Directional properties of the receiver can be observed when we try to
change its position in relation to the cable in directions indicated by the arrows.
Swinging the receiver only in directions “A” does not change the signal level
since the magnetic field detector does not change is position in relation to the
magnetic field lines. On the other hand, rotating the receiver around its axis (ar-
row “C”) will cause gradual signal deterioration until it disappears when rotating
the device by 90º. Similarly, when swinging the receiver in direction “D” (around
the axis of the receiver’s aerial). Also moving the receiver away from the cable
(“B”) will weaken the signal as a result of a decrease in field’s strength with an
increase of the distance.
For a 2-core cable in which the current flows through one of the cores in
one direction and in the opposite direction through the other core, the magnetic
field strength is much lower than in a single-core cable since the fields gener-
ated by the cores cancel each other out. The greater the distance between the
cores, the stronger is the magnetic field. This phenomenon is utilised for detect-
ing all sorts of inconsistencies in power lines e.g. cable boxes, switches, stub
cables, cable ducts constrictions etc.
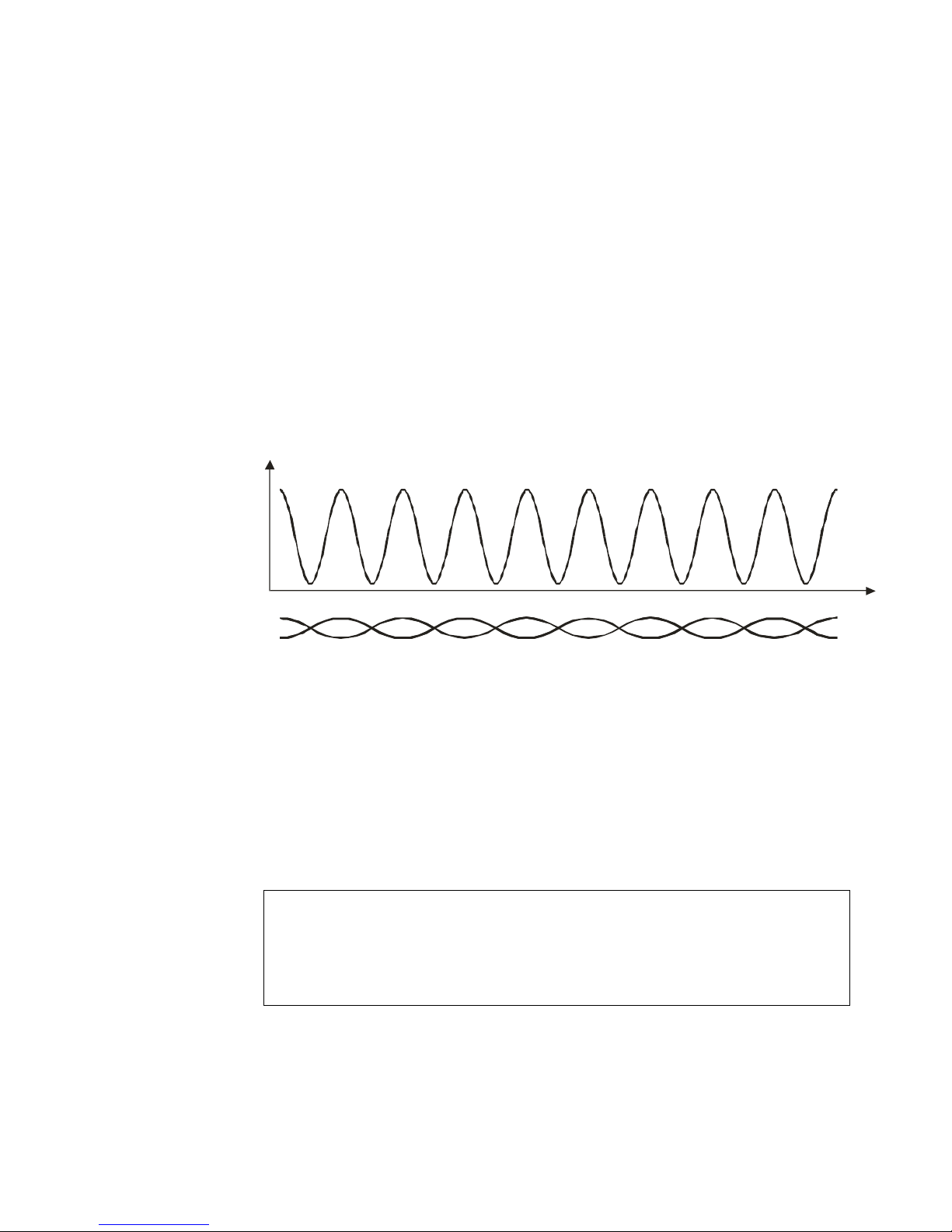
A different field distribution is created around a twisted pair cable. It is not
uniform and changes periodically depending on the relative position of the cores
(Fig. 5). It has to be taken into account when tracking a cable or locating cable
faults.
