Satel MICRA User manual
Other Satel Security System manuals

Satel
Satel SP-6500 User manual

Satel
Satel SPL-5020 User manual

Satel
Satel SP-500 User manual

Satel
Satel SOW-300 Series User manual

Satel
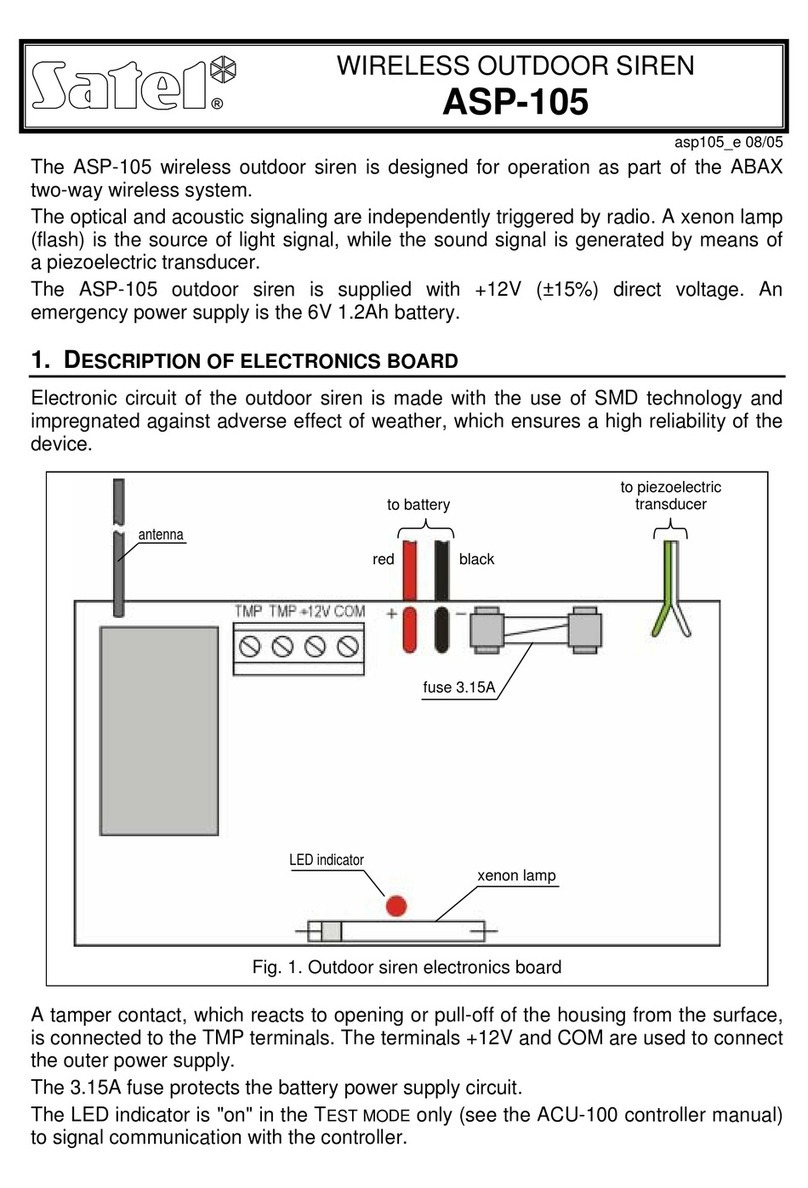
Satel ASP-105 User manual

Satel
Satel SILVER User manual

Satel
Satel CA-64 E User manual

Satel
Satel SP-4002 User manual

Satel
Satel APD-200 User manual
Satel
Satel SPL-2010 User manual

Satel
Satel SD-3001 User manual

Satel
Satel CSP-204 Installation manual

Satel
Satel Micra MPB-300 User manual

Satel
Satel ASP-205 User manual

Satel
Satel ABAX 2 User manual

Satel
Satel SPLZ-1011 User manual

Satel
Satel ECAM22 User manual

Satel
Satel ASP-200 User manual

Satel
Satel INT-TSG Owner's manual

Satel
Satel SPL-5010 User manual
Popular Security System manuals by other brands

Inner Range
Inner Range Concept 2000 user manual

Climax
Climax Mobile Lite R32 Installer's guide

FBII
FBII XL-31 Series installation instructions

Johnson Controls
Johnson Controls PENN Connected PC10 Install and Commissioning Guide

