10
General
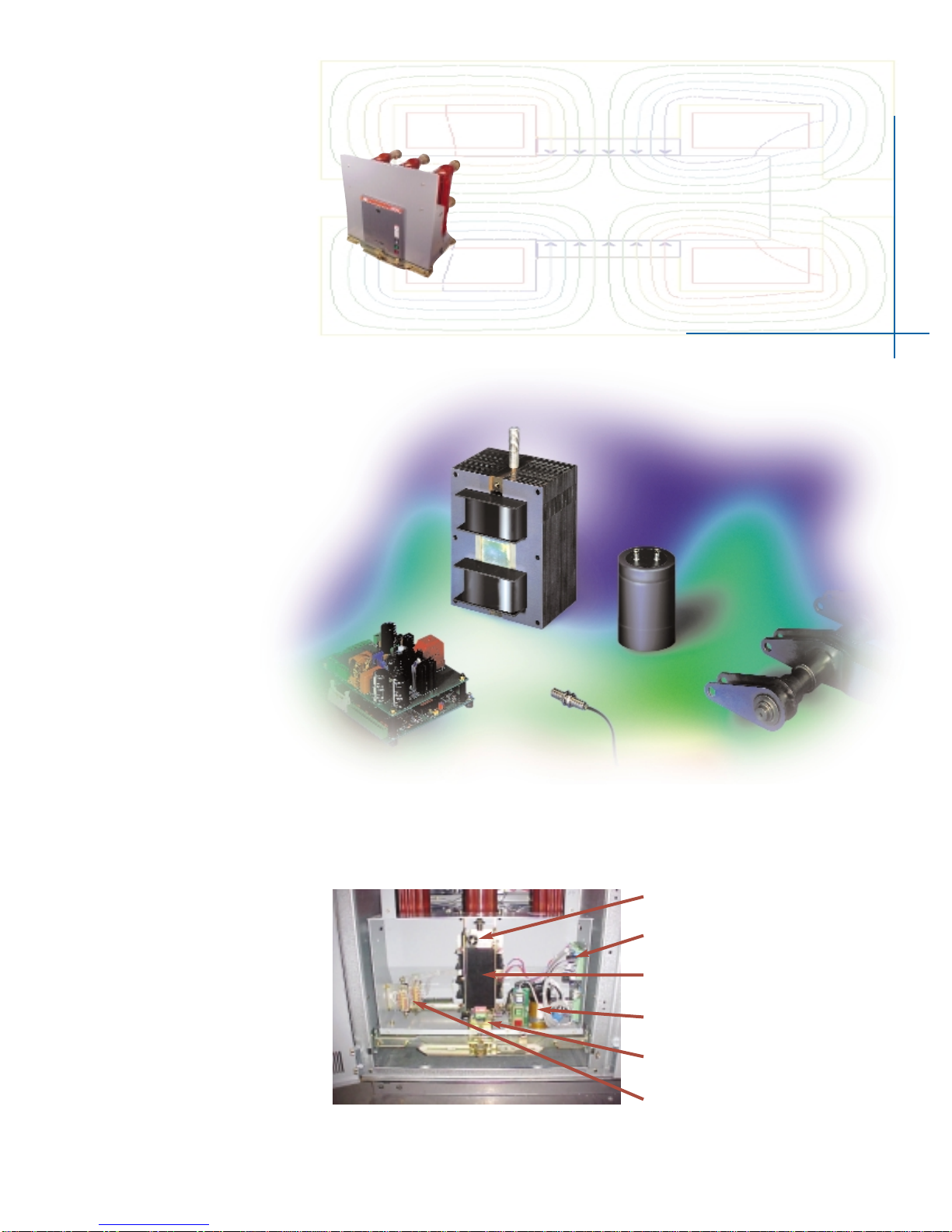
The Circuit breaker shall be an ABB AMVAC or approved equal, three-pole,
drawout (or stationary) type, electrically operated with stored energy magnetic
actuator operating mechanism. The circuit breaker is intended for use as a
general purpose device in accordance with the latest revisions of the
following ANSI standards applying to 5, 15, or 27 kV
applications: ANSI C37.04, C37.06, and C37.09.
Option: Definite purpose or non-standard ratings are
required in accordance with project data sheets, and
availability is confirmed in writing with the vendor.
Definite purpose ratings shall be in accordance with the
latest revisions of the following ANSI standards: C37.04,
C37.06, and C37.09. Circuit breakers of this same type,
rating and control features shall be electrically and
mechanically interchangeable.
Drawout Circuit Breaker Racking System and
Interlocks
The circuit breaker shall be inserted and withdrawn by
means of a breaker mounted racking system, which
can be operated with the compartment door open or
closed. The racking system shall provide smooth
consistent racking, and shall secure the breaker
from both sides of the cell in all racking
positions. During racking, the breaker shall
automatically open and close cell-mounted
safety shutters to cover stationary primary
contacts when the breaker is not in the
“Connected” position.
