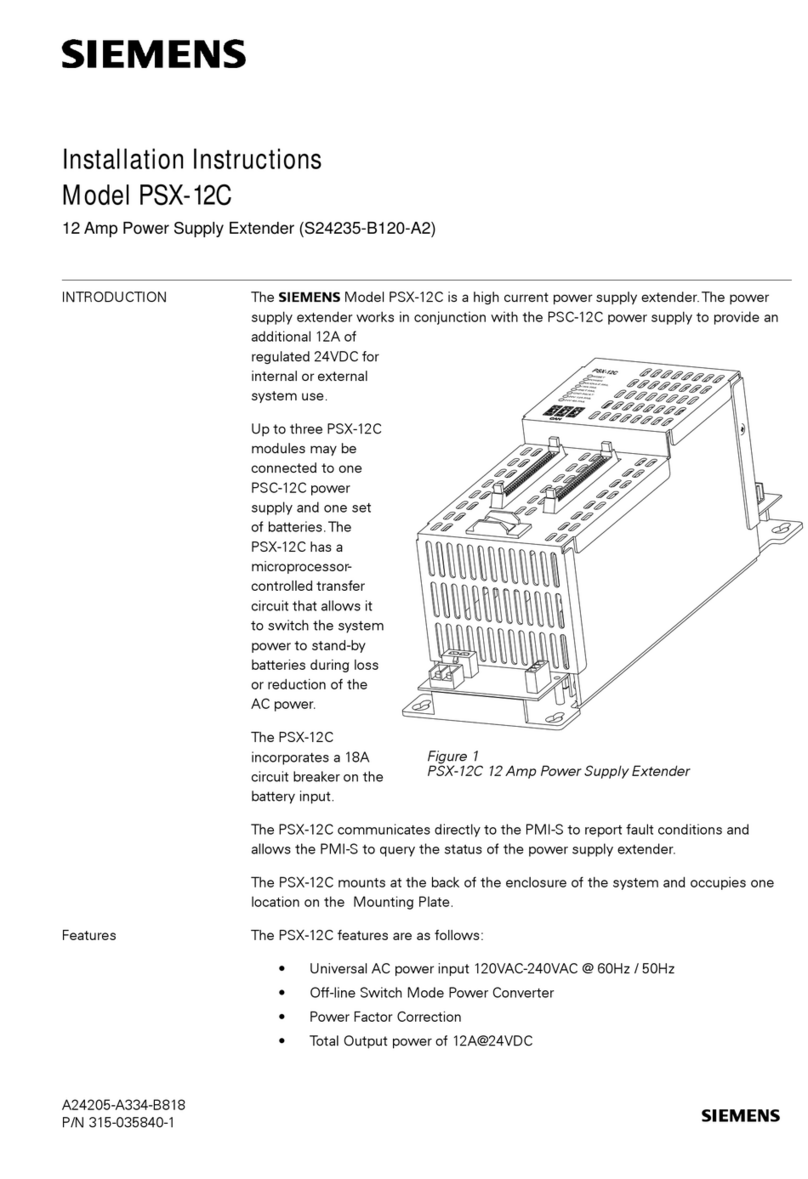
User´s Guide Power Rail Booster Version 12/2005
Copyright ©Siemens AG 2005 All rights reserved. 6ES7 972-4AA02-0XA0 Page 5 of 49
C o n t e n t s
1GENERAL REMARKS ............................................................................................................ 7
2INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................................... 9
2.1 APPLICATIONS ........................................................................................................................... 9
3GENERAL FUNCTIONS........................................................................................................ 11
3.1 BASIC FUNCTION...................................................................................................................... 11
3.2 FUNCTIONS.............................................................................................................................. 11
3.2.1 SUPPORTED PROTOCOLS ......................................................................................................... 11
3.2.2 TRANSMISSION SPEED.............................................................................................................. 11
3.2.3 LED TEST ON ACTIVATING THE VOLTAGE SUPPLY....................................................................... 12
3.2.4 SIGNAL REGENERATION............................................................................................................ 12
3.2.5 SHORT CIRCUIT DETECTION...................................................................................................... 12
3.2.6 MONITORING OF THE OUTPUT TEMPERATURE............................................................................ 12
3.2.7 COMMISSIONING AIDS............................................................................................................... 12
3.3 SETTABLE ADDITIONAL FUNCTIONS (PRODUCT RELEASE 3AND ABOVE)........................................ 12
3.3.1 DISPLAY OF THE FIRMWARE VERSION ........................................................................................ 12
3.3.2 CONTROLLING THE "IS-MASTER"SIGNAL.................................................................................... 13
3.3.3 DIAGNOSTIC MESSAGE............................................................................................................. 13
4NETWORK TOPOLOGIES FOR CONTACT RAIL SYSTEMS.............................................. 14
4.1 TERM DEFINITIONS................................................................................................................... 14
4.2 INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................................... 15
4.3 EXAMPLES OF TOPOLOGIES ...................................................................................................... 15
4.3.1 CASCADING ............................................................................................................................. 15
4.3.2 POINT-TO-POINT CONNECTION.................................................................................................. 15
4.3.3 LINE TOPOLOGY....................................................................................................................... 16
4.3.4 STAR TOPOLOGY ..................................................................................................................... 16
4.3.5 CLOSED RING CIRCUITS ........................................................................................................... 17
4.4 RAIL SECTIONS........................................................................................................................ 18
5CONFIGURATION................................................................................................................. 19
5.1 PROCEDURE............................................................................................................................ 19
5.2 CONFIGURATION WITH THE „PRB CHECKER“.............................................................................. 21
5.3 CONFIGURATION OF THE BUS PARAMETERS ............................................................................... 23
5.3.1 CONFIGURING THE PARAMETER:„NUMBER OF OLMS “................................................................ 23
5.3.2 ADAPTING THE„RETRY LIMIT“PARAMETER ................................................................................. 24
5.4 CONFIGURING THE CONTACT RAILS AND SLIDING CONTACTS....................................................... 24
5.4.1 INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................................... 24
5.4.2 CONTACT RAIL CAPACITANCE ................................................................................................... 24
5.4.3 CONTACT RESISTANCE BETWEEN CONTACT RAILS AND SLIDING CONTACTS ................................. 24
5.4.4 PREFERRED ARRANGEMENT OF THE CONTACT CONDUCTORS ..................................................... 25
5.4.5 PREFERRED ARRANGEMENT OF THE WIRES IN CABLES ................................................................ 26
6COMMISSIONING................................................................................................................. 27
6.1 SAFETY INFORMATION .............................................................................................................. 27
6.2 GENERAL INFORMATION REGARDING COMMISSIONING................................................................. 28
6.3 INSTALLATION .......................................................................................................................... 29
6.3.1 INSTALLING A PRB................................................................................................................... 29
6.3.2 INTERFACES AND CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENT ........................................................................ 30
6.3.2.1 GRAPHICAL INTERFACE DIAGRAM,GALVANIC ISOLATION ...................................................... 30
6.3.2.2 WIRING GUIDELINES FOR INTERFACES ............................................................................... 30
6.3.2.3 CONNECTING THE POWER RAIL INTERFACE........................................................................ 31
6.3.2.4 CONNECTING THE PROFIBUS INTERFACE ........................................................................ 31
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com