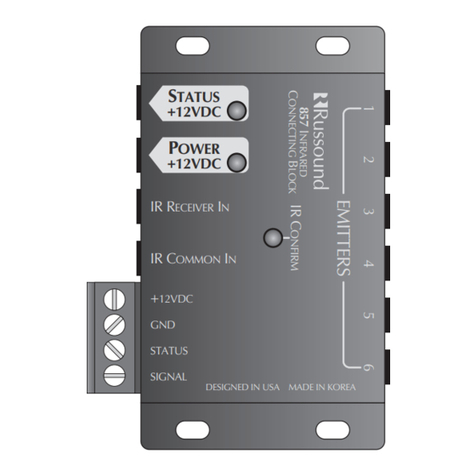
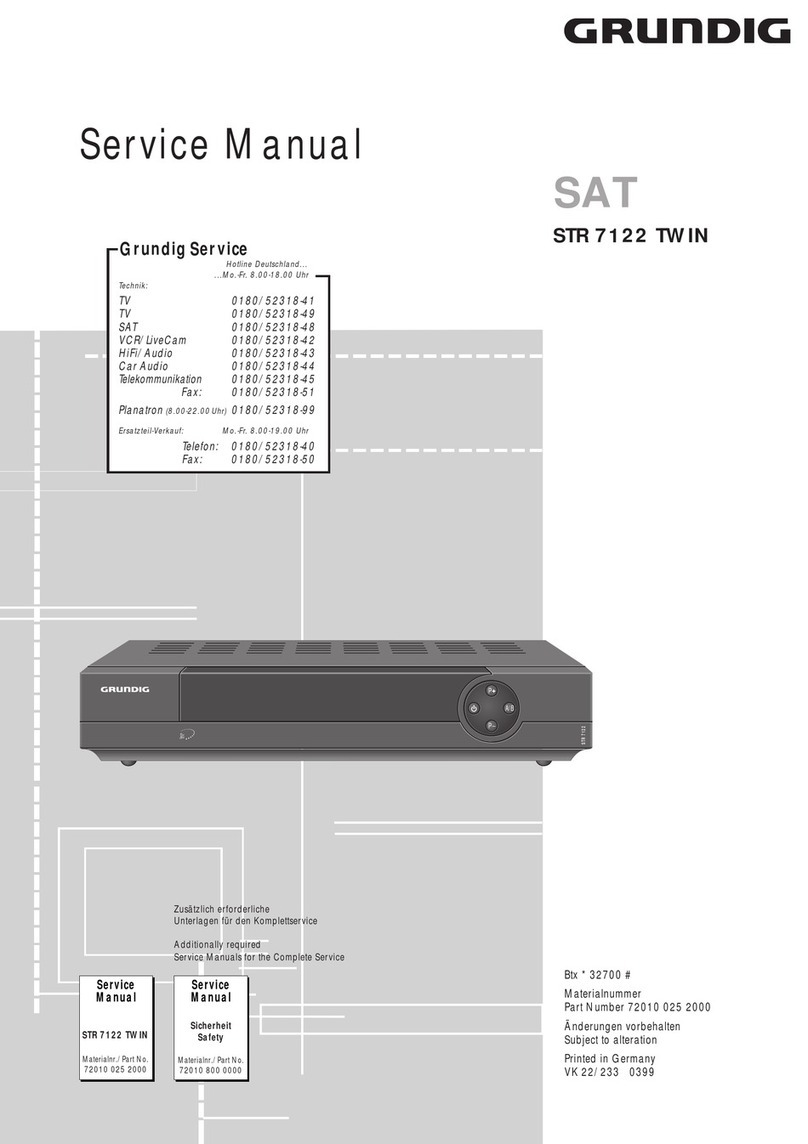
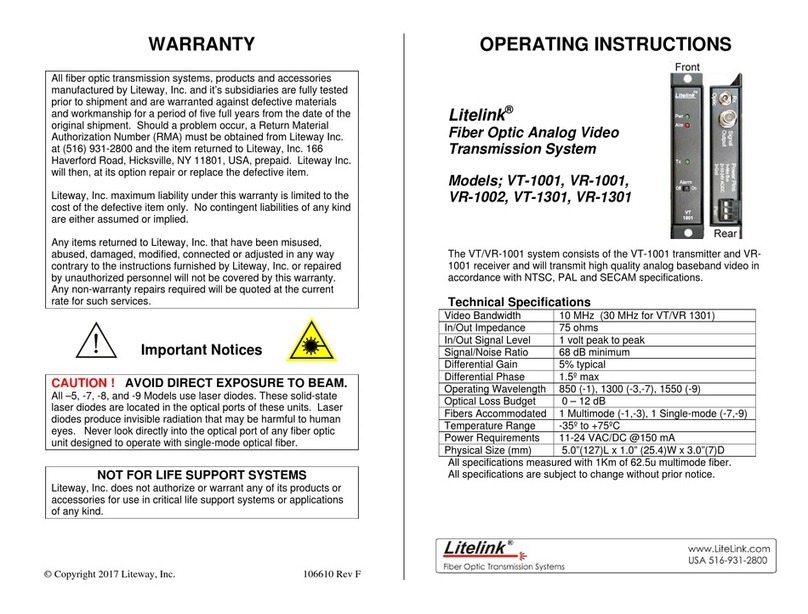
8 www.javad.com
ly depends upon the satellite geometry (Geometric
Dilution of Precision, or GDOP) and the measurement
(ranging) errors.
