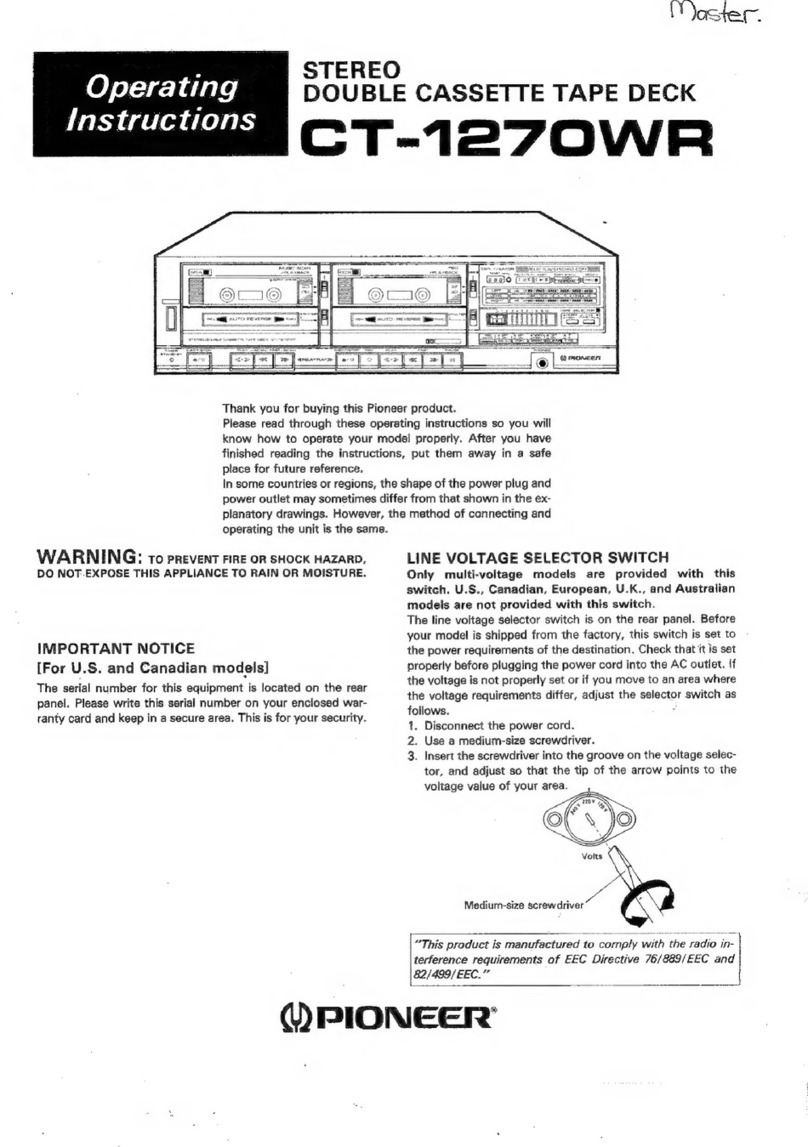
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
1.1 PLAYBACK FLOW
The signal picked up by the playback head is
amplified by the equalization amplifiers, Q1701
and Q1703. At the sametime, frequency response
iscorrected.
The output from the equalization amplifiers is
level-adjusted by variable resistor VR1703 and
then applied to Q1705. In addition to being an
amplifier, Q1705 also functions to correct fre-
quencyresponse.
When normal tape is used, Q1707 wiU be ON,
and the combination of Q1701, Q1703, and
Q1705 will set equalizationto 120ps.For metal or
CrO2 tape, Q1707 will remain OFF and equaliza-
tion will be70ps.
The output from Q1705 is applied to pin 15
of IC601 (HA11226) in the Dolby circuit. Here,it
is passed
out pin 9. This output is then applied to
pin 16 of IC602 and output from pin 9. The out-
put signal from IC602 passes
via the MONITOR
switch to LINE OUTPUT. (A description of the
Dolby circuit will be presentedlater.)
1.2 RECORDING
FLOW
The signal input to the microphone jack is first
amplified by the mic amplifier, IC1501 (NJM-
4558D), then passed
viathe INPUT selectorswitch
to the INPUT volume. Level is adjusted by the IN-
PUT volume and the signal is then applied to the
flat amp IC1701 (NJM4558D). Theamplifiedsignal
is then pa.ssed
through the MPX filter and into the
Dolby circuit. In the Dolby circuit, it is passed
through Q608, IC602 (HA11226), and IC601
(HA11226) before input to the recording ampli-
fier. From the recording amp, it is applied to the
recording head.
1.3 CONTROL
CIRCUIT
The control circuitry of this unit is contained
in CPU PD6006, expansion IC PM3001, and IC
PA3010 used in the MS function. The key signals
applied to PD6006 are transmitted to PM3001 as
16-bit serial data, and PM3001 then usesthis data
to control the various circuits.
When a mode key is activated, the 16-bit serial
data transmission is output from pin 5 of PD6006.
This is shown in Fig. 1-1. Also a clock pulse is
output from pin 7. (Data and clock pulse trans-
mission occurs once eachtime the key isactivated.)
The 16-bit serial data is applied to pin 3 of the
expansionIC, PM3001, andthe leading
edgeof the
clock pulse is read into the shift register of PM
3001 through pin 2.
After both read events are completed, a STB
(strobe) pulse is applied to pin 1, and PM3001
then starts transmitting control signals from its
various output pins in accordance with which key
wasactivated.(Referto Fig. 1-3.)
The following sections will describe the various
circuit operations occurring when a mode key is
activated. Operations will be described for the
FWD direction of travel. (Except where other-
wise specified, the pin nos. will be for PM3001.)
The DOLBY MUTE circuit shown in the signal
path diagram(Fig. 1-1)tums Q313 ON to mute all
circuik only when the position of the Dolby
switch is changed.
1. STOPModeKeyON -Power switchON
Mechanism
The 16-bit serialdata transmission from PD6006
will cause pin 7 and 8 of PM3001 to go high,
tuming SOL L and R OFF. The mechanism will
thus be placed in a STOPstatus.
Motor
Pin 4 and 5 will be low. and the reel motor will
bein a STOP
status.
Signal
Pathandothercircuits
When pin 9 ishigh, Q621, Q311, and Q1603 are
all ON. This causes
LINE OUTPUT and the head-
phone amp to be muted. If pin 11 alsogoes
high,
Q309 is tumed ON, placingthe REC AMP input at
a ground potential. When pins 12 and 13 go low,
Q302 tums OFF, stopping the bias oscillator
circuit, and extinguishing the REC IND. Muting is
applied to all circuits in a STOP status.
2. PLAY Mode Key ON
Mechanism
Pin 7 and 8 of PM3001 golow, activatingSOL L
and R. (Refer to the timing chart in Fig. 1-5.)
This places the mechanism in the PLAY mode.
Motor
Pin 4 goesto a low level, while pin 5 is held at
a middle (M) level, causingRM R (reel-motor R)
to start turning.
P06006
t--"=
Fig.1-1 PD6006
Dataoutput
3 35)S