2
Inhaltsverzeichnis
1Sicherheitshinweise.....................................................................................................................3
2Normenkonformität......................................................................................................................3
3Funktion.......................................................................................................................................4
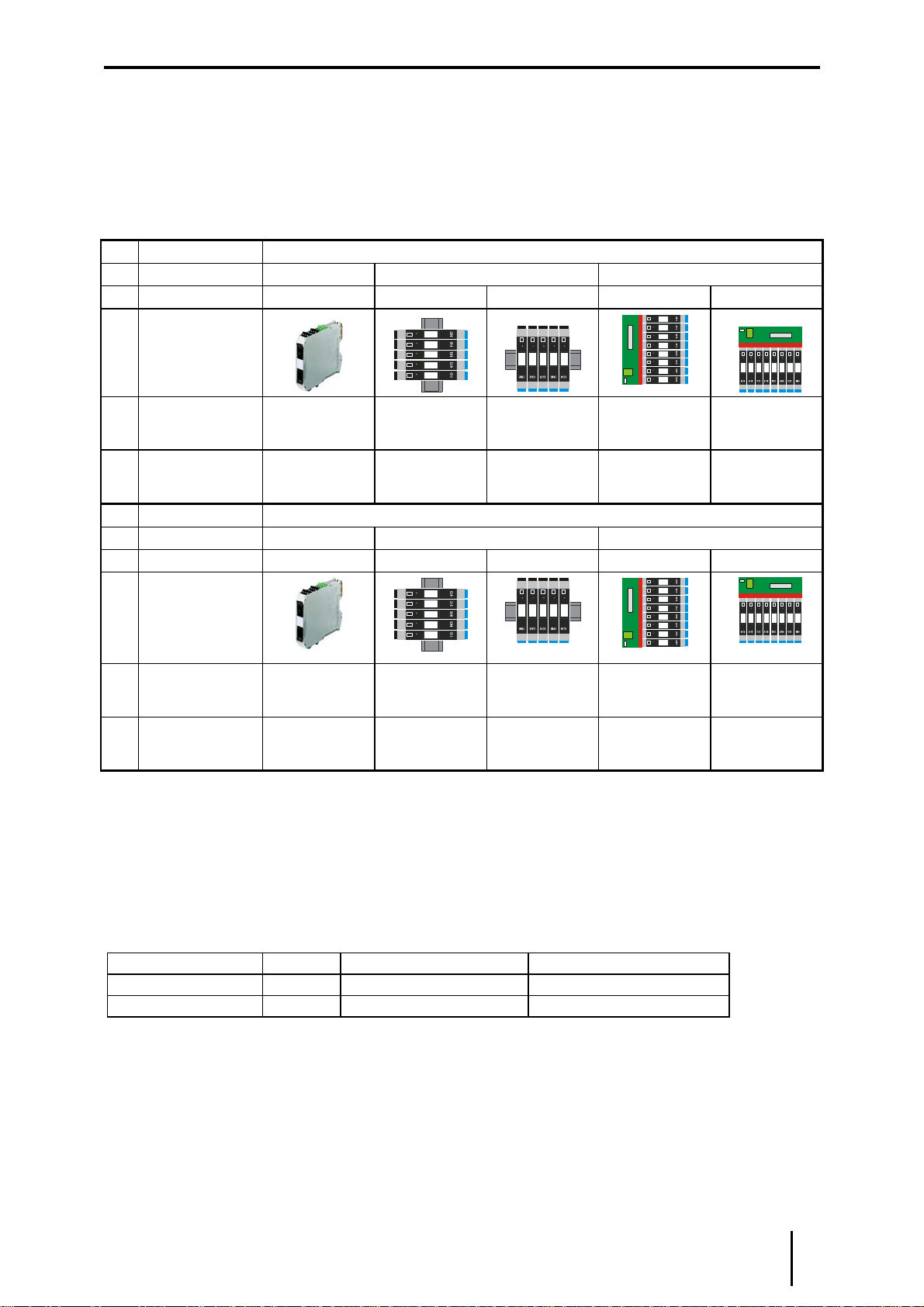
4Kennzeichnung und technische Daten ........................................................................................4
5Projektierung...............................................................................................................................5
5.1 Maximal zulässige Umgebungstemperaturen..........................................................................5
5.2 Verlustleistung.........................................................................................................................5
5.3 Projektierung der Verlustleistung in Schaltschränken..............................................................6
6Anordnung und Montage.............................................................................................................7
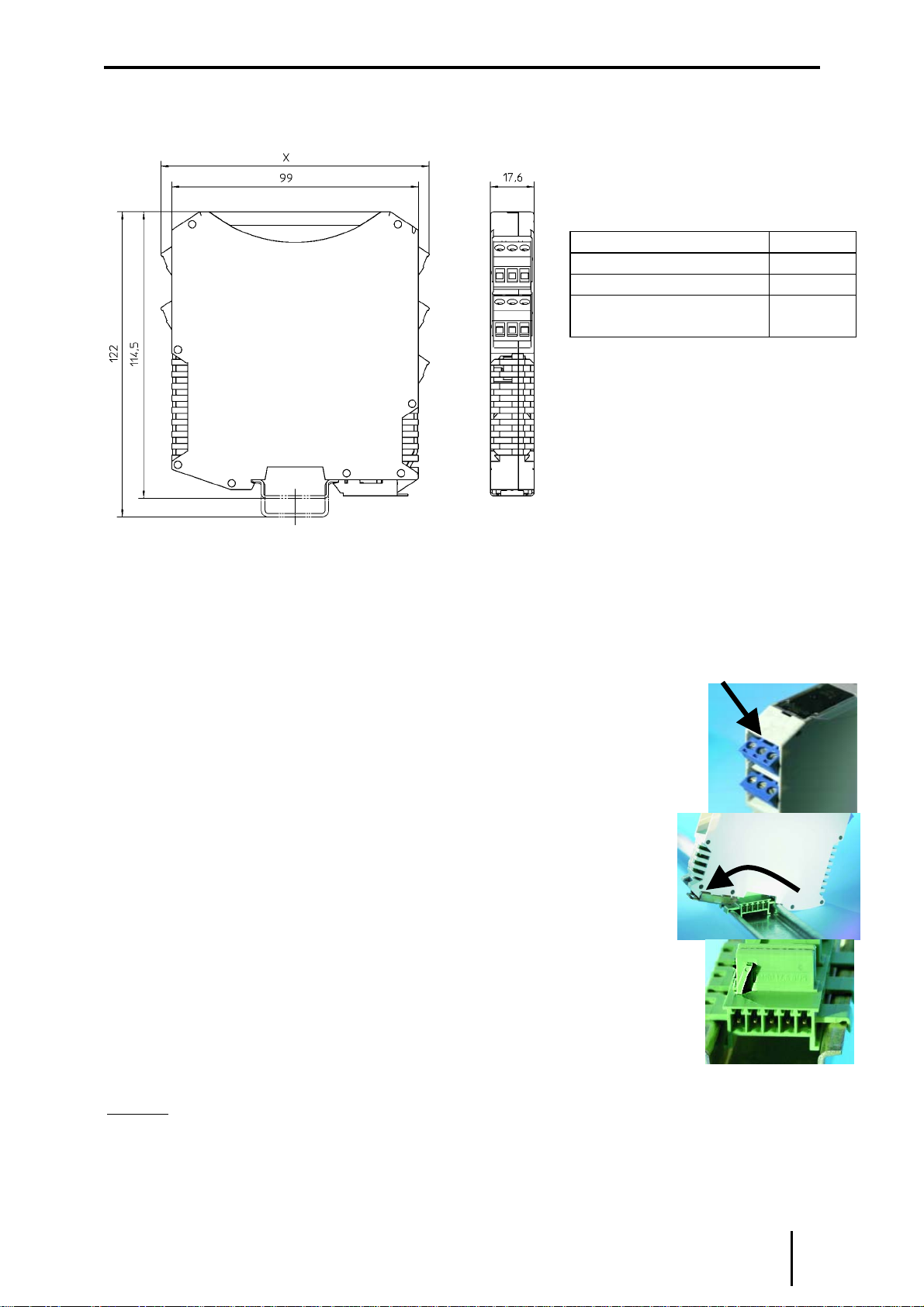
6.1 Maßzeichnung.........................................................................................................................7
6.2 Installation...............................................................................................................................7
6.3 Montage und Demontage........................................................................................................7
7Inbetriebnahme ...........................................................................................................................8
7.1 Anschlüsse..............................................................................................................................8
7.2 Anschluss von Kontakten ........................................................................................................9
7.3 Leitungsfehlererkennung.........................................................................................................9
7.4 Eingang (über Software IS pac Wizard)...................................................................................9