– Dierential positioning (DGPS and RTK) strong-
ly mitigates atmospheric and orbital errors, and
counteracts Selective Availability (SA) signals the US
Department of Defense transmits with GPS signals.
– The more satellites in view, the stronger the sig-
nal, the lower the DOP number, the higher position-
ing accuracy.
Availability – The availability of satellites aects
the calculation of valid positions. The more visible
satellites available, the more valid and accurate the
position. Natural and man-made objects can block,
interrupt, and distort signals, lowering the number
of available satellites and adversely aecting signal
reception.
Integrity – Fault tolerance allows a position to have
greater integrity, increasing accuracy. Several factors
combine to provide fault tolerance, including:
– Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM)
detects faulty GNSS satellites and removes them from
the position calculation.
– Five or more visible satellites for only GPS or only
GLONASS; six or more satellites for mixed scenarios.
– Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (WAAS,
EGNOS, etc.) creates and transmit, along with DGPS
corrections, data integrity information (for example,
satellite health warnings).
– Current ephemerides and almanacs.
Specifications
Main Features*
• GPS L1/L2/L5
• GLONASS L1/L2/L3
• QZSS L1/L2/L5/LEX
• Galileo E1/E5A/E5B/E5/E6
• BeiDou B1/B1-2/B5A/B2/B3
• SBAS L1/L5
• IRNSS L5
• Update rate 1Hz, 5Hz, 10Hz, 20Hz, 50Hz, 100Hz
• RTK rate 1Hz, 5Hz, 10Hz, 20Hz, 50Hz, 100Hz
• Real-time Data Input/Output JPS, RTCM SC104
v. 2.x and 3.x, CMR
• Real-time Data Output NMEA 0183 v. 2.x and
3.0, BINEX, RINEX
• RAIM
• Data recording up to 16GB
• IEEE 1588 protocol support
• In-Band Interference Rejection
• Multi-Base Code Dierential Rover
• Code Dierential Base
• Advanced Multipath Reduction
• Event marker
• 1 PPS timing strobe
• CAN port
• External Reference Frequency Input/Output
• Up to 2 high-speed RS232/RS422 serial ports
• 2 USB Ports (Host and Device)
• Ethernet
• WiFi 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz
• Bluetooth and Bluetooth LE
• Internal 4G LTE Mini Card
• Internal Radio Modem
• External GNSS Antenna TNC Female connector
GNSS Receiver
• Signals Tracked
• GPS C/A, L1C(P+D), P1, P2, L2C(L+M), L5(I+Q)
• GLONASS C/A, P1, P2, L2C, L3(I+Q)
• Gallileo E1(B+C), E5A(I+Q), E5B(I+Q), AltBoc,
E6(B+C)
• QZSS C/A, L1C(P+D), L2C(L+M), L5(I+Q), SAIF, LEX-
(P+D)
• BeiDou B1, B1-2, B1C(P+D), B5A(I+Q), B2, B5B(I+Q),
B3
• SBAS L1, L5
• IRNSS L5
• Autonomous Accuracy (rms) <2 m
• Static, Fast Static Accuracy (rms):
• Horizontal: 0.3 cm + 0.1 ppm * base_line_length**
• Vertical: 0.35 cm + 0.4 ppm * base_line_length
• Kinematic Accuracy (rms):
• Horizontal: 1 cm + 1 ppm * base_line_length
• Vertical: 1.5 cm + 1 ppm * base_line_length
• RTK (OTF) Accuracy (rms):
• Horizontal: 1 cm + 1 ppm * base_line_length
• Vertical: 1.5 cm + 1 ppm * base_line_length
• DGPS Accuracy (rms)
• < 0.25 m (post-processing)
* For the full list of standard and optional features see www.javad.com
** For good observation conditions and proper length of observation session
***Li-Ion batteries are the temperature limiting factor