Models PT-70CE and PT-24-35
These models are designed for hard-wiring into the a.c. system. Input voltage
selection is made at the time of a.c. wiring installation, as follows:
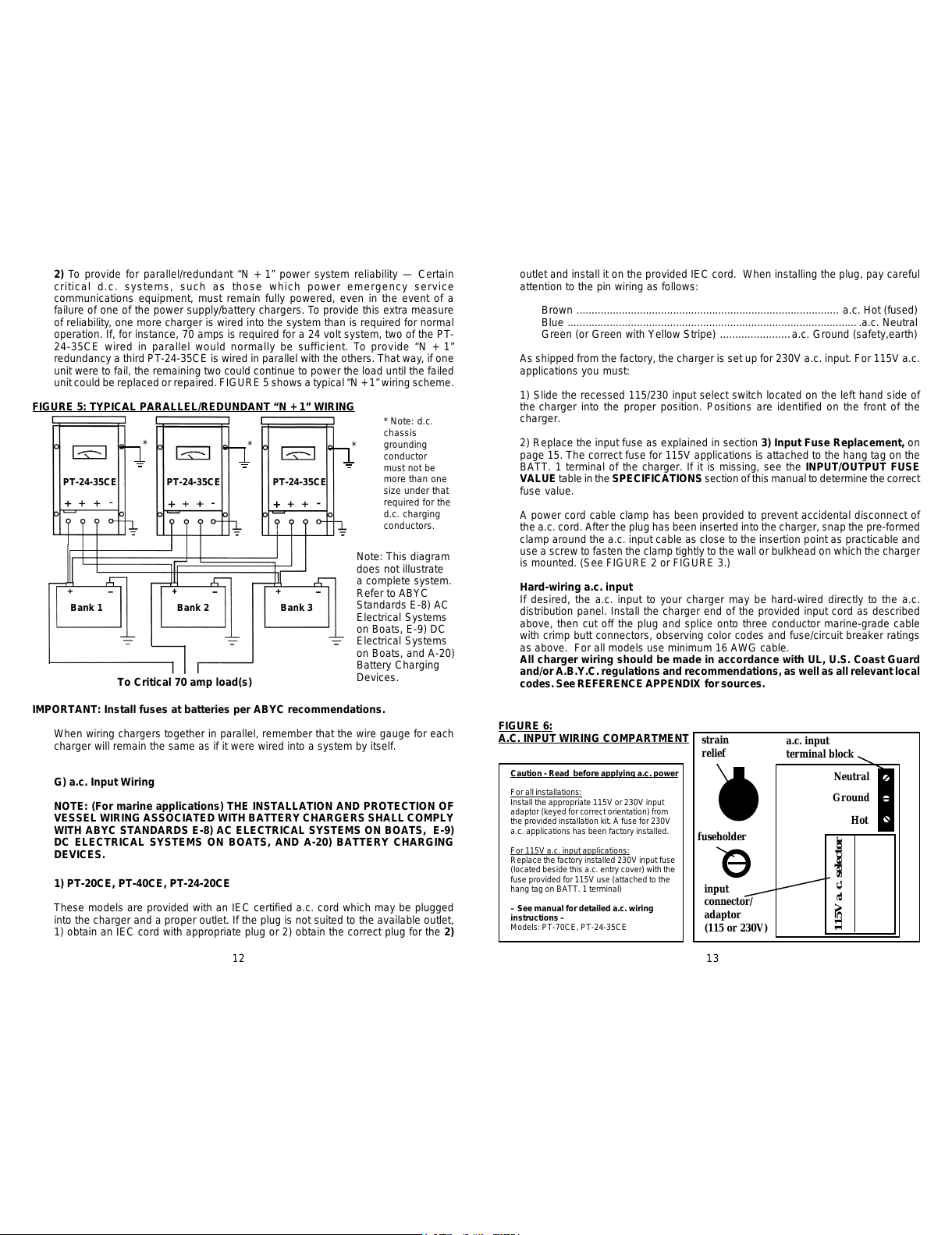
1) Read and remove the warning label (copy below) which covers the a.c. input
wiring compartment (see FIGURE 6.)
2)Select theproper connector/adaptor for your application(provided inthe installation
kit and labeled either 115V or 230V). Snap it into the adaptor receptacle. It is keyed
to ensure that it is properly positioned. Note: If the charger has previously been
used in a 115V application and must be converted for 230V use or vice-versa, the
existing connector/adaptor must be removed first. Do this by pinching hard on the
retaining tabs on either side and pulling firmly outward.
3) Snap the provided strain relief into the charger housing (oriented as shown in
FIGURE 6) and loosen the compression screw.
