout design guidelines are recommended to achieve optimum performance:
• Place the driver as close as possible to the driven power FET.
• Understand where the switching power currents flow. The high amplitude di/dt currents of the driven power FET
induces significant voltage transients on the associated traces.
• Keep power loops as short as possible by paralleling the source and return traces.
• Use planes where practical; they are usually more effective than parallel traces.
• Avoid paralleling high amplitude di/dt traces with low level signal lines. High di/dt induces currents and
consequently, noise voltages in the low level signal lines.
• When practical, minimize impedances in low level signal circuits. The noise, magnetically induced on a 10kΩ
resistor, is 10 times larger than the noise on a 1kΩresistor.
• Be aware of magnetic fields emanating from transformers and inductors. Gaps in the magnetic cores of these
structures are especially bad for emitting flux.
• If you must have traces close to magnetic devices, align the traces so that they are parallel to the flux lines to
minimize coupling.
• The use of low inductance components such as chip resistors and chip capacitors is highly recommended.
• Use decoupling capacitors to reduce the influence of parasitic inductance in the VDRV, VDD, and GND leads. To
be effective, these capacitors must also have the shortest possible conduction paths. If vias are used, connect
several paralleled vias to reduce the inductance of the vias.
• It may be necessary to add resistance to dampen resonating parasitic circuits, especially on OUTH. If an
external gate resistor is unacceptable, then the layout must be improved to minimize lead inductance.
• Keep high dv/dt nodes away from low level circuits. Guard banding can be used to shunt away dv/dt injected
currents from sensitive circuits. This is especially true for control circuits that source the input signals to the
ISL71040M.
• Avoid having a signal ground plane under a high amplitude dv/dt circuit. This injects di/dt currents into the signal
ground paths.
• Calculate power dissipation and voltage drop for the power traces. Many PCB/CAD programs have built in tools
for trace resistance calculation.
• Large power components (such as power FETs, electrolytic caps, and power resistors) have internal parasitic
inductance which cannot be eliminated. This must be accounted for in the PCB layout and circuit design.
• If you simulate your circuits, consider including parasitic components, especially parasitic inductance.
• The GaN FETs have a separate substrate connection that is internally tied to the source pin. Source and
substrate should be at the same potential. Limit the inductance in the OUTH/L to Gate trace by keeping it as
short and thick as possible.