Twisted pair cable
Magnetic field intensity
Cable length
Fig.5 Magnetic field distribution around a twisted pair cable
6 System working mode
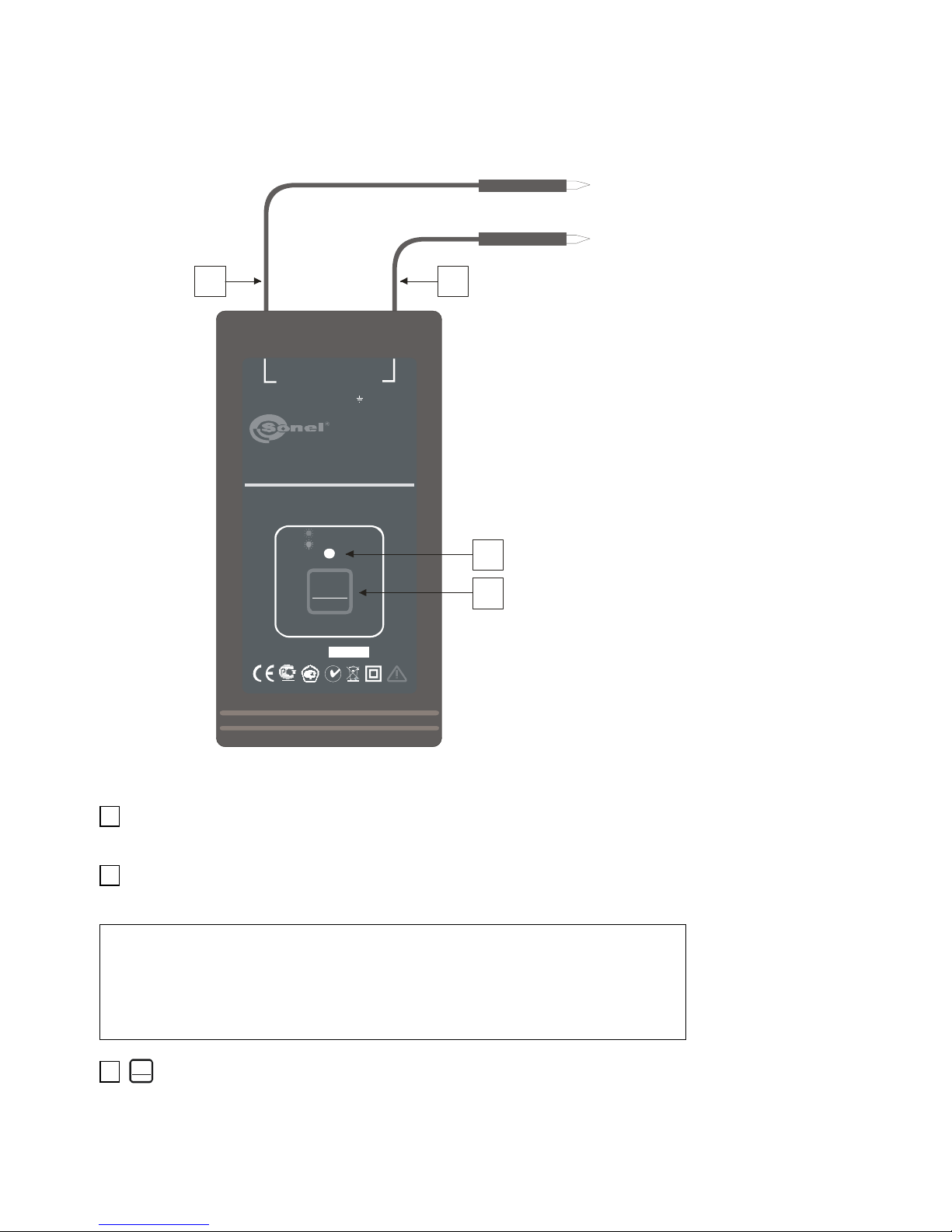
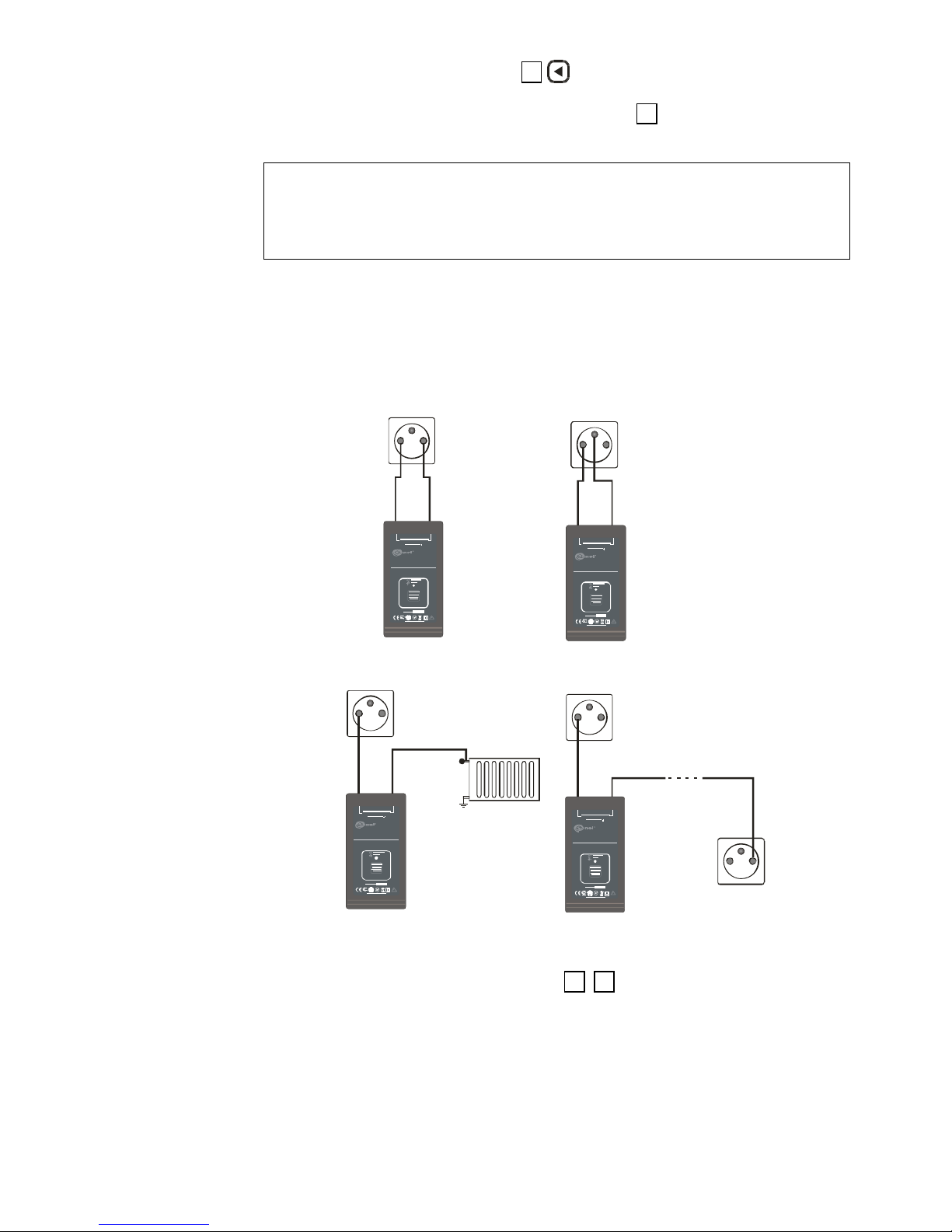
The system operates in the “M” current mode and can be used with un-
damaged leads under a voltage of 230 V AC or in closed circuits (for example,
shorted leads). It uses external direct current (minimum 12 V) or an alternating
current source (minimum 24 V).
NOTE!
The transmitter is designed to work with the rated voltage of 230V.
Connecting the device to a voltage that exceeds 250VAC can damage
the instrument.
One of the transmitter’s output terminals is connected to the phase wire of
the tested cable and the other one to the neutral wire. The voltage that exists in
this circuit is used by the transmitter to generate a current signal (max 20mA) in
a form of high frequency impulses with the amplitude modulated by a lower fre-
quency signal distributed over the time in the specific way. The magnetic com-
ponent of the field generated in this way is then detected by the receiver.