Page
:
3 of 7
Document No.U025417
Date
:
Jan/11/2019
NOTES
Residential Fire Sprinkler Systems should only be designed and installed by individuals who are completely familiar
with automatic sprinkler system design, installation procedures, and techniques.
Several criteria may apply to the installation and usage of each sprinkler. Consequently, it is recommended that the
sprinkler system designer review and develop a working understanding of the complete list of criteria prior to initiating
the design of the sprinkler system.
Questions concerning sprinkler installation and usage criteria, which are not coverage by the following instructions,
should be submitted to Contact Company. Include sketches and technical details as appropriate.
In some instances, the requirements of this document may concern specifications which are more stringent and which
take precedence over those specified in NFPA 13, 13D, 13R, or by the authority having jurisdiction.
The Model CN-RES must not be used in applications where the air pressure above the ceiling is greater than that below.
Inspect all sprinklers after installation to ensure that both the gap between the cover plate, ceiling and some air vents
on the side of the cover plate assembly are open and free from any air flow impediment.
The spray from the sprinkler is distributed radically outward and downward from the sprinkler deflector. Consequently,
the sprinklers must be located such that there will be no blind spaces shielded from spray by partitions, room dividers,
overhangs or other parts of the dwelling structure.
The number of sprinklers within each compartment (as defined by NFPA 13, 13D, or 13R) must be kept as small as
possible. Do NOT use more sprinklers than necessary to cover a particular space.
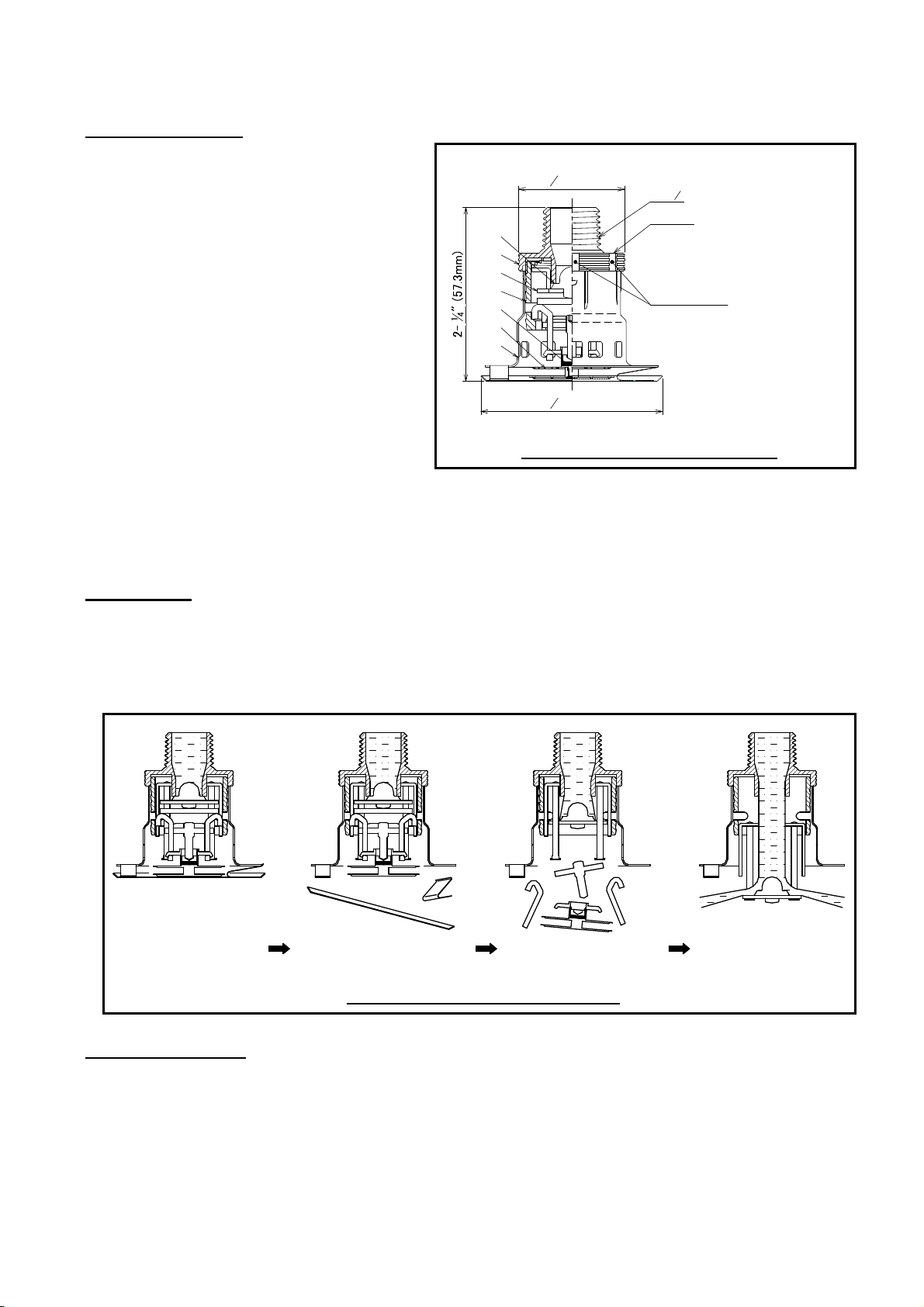
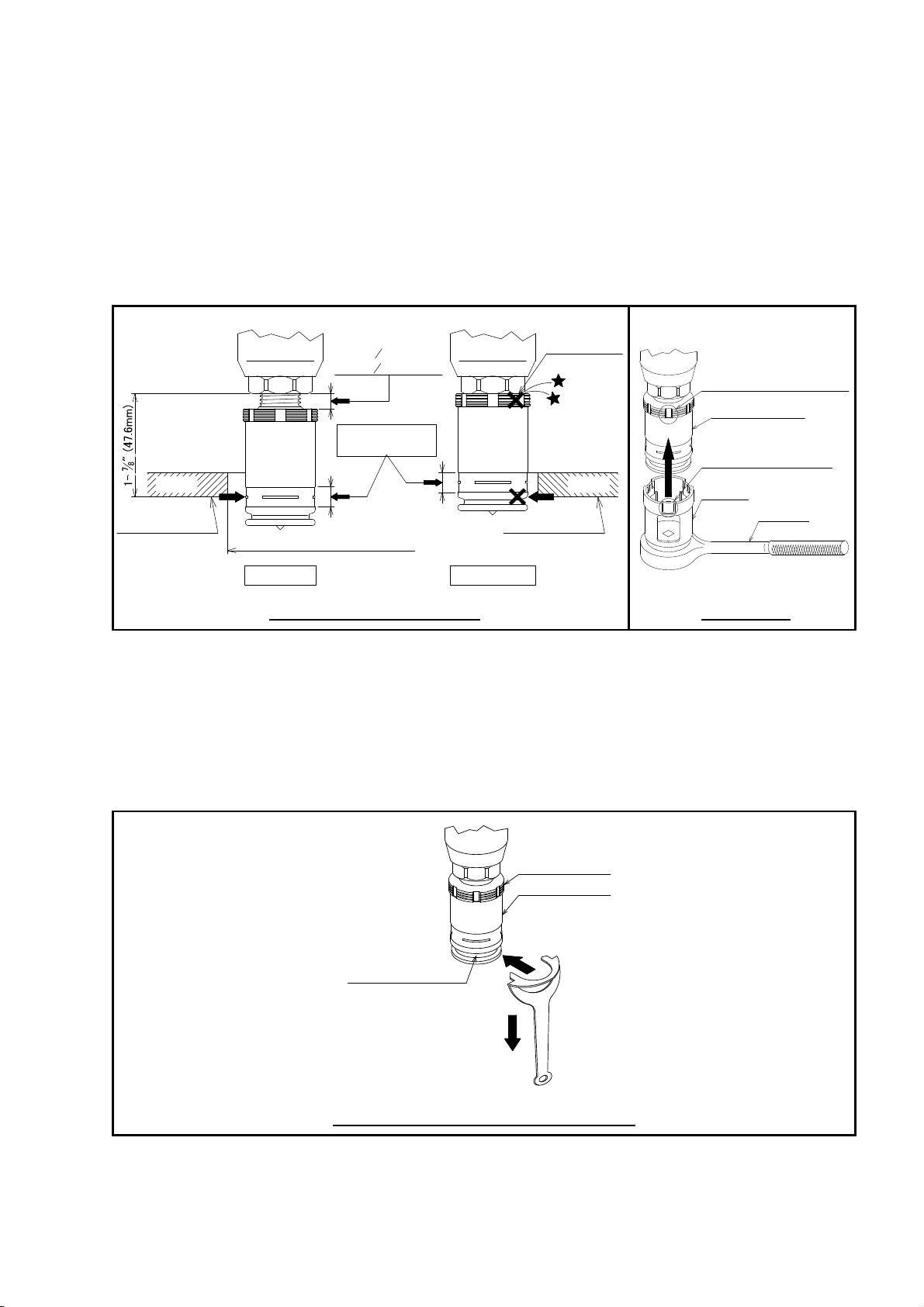
Use only the Cover Plate provided with the Model CN-RES. The sprinkler must be secured in place by firmly fastening
the sprinkler system piping to the structure. If the sprinkler is not properly secured in position, reaction forces
resulting from sprinkler operation could alter its orientation and its water distribution pattern.
Obstruction to Water Distribution
Locations of sprinklers must follow the obstruction rules of NFPA 13 for Residential Sprinklers.
General Service Conditions
The Model CN-RES must only be utilized in WET PIPE sprinkler systems.
Heat Source Criteria
Refer to NFPA 13D or 13R for the requirements relating to the prevention of possible activation of the Heat Responsive
Element of Model CN-RES, due to exposure to a heat sources other than an actual fire.
Precautionary Warnings for Corrosive Environments
The Model CN-RES should not be installed where they may be subjected to a corrosive environment including the following:
(1) Chlorine ion and Chloride environment.
Stress corrosion cracking may be caused by exposure to environments with Chlorine ion and Chloride. Exposure to this
environment may result in sprinklers operating under Non-Fire conditions or Not Operating when exposed to an actual fire.
