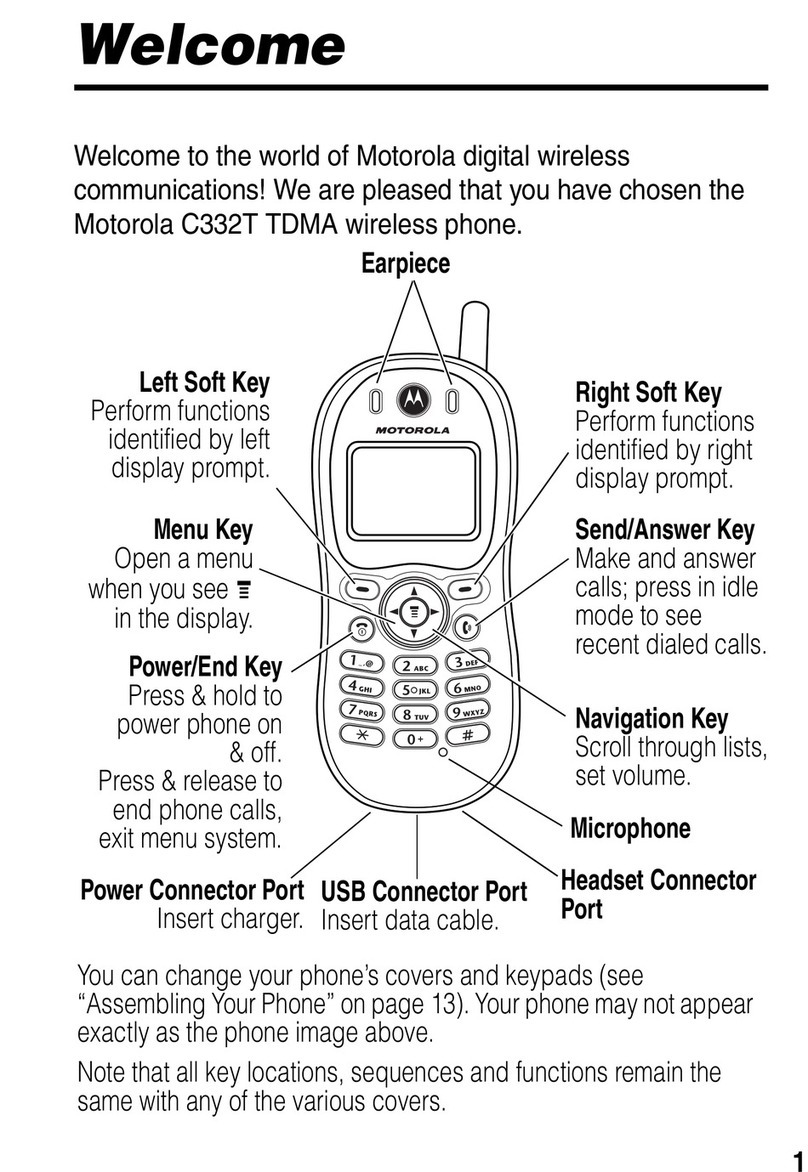
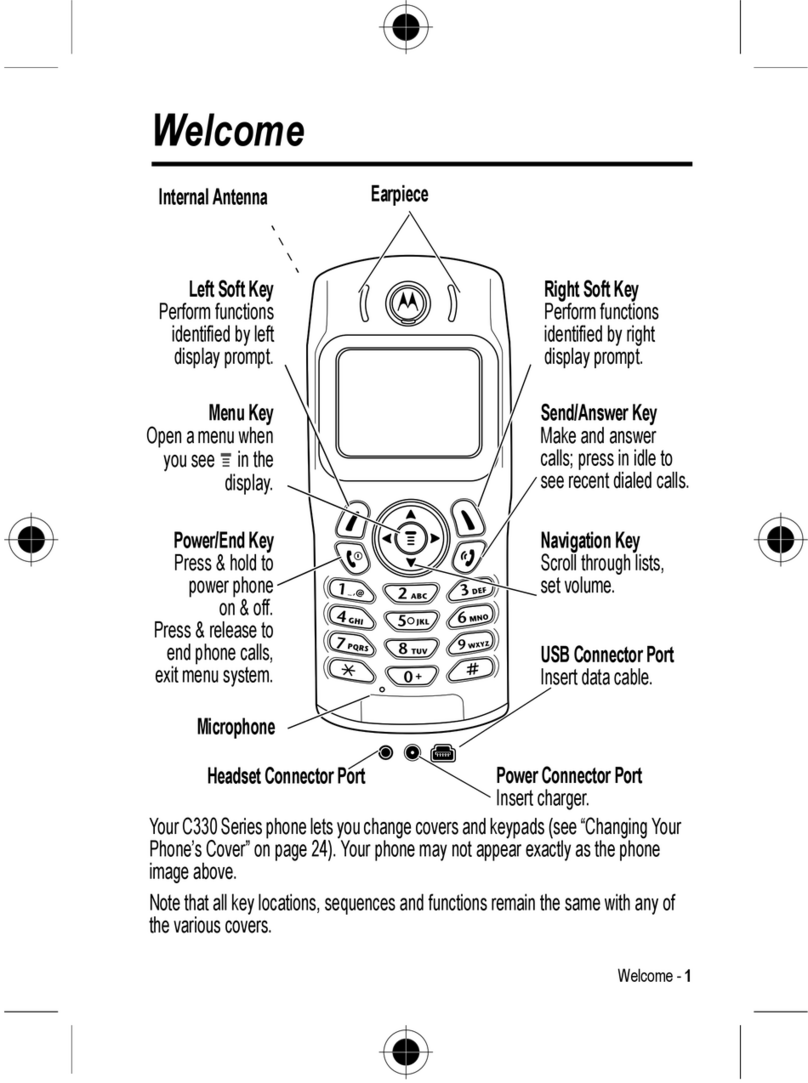
W208 Level 3 Circuit Description
Service Engineering & Optimization
- 7 -
applies this signal to the voice signal interface for eventual baseband modulation. In the
downlink path, the codec circuitry changes voice component data received from the voice
serial interface into analog audio. The voice codec support an 8/16 kHz sampling
frequency. The stereo audio path converts audio component data received from the I2S
serial interface into analog audio. The following paragraphs describe these
uplink/downlink and audio stereo functions in more details.
1.3.1 Voice Downlink Patch
The VDL path receives speech samples at the rate of 8 kHz from the Locosto-Plus IC U101
(DSP) via the VSP and converts them to analog signals to drive the external speech
transducer.
The digital speech coming from the Locosto-Plus IC U101 (DSP) is first fed to a speech
digital filter that has two functions. The first function is to interpolate the input signal and
to increase the sampling rate from 8 kHz up to 40 kHz to allow the digital-to-analog
conversion to be performed by an over-sampling digital modulator. The second function is
to band-limit the speech signal with both low-pass and high-pass transfer functions. The
filter, the PGA gain, and the volume gain can be bypassed by programming.
The interpolated and band-limited signal is fed to a second order Σ-∆digital modulator
sampled at 1 MHz to generate a 4-bit (9 levels) over-sampled signal. This signal is then
passed through a dynamic element-matching block and then to a 4-bit digital-to-analog
converter (DAC).