7.5 Signalverarbeitung (über Software IS pac Wizard)................................................................10
7.6 Ausgang (über Software IS pac Wizard)................................................................................10
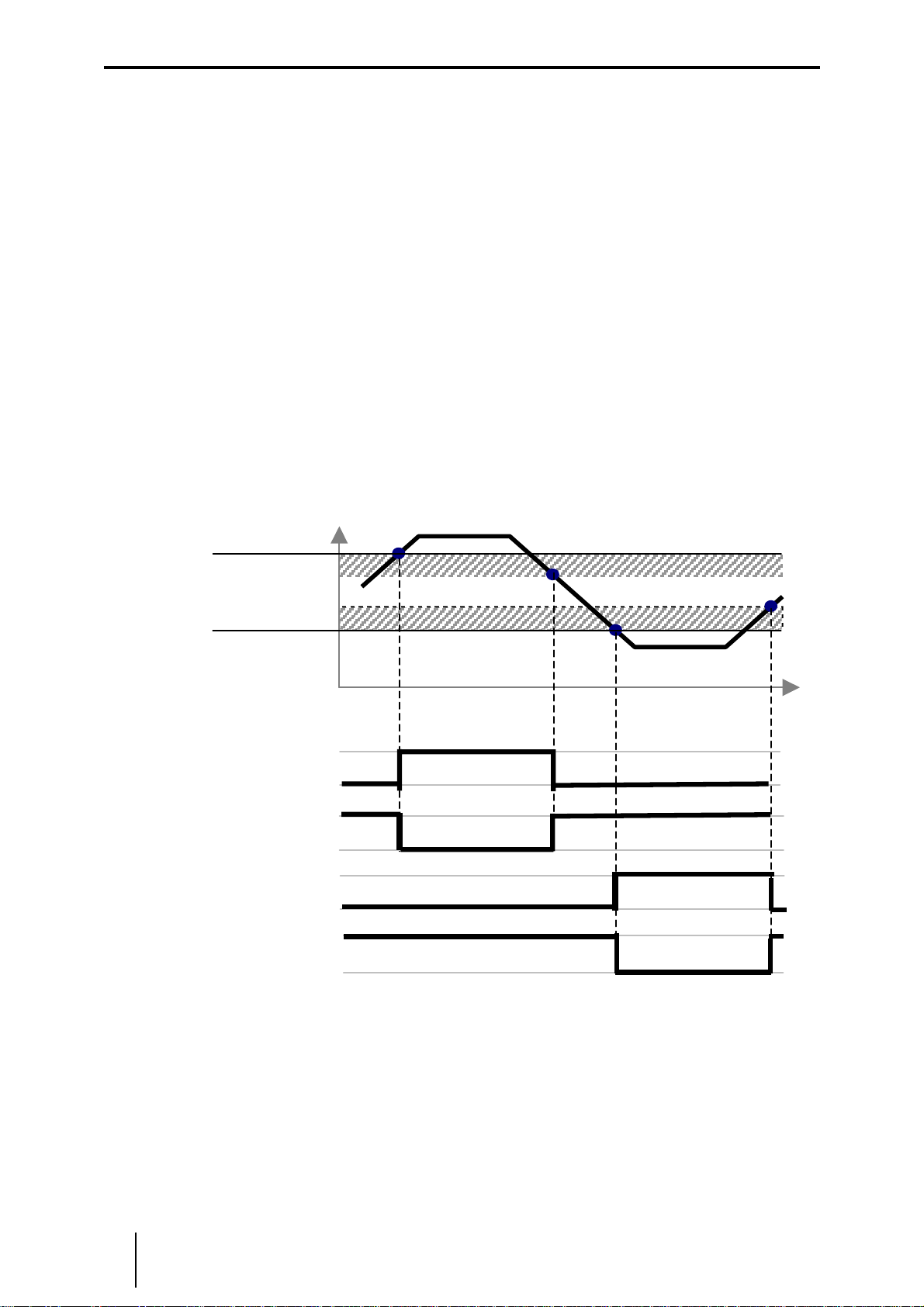
7.7 Grenzwerteinstellung (über Software IS pac Wizard) ............................................................10
7.8 Wiedereinschaltsperre (über Software IS pac Wizard)...........................................................10
7.9 Anlaufüberbrückung ..............................................................................................................11
8Betrieb- und Betriebszustände ..................................................................................................11
9Reparatur und Instandhaltung...................................................................................................11
10 Zubehör und Ersatzteile.............................................................................................................11
Content
1Safety instructions.....................................................................................................................12
2Conformity to standards.............................................................................................................12
3Function.....................................................................................................................................13
4Marking and technical data........................................................................................................13
5Engineering...............................................................................................................................14
5.1 Max. ambient temperatures...................................................................................................14
5.2 Power dissipation ..................................................................................................................14
5.3 Engineering of the power dissipation in cabinets...................................................................15
6Engineering Arrangement and Fitting........................................................................................16
6.1 Dimensions............................................................................................................................16
6.2 Installation.............................................................................................................................16
6.3 Mounting and dismounting.....................................................................................................16
7Commissioning..........................................................................................................................17
7.1 Connections ..........................................................................................................................17
7.2 Connecting contacts..............................................................................................................18
7.3 Line fault detection ................................................................................................................18
7.4 Input (via configuration software IS pac Wizard)....................................................................18
7.5 Signal processing (via configuration software IS pac Wizard)................................................18
7.6 Output (via configuration software IS pac Wizard).................................................................19
7.7 Set-up of the limit value switch (via configuration software IS pac Wizard)............................19
7.8 Re-closing lockout function (via configuration software IS pac Wizard) .................................19
7.9 Start-up delay........................................................................................................................20
8Operation and operational states...............................................................................................20
9Maintenance and repair.............................................................................................................20
10 Accessories and spare parts .....................................................................................................20
EG-Konformitätserklärung / EC-Declaration of Conformity ....................................................................21
EG-Baumusterprüfbescheinigung..........................................................................................................22
EC-Type Examination Certificate...........................................................................................................23