Aeotec
Aeotec Siren Gen5 quick start guide

IDEAL
IDEAL Accenta Engineering information

Swann
Swann SW-P-MC2 Specifications

Ecolink
Ecolink Siren+Chime user manual
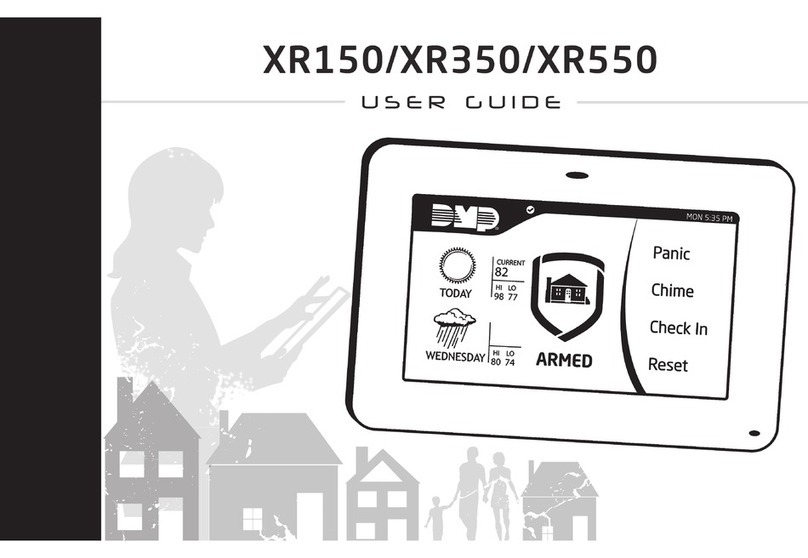
Digital Monitoring Products
Digital Monitoring Products XR150 user guide

EDM
EDM Solution 6+6 Wireless-AE installation manual

Siren
Siren LED GSM operating manual
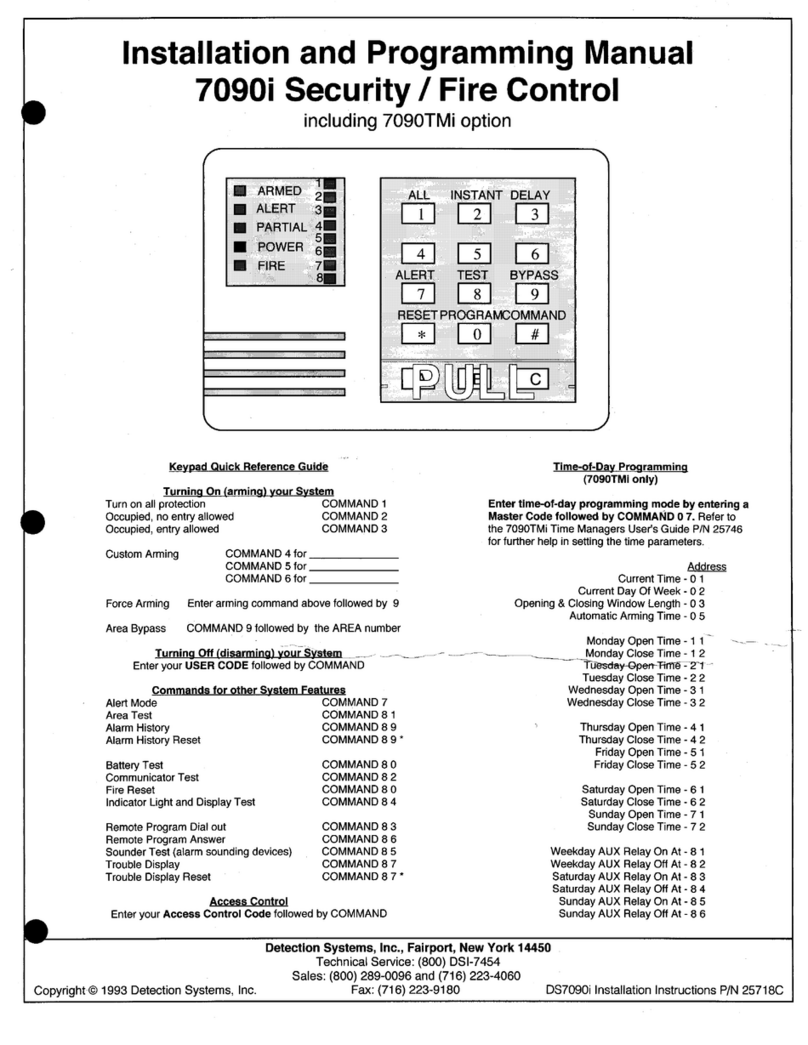
Detection Systems
Detection Systems 7090i Installation and programming manual