Due to the over-sampling conversion, the analog signal obtained at the output of the 4–bit
DAC is mixed with a high frequency noise. Because a 4–bit digital output is used, a
first–order RC filter (included in the output stage) is enough to filter this noise.
The volume control and the programmable gain are performed in the TX digital filter.
Volume control is performed in steps of 6 dB from 0 dB to -24 dB. In mute state,
attenuation is higher than 40 dB. A fine adjustment of gain is possible from -6 dB to +6 dB
in 1–dB steps to calibrate the system depending on the earphone characteristics. The
earphone amplifier provides a full differential signal on the terminals EARP Triton-Lite Pin
J2 and EARN Triton-Lite Pin H2. The 8Ohm speaker amplifier provides a differential
signal on the terminals SPKP Triton-Lite Pin L6, K6 and SPKN Triton-Lite Pin M6, M7.
1.4 Earpiece Receiver
The Receiver J10 is connected to EARP Triton-Lite Pin J2 and EARN Triton-Lite Pin H2.
1.5 Headset
The headset uses a standard 2.5mm phone jack. The headset circuit contains analog
switches (U602 and U605), which are normally switched to receiver earpiece after power
on. When system turns on, the signal HS_EN (U101 Pin T3) are applied. When earphone
plug in, the phone will detect this action and make an appropriate response to answer a
call while incoming call occur. The interrupt for the headphones is detected on the
HS_DETECT (U101 Pin C6) line from Pin 6 of Headset Jack J602. This signal will be
pulled to high when the headset is connected.
1.6 Speaker Phone
When the handset set the hand-free mode, the Triton-Lite will switch from EARP/EARN
to SPKP/SPKN trace and receiver signal will be through Audio amplifier U601 to Speaker.