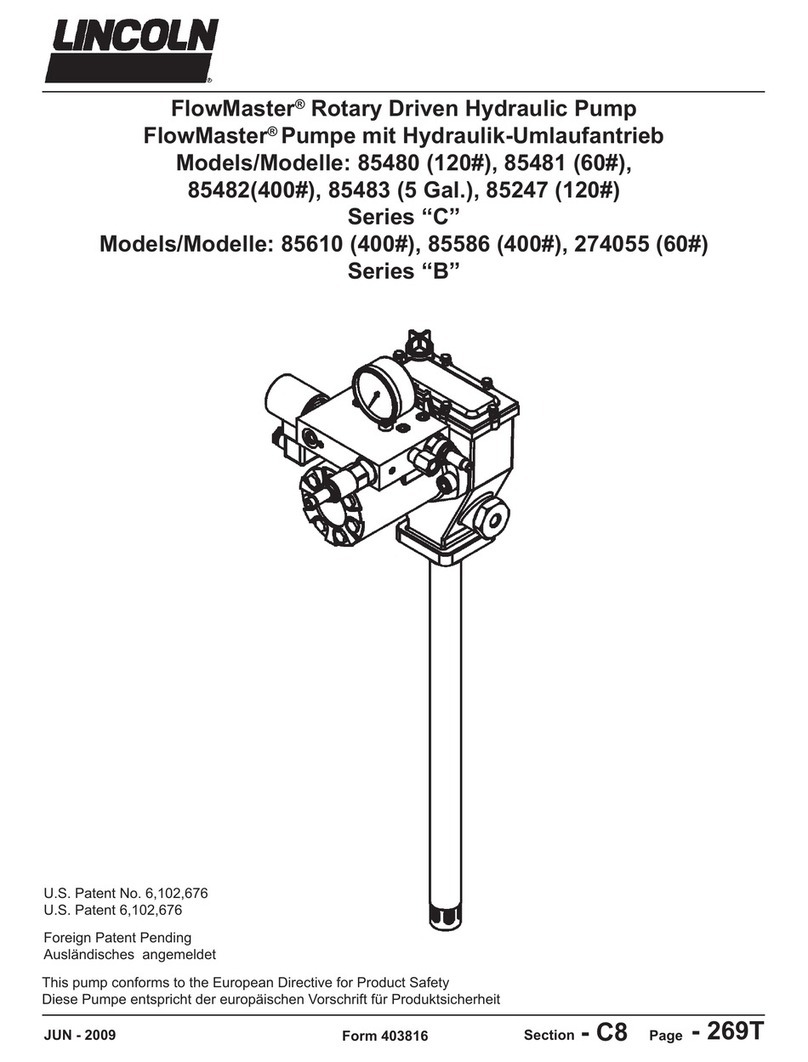
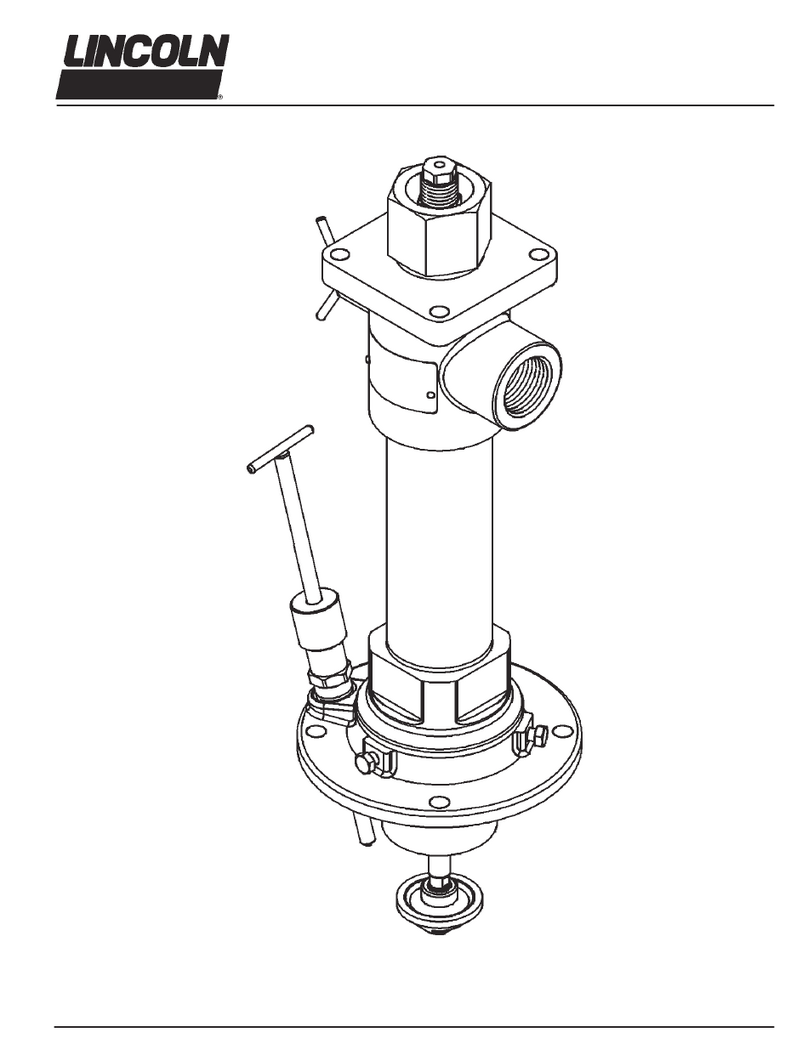
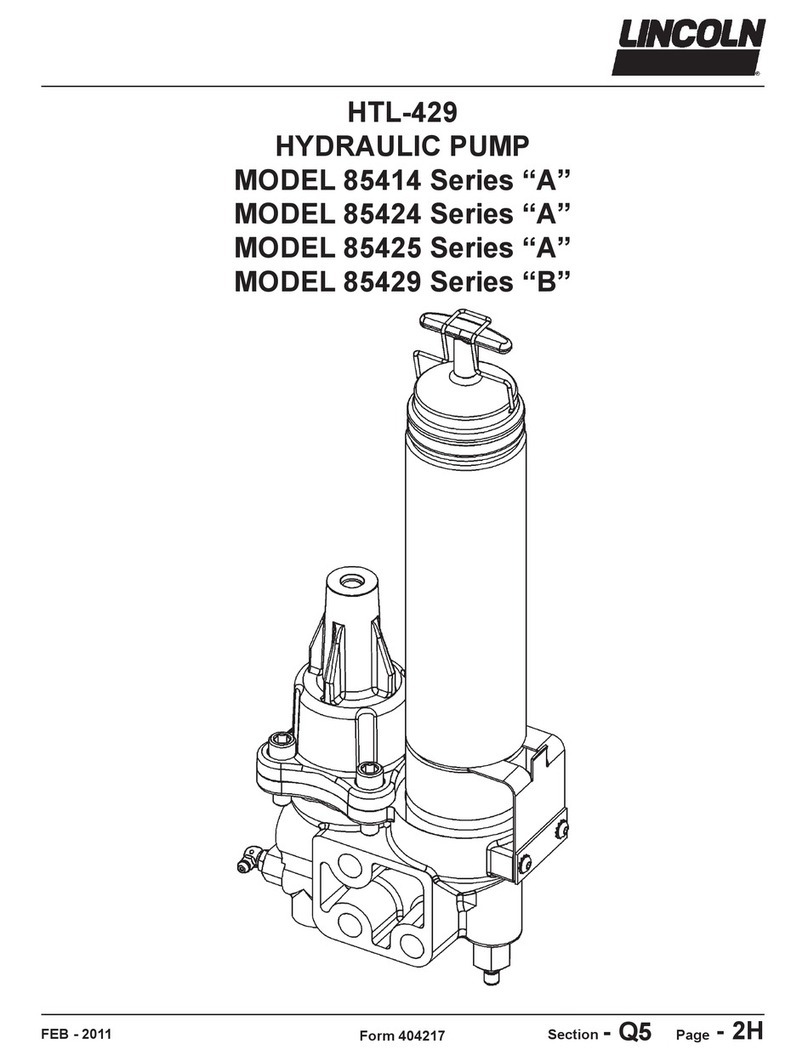
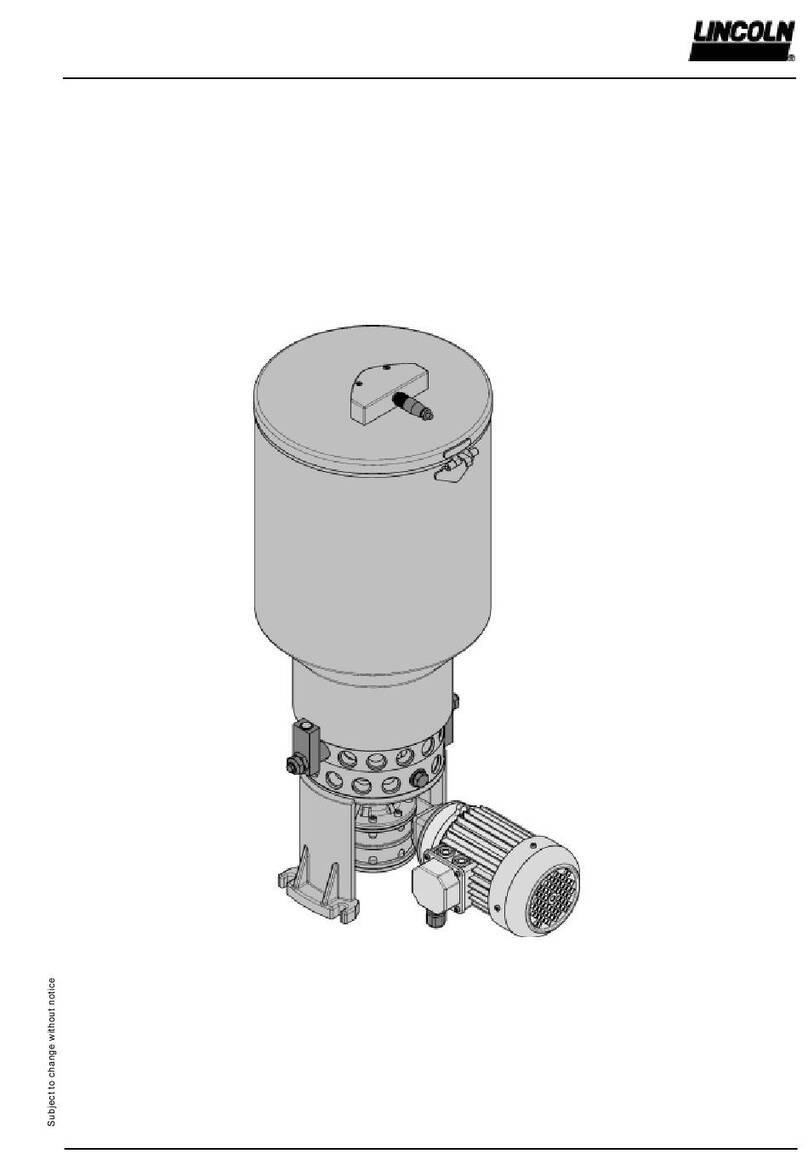
C.
D.
will be more prevalent when pump
ing viscous liquids. When pumping
thick heavy materials the suction
line must be kept as large in diameter
and as short as possible, to keep
suction loss minimal.
Low flow rate and slow cycling rate
indicate restricted flow through the
discharge line. Low flow rate and
fast cycling rate indicate restriction
in suction line or air leakage into
suction.
Unstable cycling indicates improper
check valve seating on one chamber.
This condition is confirmed when
unstable cycling repeats consistently
on alternate exhausts. Cycling that
is not consistently unstable may
indicate partial exhaust restriction
due to freezing and thawing of ex-
haust air. Use of an anti-freeze lubri-
cant in an air line lubricator should
solve this problem.
CHECK VALVE SERVICING
Whether removing cap-
screws on suction or discharge
valve retainer/cap, make sure
all pressure on suction and
discharge side of pump has
been relieved. Re-lock wire the
capscrews before continuing
use.
Need for inspection or service is
usually indicated by poor priming, un-
stable cycling, reduced performance or
the pump’s cycling but not pumping.
Inspect the surfaces of both check
valve and seat for wear or damage that
could prevent proper sealing. If pump is
to prime properly, valves must seat air
tight.
DIAPHRAGM SERVICING
Remove the eight nuts securing the
outer diaphragm chamber flange and
remove the chamber. Loosen the cap-
screw securing the diaphragm and plate
to the rod by leaving the diaphragm
engaged with the capscrews around
the outer flange, preventing rotation of
the rod. DO NOT USE AWRENCH ON
THE DIAPHRAGM ROD. FLAWS ON
THE SURFACE MAY DAMAGE BEAR-
INGS AND SEAL.
