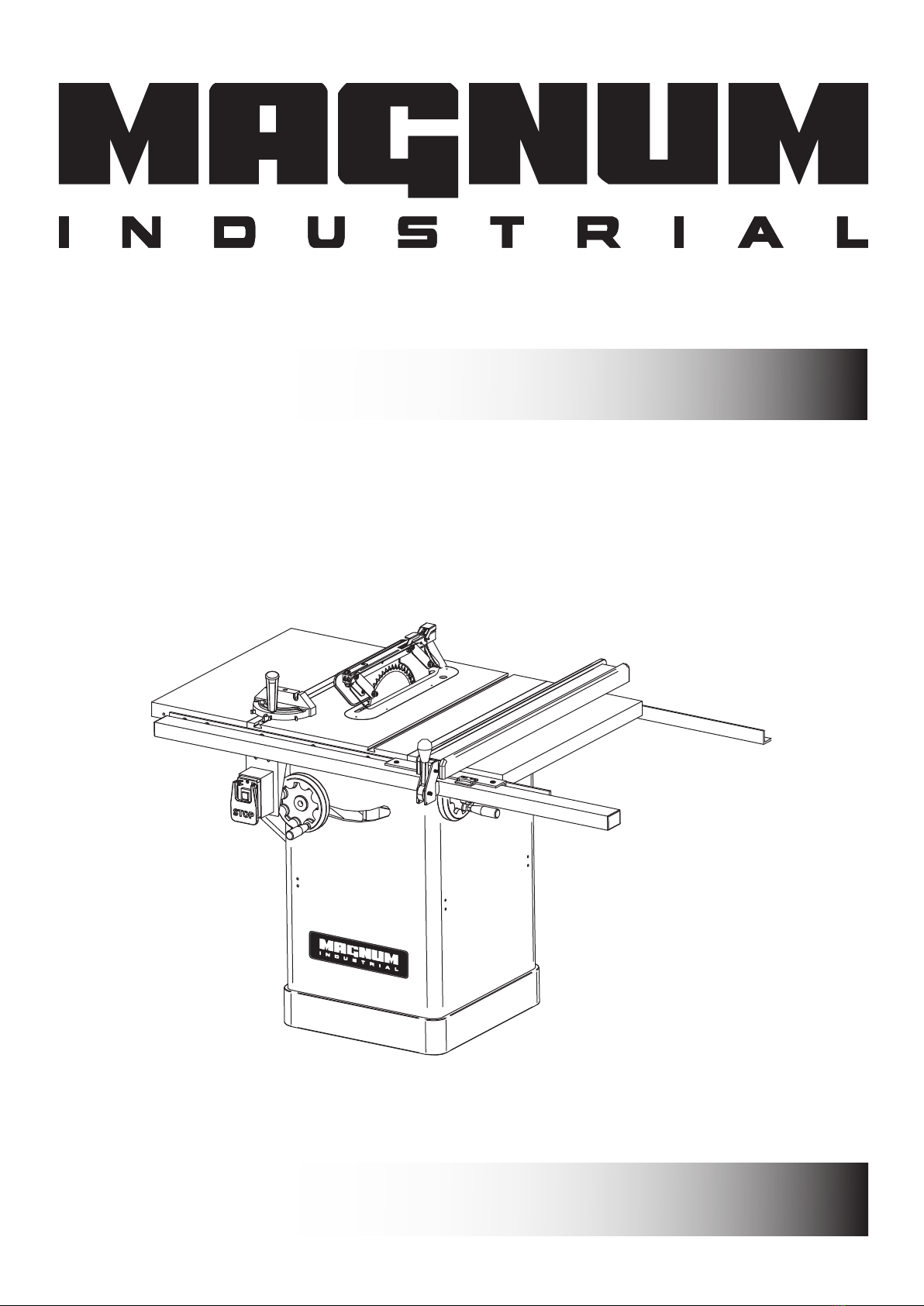
7
standing in front and in line with the saw blade.
b) Never reach over or in back of the saw blade to pull or to support the workpiece. Accidental
contact with the saw blade may occur or kickback may drag your fingers into the saw blade.
c) Never hold and press the workpiece that is being cut off against the rotating saw blade. Pressing
the workpiece being cut off against the saw blade will create a binding condition and kickback.
d) Align the fence to be parallel with the saw blade. A misaligned fence will pinch the workpiece
against the saw blade and create kickback.
e) Use a feather board to guide the workpiece against the table and fence when making non-
through cuts such as rabbeting, dadoing or resawing cuts. A feather board helps to control the
workpiece in the event of a kickback.
f) Use extra caution when making a cut into blind areas of assembled workpieces. The protruding
saw blade may cut objects that can cause kickback.
g) Support large panels to minimise the risk of saw blade pinching and kickback. Large panels tend
to sag under their own weight. Support(s) must be placed under all portions of the panel
overhanging the table top.
h) Use extra caution when cutting a workpiece that is twisted, knotted, warped or does not have a
straight edge to guide it with a miter gauge or along the fence. A warped, knotted, or twisted
workpiece is unstable and causes misalignment of the kerf with the saw blade, binding and
kickback.
i) Never cut more than one workpiece, stacked vertically or horizontally. The saw blade could pick
up one or more pieces and cause kickback.
j) When restarting the saw with the saw blade in the workpiece, centre the saw blade in the kerf
so that the saw teeth are not engaged in the material. If the saw blade binds, it may lift up the
workpiece and cause kickback when the saw is restarted.
k) Keep saw blades clean, sharp, and with sufficient set. Never use warped saw blades or saw
blades with cracked or broken teeth. Sharp and properly set saw blades minimise binding,
stalling and kickback.
4) TABLE SAW OPERATING PROCEDURE WARNINGS
a) Turn off the table saw and disconnect the power cord when removing the table insert, changing
the saw blade or making adjustments to the riving knife, anti-kickback device or saw blade guard,
and when the machine is left unattended. Precautionary measures will avoid accidents.
b) Never leave the table saw running unattended. Turn it off and don’t leave the tool until it comes
to a complete stop. An unattended running saw is an uncontrolled hazard.
c) Locate the table saw in a well-lit and level area where you can maintain good footing and
balance. It should be installed in an area that provides enough room to easily handle the size of
your workpiece. Cramped, dark areas, and uneven slippery floors invite accidents.