ABB CWC Manual
Other ABB Relay manuals

ABB
ABB Sentry BSR23 User manual

ABB
ABB CP Series Manual

ABB
ABB Relion REC615 User manual

ABB
ABB E45 DU User manual
ABB
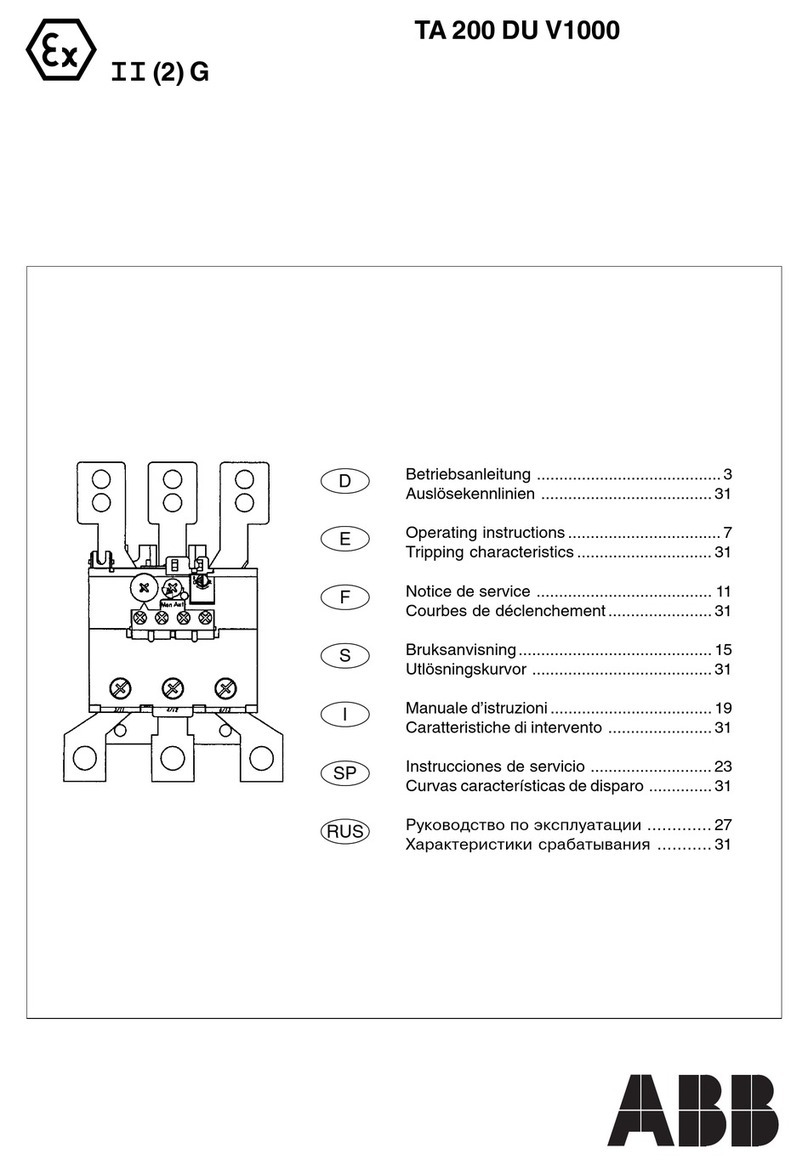
ABB TA 200 DU V1000 User manual

ABB
ABB HT595115 User manual

ABB
ABB SGR-51 User manual

ABB
ABB REJ 527 User manual

ABB
ABB RELION Series Installation and operation manual

ABB
ABB Relion 670 series Instructions for use