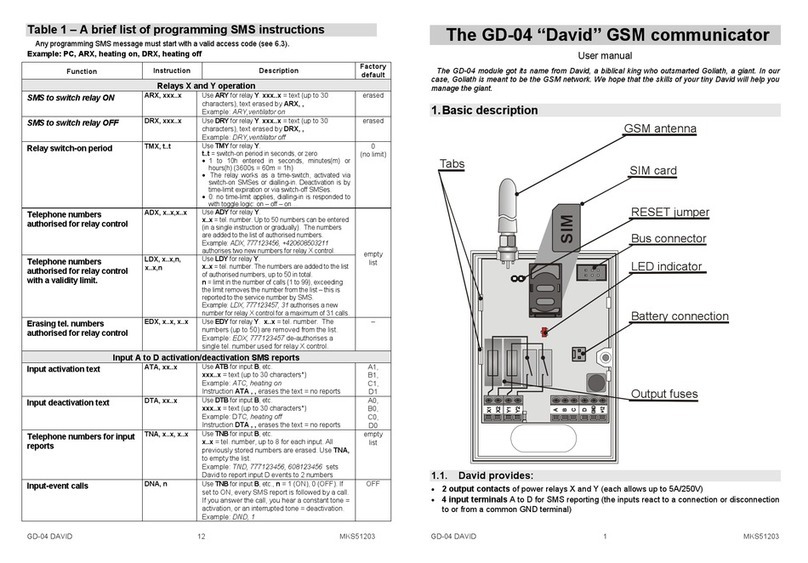
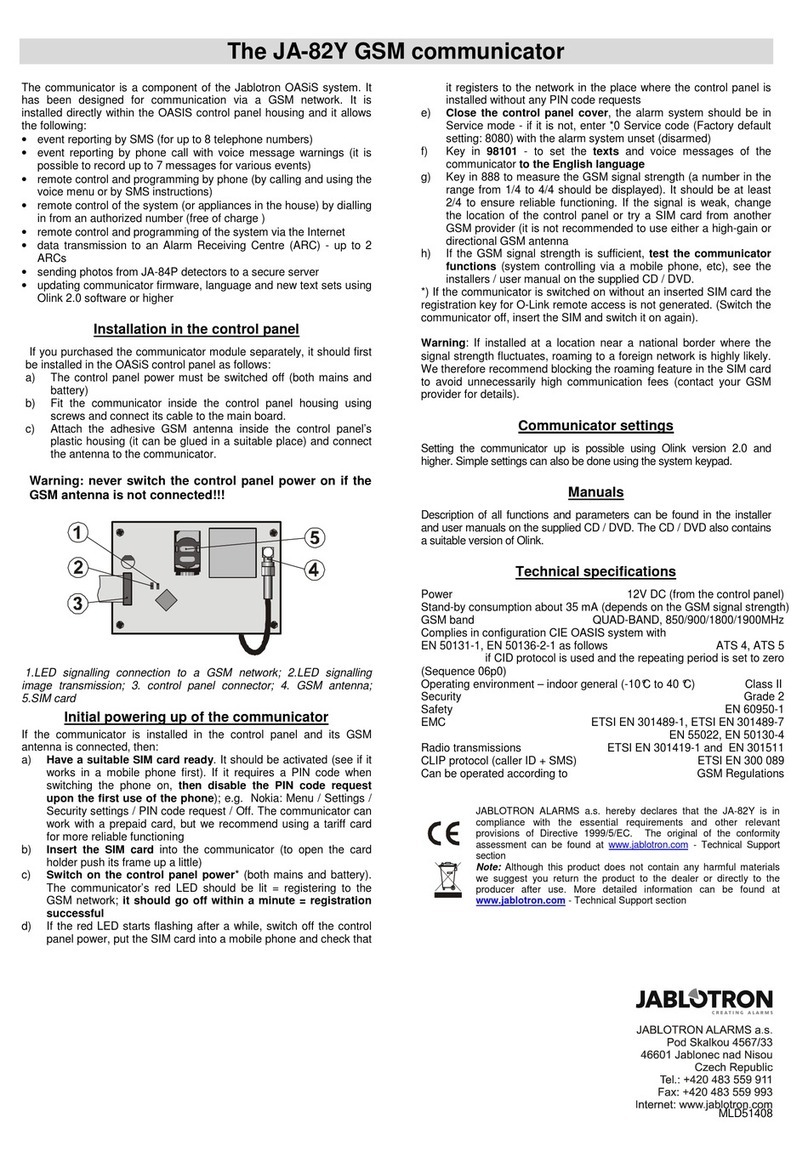
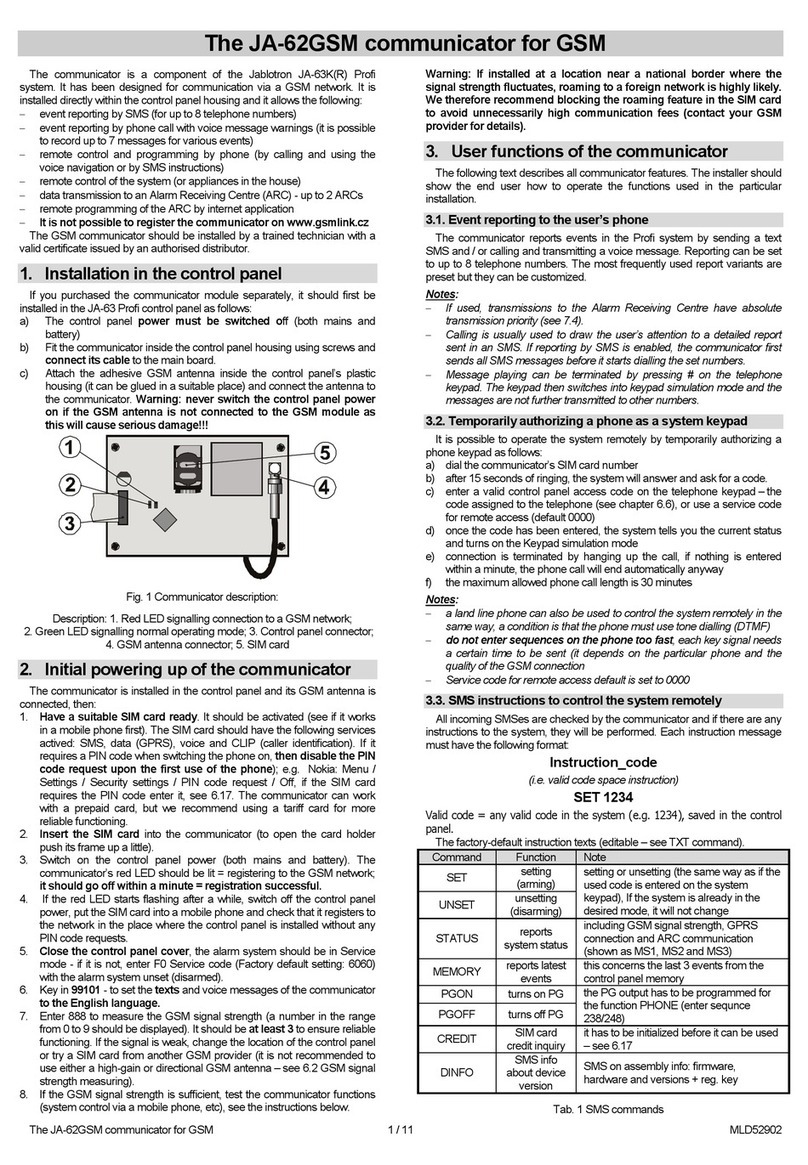
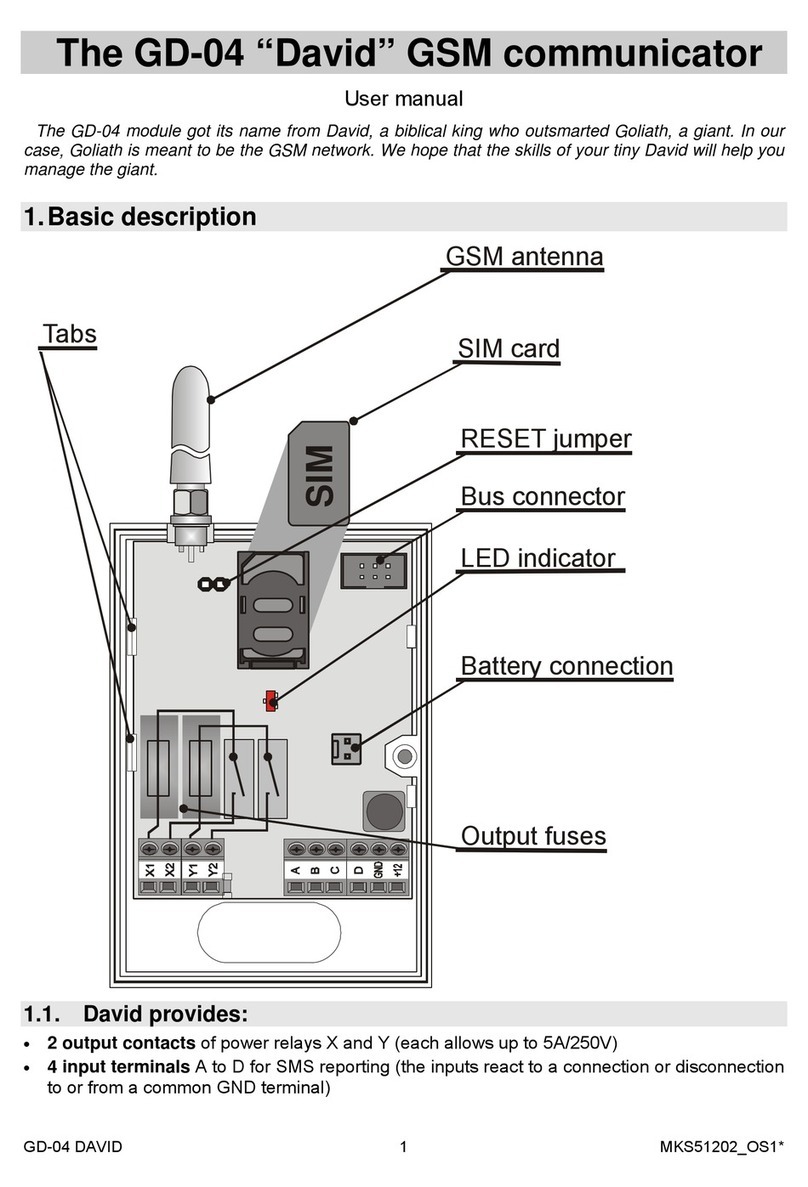
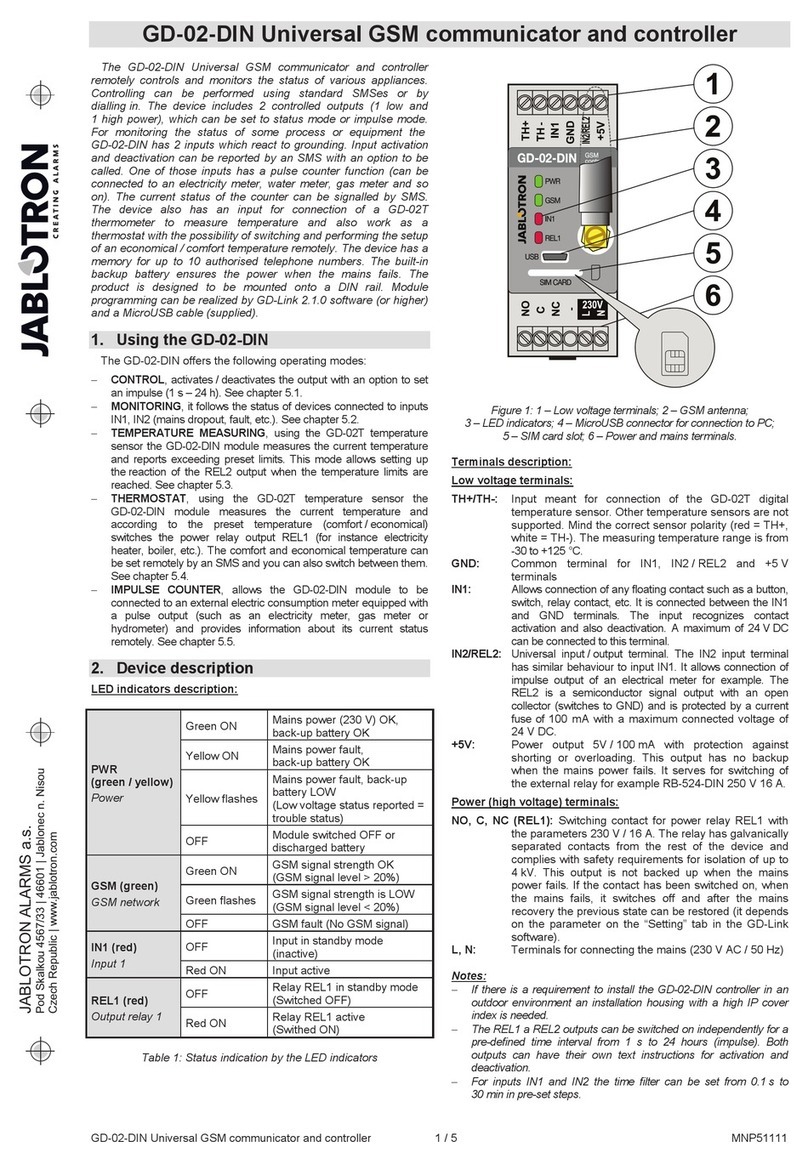
Digital communicator JA-65X 1/7 MFM53103
Digital communicator JA-65X – installation manual
The JA-65X digital communicator is designed for JA-63 and
JA-65 alarm control panels. If the 65X module is installed, the
control panel can communicate with a Monitoring Station, send
voice messages, SMS messages and dial a numeric Pager as
well as communicate with a remote PC. A standard analog
telephone line (type TNV 1-3) must be connected to the module for
these functions.
