Table of Contents
Manual No. 016-0171-548 Rev. C i
Chapter 1 Introduction............................................................................. 1
Receiver Overview ....................................................................................................................1
USB Capability ....................................................................................................................1
Updates ...............................................................................................................................2
Overview of DGPS Systems .....................................................................................................2
Sources of Error ..................................................................................................................3
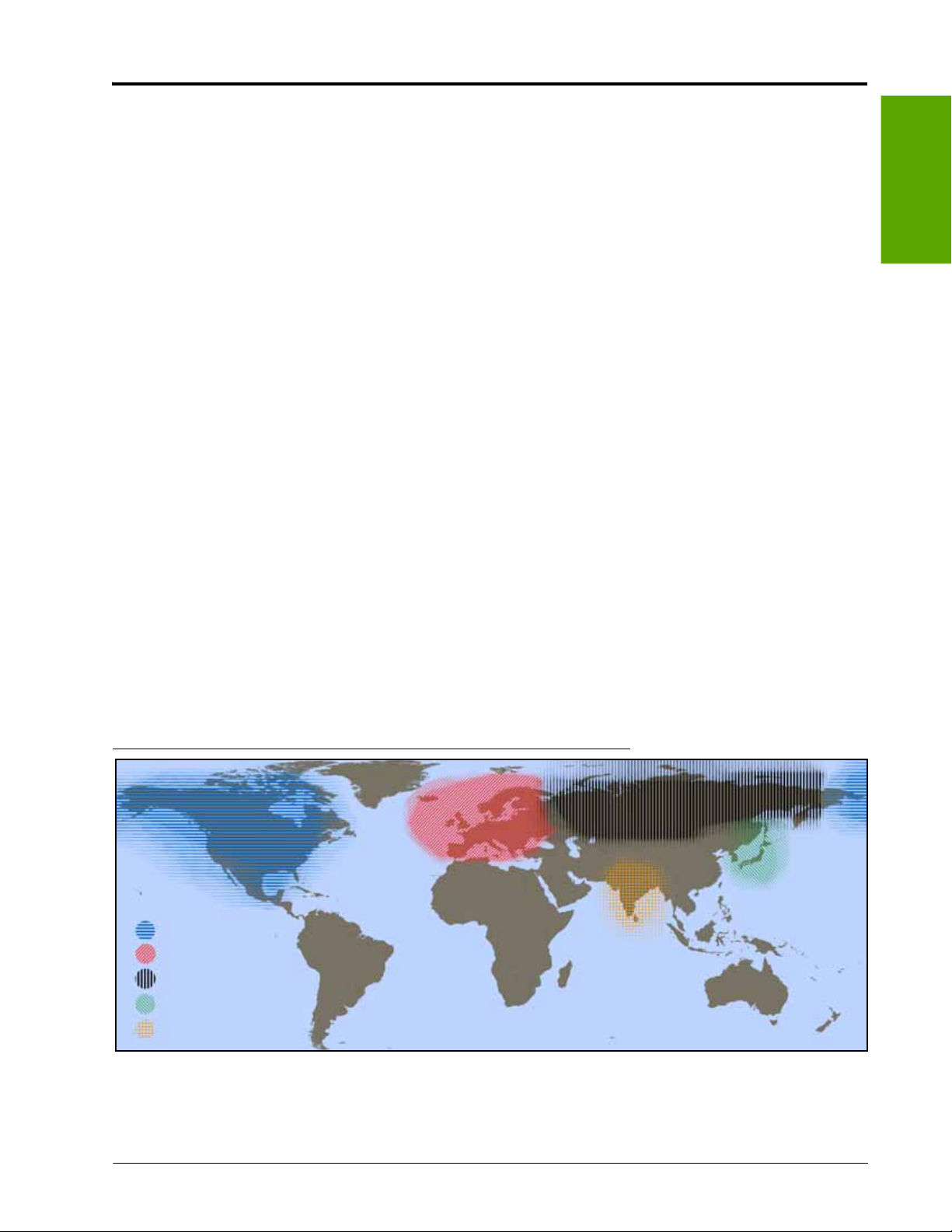
Differential GPS (DGPS) Correction Sources .....................................................................3
Chapter 2 Installation and Initial Start Up.............................................. 7
Mounting GPS Receiver Equipment .........................................................................................7
DGPS Receiver ...................................................................................................................7
DGPS Antenna Mounting ....................................................................................................7
Powering the GPS Receiver .....................................................................................................8
Initial Startup ..............................................................................................................................9
Subscription Services ..........................................................................................................9
Normal Operation ......................................................................................................................9
Chapter 3 Display Menus....................................................................... 11
Overview ................................................................................................................................. 11
Home Display Screen .............................................................................................................12
OmniSTAR® XP/HP Restart .............................................................................................13
Receiver Display Menu ...........................................................................................................13
Receiver Information .........................................................................................................13
GPS Engine Information ....................................................................................................14
GPS Display Menu ..................................................................................................................15
GPS Signal Information .....................................................................................................15
Dilution of Precision (DOP) Information ............................................................................16
Position Information ...........................................................................................................16
Speed and Course Over Ground (COG) Information ........................................................17
Standard Deviation Information .........................................................................................17
OmniSTAR® Display Menu .....................................................................................................18
Carrier and Signal Status ..................................................................................................19
Virtual Base Station Subscription Information ...................................................................19
OmniSTAR HP Expiration Information ..............................................................................20
OmniSTAR Subscription Information .................................................................................20
OmniSTAR Satellite Frequency .........................................................................................20
OmniSTAR Serial Number ................................................................................................21
OmniSTAR Service ID Number .........................................................................................21
RTK Display Menu ..................................................................................................................22
Baseline Information ..........................................................................................................22