Lilin 6122 IP Camera © 2014 I-View Now, LLC. All Rights Reserved. Page 4
Workflow
The following steps describe a high level workflow to be followed in order to properly configure and install a Lilin 6122 IP
Camera to work with I-View Now. Subsequent sections will provide more detail on each step outlined here.
1. Network Setup: Configure the IP camera and router/firewall at the site so the camera can connect to the
Internet. Router/Firewall instructions will vary by location, manufacturer and site LAN configuration. In
addition, data from this step needs to be input into the i-viewnow.com portal, such as the External IP Address
for the site, as well as the “Client Port”. These are necessary so that the I-View Now portal can gain access to
the camera for “Live Views” and retrieving video “Clips” associated with alarm events. Finally, a static IP must
be available for the camera on site which the router will send I-View requests to as well as services on specific
ports.
2. Configure SMTP email: This will be used to communicate alerts and alarms to I-View Now. The SMTP server and
SMTP ID provided on the “Installer Data” Worksheet is necessary for this step. A separate document will cover
setting up an alarm panel to initiate SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) email messages to the I-View email
server.
3. User Setup: Change the default administrator login password from ‘pass’ to a unique password. I-View Now
will be using this password to log into the device programmatically for ‘Live View’ and ‘Clip’ retrieval.As such I-
View Now recommends using the suggested password on the “Installer Data” worksheet. If a password for the
admin account on the camera differs from the one provided on the worksheet, this needs to be communicated
to I-View administrators in order to update the database.
4. Alarm Input Setup: The technician will configure alarm inputs on the back of the camera to perform two actions:
1. Trigger recording on all connected cameras
2. Send SMTP (email) alerts to I-View Now when an alarm event occurs
5. Recording Setup: The camera can be set to record by schedule or by events. Event recording from alarm inputs
is the recommended approach for I-View Now although other modes, such as motion detection, are possible
with some caveats. These are described in more detail in this section.
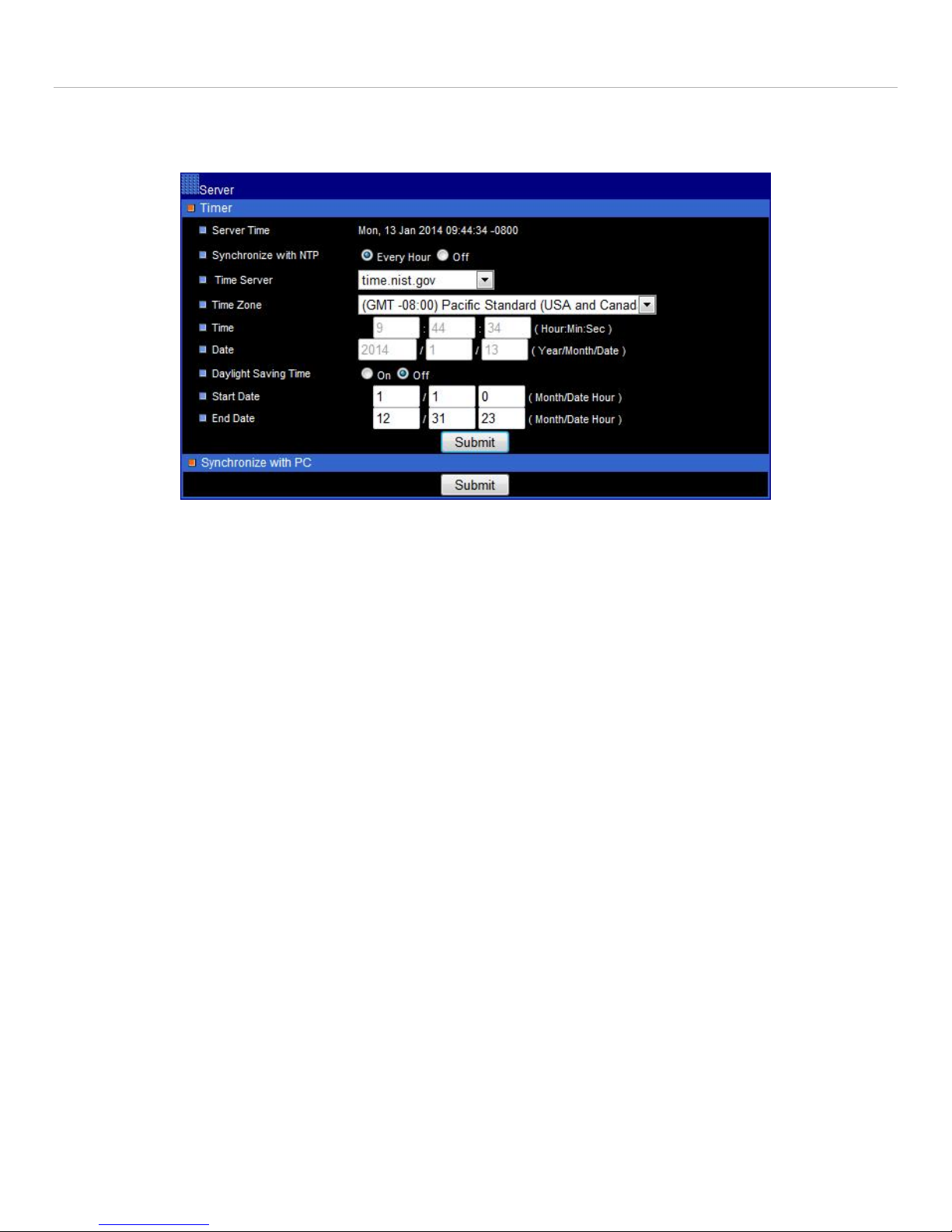
6. Configure I-View Now Entry Delay: Entry delay is configured through the I-View Now portal.
7. Test: Here you will test the individual inputs on the camera as they are connected to your alarm panel relays or
other input devices. It is recommended that you test all inputs for functionality and to ensure the proper
workflow is configured within the I-Viewnow.com portal.
8. Trouble Shooting: This section is provided to help the technician troubleshoot common problems encountered
while installing this particular type of camera.