1 Installation of the digital telephone
communicator
•Use the provided
telephone cable to
connect the telephone
line to the IN jack on the
X module (see diagram )
•Connect a telephone, fax
or other phone operated
device to the OUT jack,
marked with a phone
symbol
•When the control panel
is in normal stand-by mode, the phone line and any
attached device will operate as normal
Note: The communicator must be plugged directly to a
telephone line socket. All other devices (telephone, facsimile
machine, modem etc.) should be connected to the
communicator output.
2 Voice & SMS messages setting
A control panel equipped with the X module can automatically
send 2 voice and 5 short text messages (or dial a Pager). The
most convenient programming of the dialer is via a connected
PC using the Comlink software. Programming can also be
performed manually from the keypad:
•Enter the programming mode (F 0 Service Code,
factory default = 6060), indicated by „P“
•Any unfinished programming sequence can be
terminated by pressing the Nkey.
•To exit the programming mode, press the N key („P“
will turn off). If any fault is indicated when you try to exit
the programming mode, the control panel will inform
you about the problem.
•Telephone numbers and messages can also be set up
in the User Mode when enabled (see installation
manual of the control panel).
2.1 Telephone numbers for voice message
sending sequence: 7xxx....xxFy
Store telephone numbers for voice message by entering:
7 xx... xx F y
where:
xx...xx = telephone number
y= memory number from 1 to 4
A telephone number can have a maximum of 16 digits. A
pause can be entered by F0
Example: to store tel. number 0 123456 to memory no. 2 enter:
7 0 F0 12345 F2
Note: enter a pause (F0) after the last digit of a number which is
calling a mobile phone. This way the number will be called only
once and the dialer will not check the line signals (some mobile
phone systems do not generate standard telephone line signals).
To delete a telephone number enter: 7 F0 Fy
where:
y = memory number from 1 to 4
note: entering 7 F0 F0 will erase all tel. numbers, including the
SMS settings
When activated, the dialer will disengage all other devices
hooked up to the phone line. It will then, one by one, call all
programmed numbers and play the user recorded message
which corresponds to the event. If the dialer makes a successful
connection to a programmed number, it will not call that number
again. If the number is busy, the dialer will make 3 more
attempts to call it. Empty tel. number memories are skipped. If
all memories are empty, the dialer is completely disabled. If the
dialer is also programmed to communicate with a monitoring
station, the data will first be sent to the monitoring station.
Factory default setting: all telephone numbers are deleted.
2.2 Automatic SMS sending
sequence: 7xxx....xxF5
If Jablotron’s SMS server service is provided in your country
(check with your distributor), the following setting allows the
control panel to send alarm text messages (SMS) automatically
to a desired mobile phone:
7 xx…x F9 yy....y F7 00F9 F7zz..z F5
where:
xx…x = telephone number of the SMS server (check with
your distributor if this service is provided in your
country)
F9 = separator (recognition of server’s reaction)
yy…y = mobile phone number (where the SMS should be
sent to)
F7 = event code separator
00F9 = automatic event code – control panel will insert
there a digital code representing the alarm
(depends on setting in section 2.4)
F7 = ID separator
zz..z = optional ID number which will be sent as a part of
the SMS (ending). ID distinguishes which alarm
system sent the SMS). If ID is not required, do not
enter it
F5 = storing of the sequence to memory 5 (32 digits can
be stored to memory 5 as a maximum - separators
F9 and F7 takes only 1 digit each).
How the SMS server works: when activated, the control panel
dials the SMS server. After the connection is established, it
sends telephone number of the mobile phone, to which the SMS
should be sent. Then the control panel specifies what happened
by a digital code and in the end the ID number is transferred (if
programmed). In this moment the SMS server makes
corresponding text message and this message is sent to the
GSM network.
Example: If SMS server number is 483559876, SMS should be
sent to number 606123456 and ID number of the installation is
41 enter: 7 483559876 F9 606123456 F7 00F9 F7 41 F5
Deleting of automatic SMS sending – to erase SMS sending
enter: 7 F0 F5
Note: memory 5 can also be used to dial a Pager instead of SMS
sending. To dial a Pager enter 7 xx..x F9 zzz....z F5 where xx..x
is number of the provider, zz…z is number of the pager and code
of the message (check with a local Pager provider for details).
Pause in the dialing can be entered with F0,