4) Strip about 1/4" of insulation off the ends of each a.c. input wire and feed the a.c.
input cord through the strain relief. 16 gauge (AWG) wire is sufficient for most
installations up to 20 feet in length. (Maximum gauge wiring terminal will
accommodate is 12 (AWG). Consult ABYC or USCG regulations for installations
with a.c. input wiring over 20 feet.
5) With narrow blade (1/8") flat tip screwdriver loosen the compression screw
terminals on the a.c. terminal block beside the connector/adaptor. Insert each a.c.
input wire into the appropriate terminal. The HOT and NEUTRAL terminals are the
outer terminals and are labeled on the circuit board to which terminal block is
attached. The GROUND wire is attached to the center terminal. Standard color
coding of a.c. wiring is as follows:
Europe USA
Brown........................................................Black ........................... .a.c. Hot (fused)
Blue...........................................................White ...................................a.c. Neutral
Green (or Green with Yellow Stripe)....... Green ............a.c. Ground (safety,earth)
6) Tighten the compression screw on the strain relief. Install the a.c. input wiring
cover which is provided in the installation kit. The screws which attach the wiring
cover to the charger have already been installed and will need to be removed first.
ALL MODELS: a.c. input for the charger must be plugged into an appropriate,
over-current protected three prong outlet (PT-20CE, PT-40CE and PT-24-20CE)
OR routed through a separate dedicated fuse or circuit breaker on an a.c.
distribution panel (PT-70CE, PT-24-35CE) with proper safety/earth chassis
ground in accordance with all local codes and ordinances.
Use the table below to determine the proper fuse or circuit breaker value,
depending on model and whether the application is 115 or 230V a.c.:
a.c. Fuse/Circuit Breaker Table
Model 115V a.c. 230V a.c
PT-20CE 10 amp 5 amp
PT-40CE, PT-24-20CE 15 amp 10 amp
PT-70CE, PT-24-35CE 20 amp 10 amp
CAUTION (230 V a.c applications only): If a.c. input is derived from a source
consisting of two HOT leads (phase-to-phase 230V a.c. input voltage), an
external fuse or circuit breaker must be used to protect the unfused (formerly
NEUTRAL, now HOT) lead.
3) Input Fuse Replacement
The a.c. input of your charger is protected by an input fuse. The input fuseholder is
located near the bottom of the unit on the left side (20 and 40 amp models) or on the
bottom of the unit, beside the a.c. strain relief (35 and 70 amp models). The proper
value for the input fuse is indicated on the lower left corner of the front panel. If the
input fuse needs replacing it must be replaced with the proper type and value. Use
standard or fast-blow fuses. Never use a slow-blow fuse.
Caution: Ensure that a.c. power to the charger has been disconnected before
attempting to open the fuseholder. To remove the fuse for replacement, insert a flat
tip screwdriver into the fuseholder cover and turn counterclockwise until the spring-
loaded cover releases. To replace the fuseholder cover, depress it fully into the
fuseholder and turn it clockwise until it locks into position (about a quarter turn).
Warning: Do Not replace the gray slotted cap of the fuseholder without a fuse
installed. It will not be retrievable. If this occurs, contact the factory.
All charger wiring should be made in accordance with UL, U.S. Coast Guard
and/or A.B.Y.C. regulations and recommendations, as well as all relevant local
codes. See section IX) REFERENCE APPENDIX. for sources.
IV) OPERATION
A) Three Stage Charge Regimen
The Phase Three Battery Charger features the three stage charge regimen which is
widely recommended by battery manufacturers for allowing the fastest possible
rechargetime without loss of batteries’ electrolyte (gel or liquid) which may be caused
by sustained charging at higher voltages.
This three stage regimen is initiated each time a.c. is first applied, when drained
batteries are most likely to be encountered. (This also occurs when the reinitialize
button on the optional remote panel is activated — see section D - Remote Panel
Option on page 18) The regimen proceeds as follows:
1) Bulk Charge - When batteries are significantly discharged the charger responds
initially by delivering a high amount of d.c. current, at or near the charger’s maximum
rated output, in order to rapidly replenish them. It is during this stage that charging
current is maintained at a high level as battery voltage increases. Bulk charging
continues until battery voltage reaches the “charge” voltage level (where batteries
are at about 75-80% of capacity). A current limit circuit prevents charger overload
during this maximum output stage.
2) Absorption Charge -During thissecond stageof thecharge cycle,battery voltage
is maintained at the “charge” voltage level. Output current begins to taper off as the
battery plates become saturated. Charge voltage is maintained until the current
sensing circuit detects that output current has tapered to about 5-15 % of charger
rating*. At this point the batteries are at about 95 % of full charge and the Phase
Three charger switches to the third and final stage of the charge cycle.
* Note: The absorption phase may also be ended by the time-out circuit. See section
B following for a complete explanation of the purpose and functioning of the time-
out circuit.
14 15