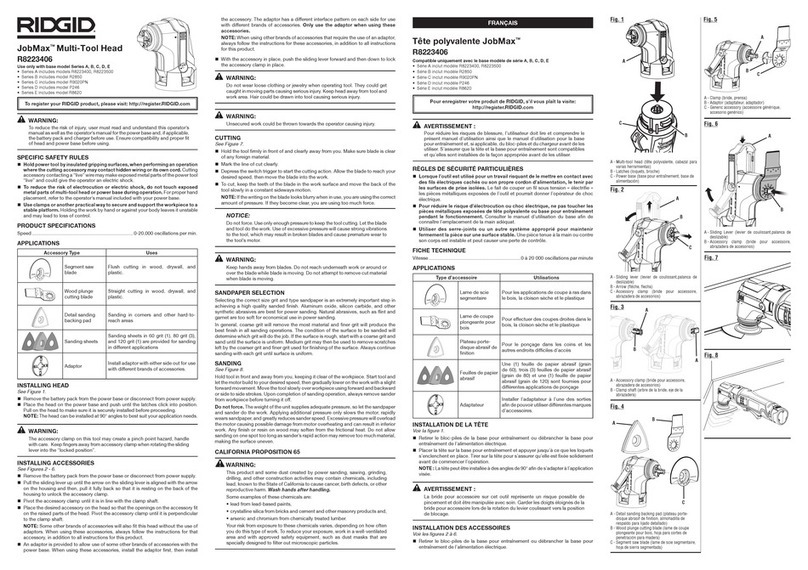
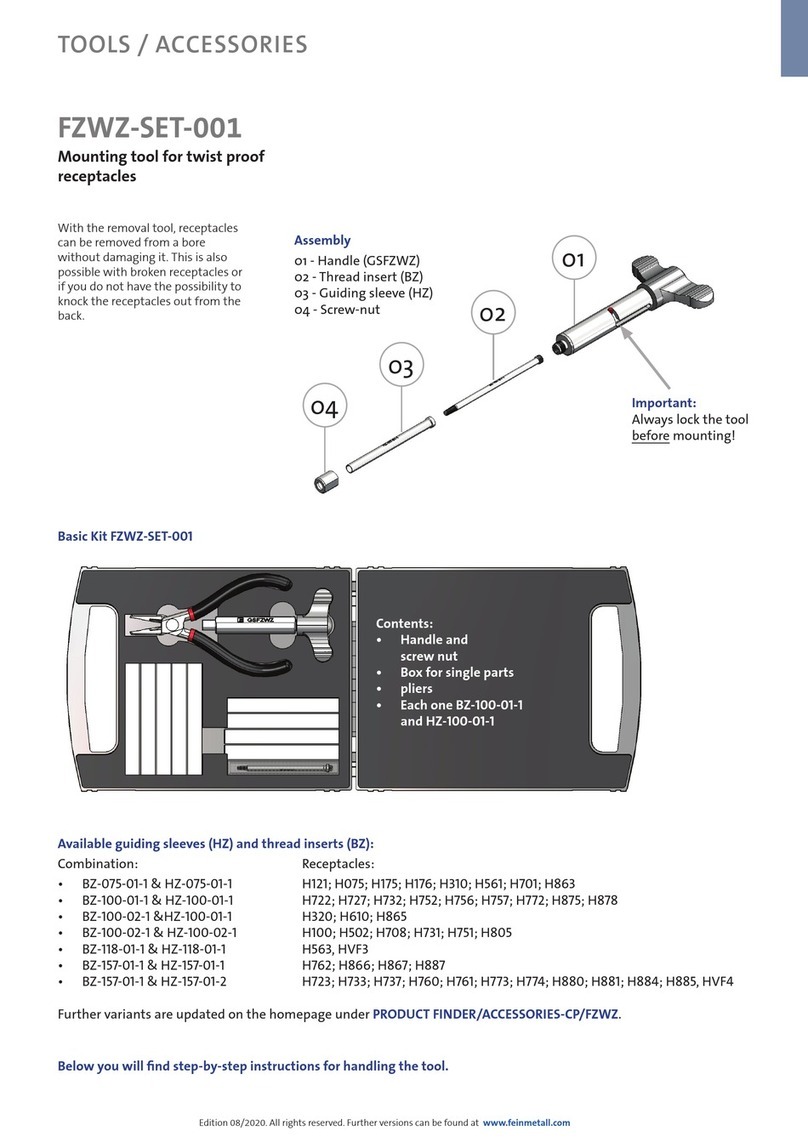
WARNING
• Read operators manual. Operator must be prop-
erly trained before using tool.