During reassembly make certain that
the rubber bumper is on the rod on each
side. install the diaphragm with the
natural bulge outward as indicated on
the diaphragm. Install the heavier plate
on the outside of the diaphragm and
make certain that the large radius side
of both plates aretoward the diaphragm.
Place the sealing washer between the
inner diaphragm plate and the end of
the rod. Tighten thecapscrew toapprox-
imately 25 ft. Ibs (3.456 kilograms/
meters). Torque while allowing the dia-
phragm to turn freely with plates. Use a
wrench on the capscrew of the opposite
side to keep rod from rotating. If the
opposite chamber is assembled, the rod
need not be held.
When reassembling the outer
chambers and the manifold, the bolts
securing the manifold flange to the
chamber should be snugged prior to
tightening the chamber bolts, to insure
that the chamber port flange is square
with the manifold flange. Finish tight-
ening the manifold flange bolts after
chamber bolting is secured.
AIR DISTRIBUTION
VALVE SERVICING
The spool and sleeve are rust and
corrosion resistant brass and hardened
stainless steel. The spool is closely
sized to the sleeve and should slide
freely. Accumulation of dirt and oils may
prevent thepump from cycling. Remove
the valve body from the center pump
housing, remove the end caps, and push
the spool out of the sleeve. Wash the
parts in cleaning solvent or kerosene,
and check the spool and sleeve for
possible roughness, nicks or scratches.
Use afine stone or crocus cloth to care-
fully remove any irregular marks on the
surfaces. When the spool slides freely
on the sleeve, coat the parts with light
oil and reassemble. The four capscrews
inserted through the valve body cap to
hold the air valve to the intermediate
section should be torqued to 150 in./lbs.
(1.728 kilograms/meter).
PILOT VALVE SERVICING
This assembly is reached by remov-
ing the air distribution valve body from
the pump and lifting the pilot valve out
of the intermediate housing.
Most problems with the pilot valve
can be corrected by replacing the o-
rings. Always grease the spool prior to
Inserting it into the sleeve. If the sleeve
IS removed from the body, reinsertion
must be at the chamfered side. Grease
the o-rings to slide the sleeve into the
valve body Securely insert the retain-
ing ring around the sleeve. When rein-
serting the pilot valve, push both plung-
ers (located inside the intermediate
bracket) out of the path of the pilot
valve spool ends to avoid damage,
PILOT VALVE ACTUATOR
SERVICING
Bushings for the pilot valve actua-
tors are held in the inner chambers with
retaining rings. An o-ring IS behind
each bushing. If the plunger has any
sideways motion check o-rings and
bushings for deterioration /wear. The
plunger may be removed for inspection
or replacement. First remove the air
distribution valve body and the pilot
valve body from the pump. The plung-
ers can be located by looking into the
intermediate. It may be necessary to
use afine piece of wire to pull them out,
The bushing can be turned out through
the inner chamber by removing the outer
chamber assembly. Replace the bush-
ings if pins have bent.
ANote about Air Valve
Lubrication
The Lincoln pump’s pilot valve and
main airvalve assemblies aredesigned
to operate WITHOUT lubrication. This
is the preferred mode of operation.
There may be instances of personal
preference, orpoor quality air supplies
when lubrication of the compressed air
supply is required. The pump air sys-
tem will operate with properly lubri-
cated compressed air supplies. Proper
lubrication of the compressed air sup-
ply would entail the use of an air line
lubricator (available from Lincoln) set
to deliver one drop of 10 wt, non-
detergent oil for every 20 SCFM of air
the pump consumed at its point of op-
eration. Consult the pump’s published
Performance Curve to determine this
It is important to remember to in-
spect the sleeve and spool set rou-
tinely. It should move back and forth
freely. This IS most important when the
air supply is lubricated. If aIubricator
is used, oil accumulation will, overtime,
collect any debris from the compressed
air. This can prevent the pump from
operating properly.
RETAIN THIS INFORMATION FOR FUTURE REFERENCE
When ordering replacement parts, list: Part Number, Description, Model Number, and Series Letter.
LINCOLN provides aDistributor Network that stocks equipment and replacement parts.