Contents UM1956
2/31 DocID028406 Rev 1
Contents
1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Product marking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4 Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
5 Quick start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.1 Getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5.2 System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
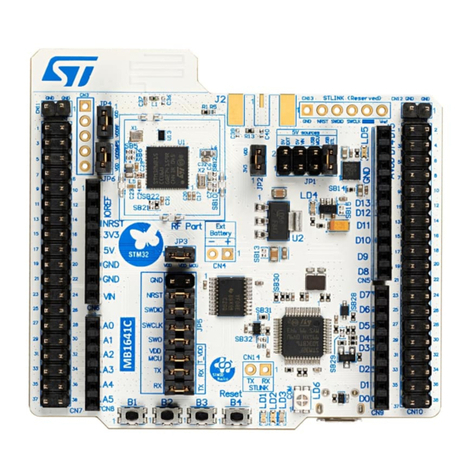
6 Hardware layout and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
6.1 Embedded ST-LINK/V2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6.1.1 Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1.2 ST-LINK/V2-1 firmware upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.2 Power supply and power selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.2.1 Power supply input from USB connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
6.2.2 External power supply inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
VIN or +5V power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
+3V3 power supply. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
6.2.3 External power supply output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.3 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.4 Push button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6.5 JP1 (IDD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.6 OSC clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.7 USART virtual communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.8 Solder bridges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.9 Arduino Nano connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
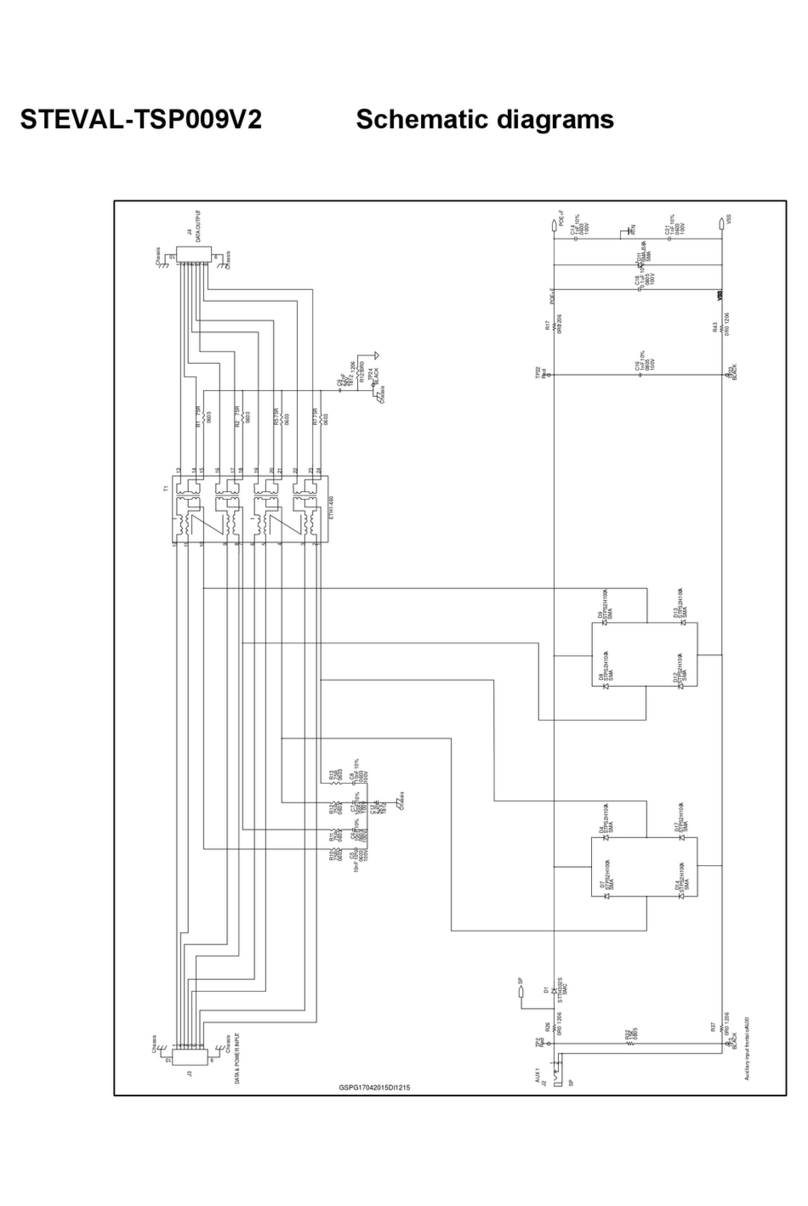
7 Electrical schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Appendix A Mechanical dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29