The racking system shall have
three distinct positions. In
addition to the withdrawn
position (free movement):
“Disconnected” (both
primary and secondary
contacts disengaged), “Test”
(primary contacts disconnected and
shutter closed), and “Connected” (primary and
secondary contacts engaged). Positive stops shall be provided for all three positions, with deliberate operator intervention required to
enable continued insertion or withdrawal of the circuit breaker from any position. The racking system and all moving parts of the
breaker-cell interface, including the secondary coupler, shutter actuator and ground contact, shall be capable of 500 complete
rack-in/rack-out operations without maintenance.
It shall not be possible to insert or withdraw a closed breaker, and the breaker shall not be allowed to close within a cell unless it is in the
“Connected”, “Test”, or “Disconnected” position. Electrical and mechanical blocking means shall be employed to preclude breaker
contact closure in any position other than “Connected”, “Test”, or “Disconnected”. The stored energy capacitors shall be automatically
discharged in the “Disconnected” position prior to removing the circuit breaker from the circuit breaker compartment.
Controls
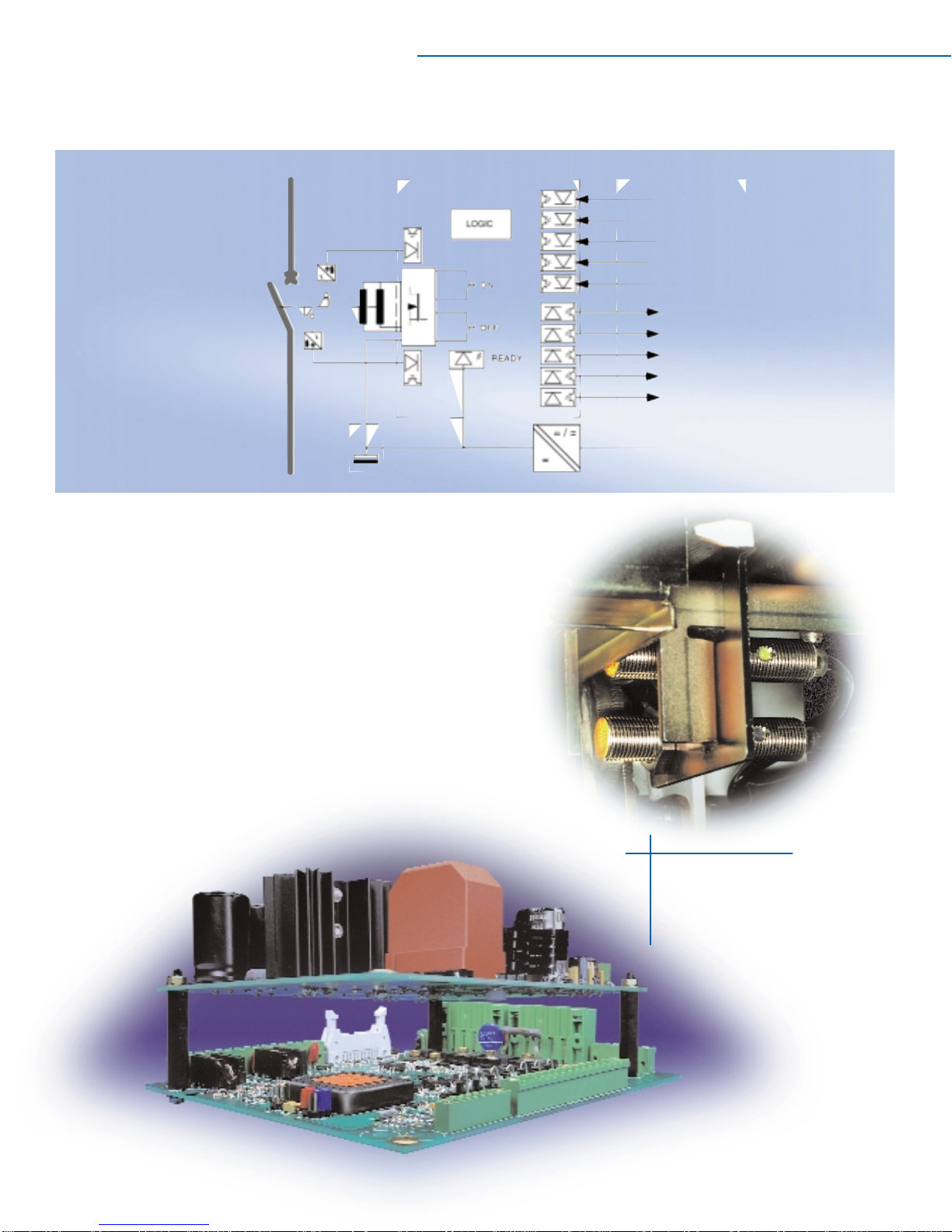
Opening and closing speed shall be independent of the operator or of the control voltage within the rated control voltage range. Circuit
breaker charge, close, and trip circuits shall be electrically separated, and control voltage for each circuit shall be independently selectable
from the full range of ANSI preferred control voltages. Manual provisions shall be provided for tripping the circuit breaker. These
provisions shall be installed and easily accessible at the front of the breaker.
AMVAC. Circuit breaker specifier's guide.