• Wear eye protection.
• Do not exceed pressure and temperature ratings of
the tool and any attachment, valve or fitting. Only
tap into lines that contain specified media.
Model RT 3422 Tapping Tool
Water: 500 psig @ 100°F (40°C)
Air, Steam, Natural Gas: 150 psig @ 370° F (172°C)
Tapping Tool Safety
1. Only trained personnel should use this tapping
tool. Incorrect use of this tool can result in serious
personal injury, environmental damage, and/or prop-
erty damage.
2. Always wear eye protection. Cutters and drills are
hard and can shatter.
3. Do not exceed recommended pressure ratings.
Attempting to tap into main with pressures beyond the
maximum limits of this tool or a fitting may result in
their failure.
4. Only tap into pressurized mains that carry water,
air, steam or natural gas. Other media may attack
the seals of this tool.
5. When using power tools to drive this tapping
tool, understand and follow all the safety in-
structions associated with that power tool. Air
power ratchets are generally a safer choice due to
the inherent explosion and shock hazards asso-
ciated with electrical tools.
• Electrical tools should not be used for natural
gas taps. Only use air or manual ratchets.
Electrical tools cause sparks which may ignite the
gas.
• Grounded electrical tools should be plugged
into a properly grounded outlet. If tool should
electrically malfunction or breakdown, grounding
provides a low resistance path to send electricity
away from the user.
• Electrical tools should be plugged into an outlet
protected with a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter
(GFCI). Reduces risk of electrical shock.
6. Use only right angle electrical drills or air ratchets
to rotate the cutter. Tool must be fed at a con-
trolled rate. Failure to use a right angle drive or to
carefully control the tool feed rate may result in the
cutter suddenly stopping which will cause the power
tool driver to suddenly twist.
7. Main being tapped must be securely mounted to
prevent any movement. Movement could cause
tool breakage during the tapping operation.
8. Follow all applicable regulations and safety pre-
cautions regarding the work area.
• When working below grade, have an adequate es-
cape route before starting the tap. Such pre-
cautions reduce the risk of injury.
• When working on a scaffold or lift, the operator,
tool, and drive assembly should all be properly
secured. Will prevent injury in the event of a fall or
dropping a tool.
9. Vent pressure bleed valve away from work area
and personnel. When working over equipment
or personnel, use a hose attachment on the
bleeder valve to control fluid discharge. Discharge
directed at personnel could result in serious injury.
10. Do not use this tool to support the operator.
Could result in tool breakage or malfunction.
11. Tool is made to tap into pressurized lines. Follow
instructions in operator’s manual on tool uses.
Other uses may increase the risk of injury
NOTE! Keep this manual in the pocket provided in the
toolbox.
Description, Specifications,
and Equipment
Description
The Model RT3422 Tapping Tool is designed to perform
pressurized taps using a saddle-mounted valve or
welded nipple on steel, plastic, ductile iron and cast
iron pipe. It is capable of tapping water lines under
pressure up to 500 psi and steam, air, and natural gas
mains up to 150 psi. Weighing only 18 lbs, the Model
RT3422 can produce 3/4″ – 2″taps fast and easy. The
cutter is rotated by an 11/16″ hand ratchet or can be op-
erated by an air ratchet or right angle drill if desired. A
self cleaning acme threaded barrel permits easy feeding
of the cutter into the pipe and resists the force of the
pressurized pipe when the cut is made.
Ridge Tool Company 3
RT3422 Tapping Tool