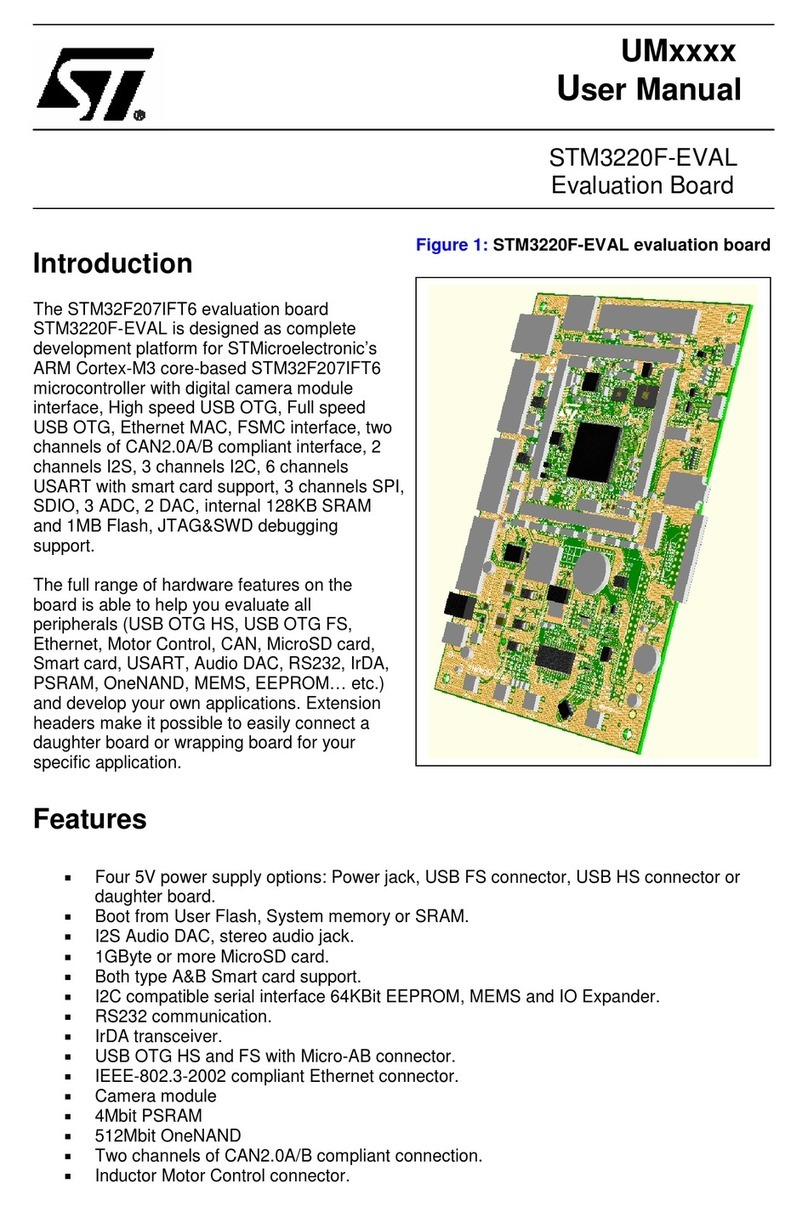
UM0432 Contents
3/53
7.4.6 "3-phase PMAC motor (sinewave)" settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7.4.7 "3-phase PMAC motor (sinewave)" advanced settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
7.4.8 Changing the maximum current allowed by GUI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7.4.9 Compiling the firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7.4.10 Programming the firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
7.4.11 Setting the option bytes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.4.12 Configuring the DC input range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.4.13 Jumper settings table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
7.4.14 Board connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.4.15 Changing the maximum allowed bus voltage level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.4.16 Changing the maximum allowed current level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.5 Driving the BLDC motor (trapezoidal - sensorless) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.5.1 Specific connection (sensor) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.5.2 Specific jumper settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.5.3 LED action after power-on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
7.5.4 Setting the potentiometers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.5.5 Running the motor (LED action) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.5.6 Changing the real-time parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.5.7 Stopping the motor (LED action) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
7.5.8 Configuring the system for BEMF amplification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
7.5.9 Detecting the BEMF during the PWM on time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
7.5.10 Detecting the BEMF using the internal reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7.5.11 Detecting the BEMF using the external reference VBus/2 . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7.5.12 Detecting the BEMF using the external reference and reconstructed
neutral point of the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
7.6 Driving the BLDC motor (trapezoidal - sensored) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
7.6.1 Specific sensor connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
7.6.2 Specific jumper settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
7.6.3 LED action after power-on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7.6.4 Setting the potentiometers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7.6.5 Running the motor (LED action) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7.6.6 Changing the real-time parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7.6.7 Stopping the motor (LED action) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7.7 Driving the BLAC motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7.7.1 Specific sensor connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7.7.2 Specific jumper settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7.7.3 LED action after power-on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45