(2) Sprinkler system piping with Copper.
Sprinkler systems should be constructed in compliance with the applicable standards and the requirements for the copper
piping when copper piping is used in the sprinkler system. (Reference standards NFPA 13, ASTM B813, B828, and CDA
(Copper Development Association) – Solder Joint)
All residual flux must be removed from the interior and exterior of copper piping by thoroughly flushing before installation of
the Sprinkler Heads. Otherwise, residues of flux may cause corrosion and leakage in the sprinkler system.
Sprinkler Spacing Criteria
The minimum spacing between sprinklers is 8 feet (2.4m). The maximum spacing between sprinklers cannot go beyond the
coverage area calculated by using the specific hydraulic factors. (Ref. Table A)
Hydraulic Design Criteria
The minimum required sprinkler flow rates for system designed to NFPA 13D or 13R are given in Table A as a function of
temperature rating and the maximum allowable coverage areas. The sprinkler flow rate is the minimum required discharge
from the most hydraulically demanding sprinkler from each of the total number of “design sprinklers” as specified in NFPA 13D
or 13R.
For systems designed to NFPA 13, the number of designed sprinklers is to be the four most hydraulically demanding
sprinklers. The minimum required discharge from each of the four sprinklers is to be the greater of the followings;
・ The flow rates given in Table A for NFPA 13D and 13R as a function of temperature rating and maximum allowable
coverage area.