Analog Devices ADSP-CM411F User manual
Other Analog Devices Computer Hardware manuals
Analog Devices
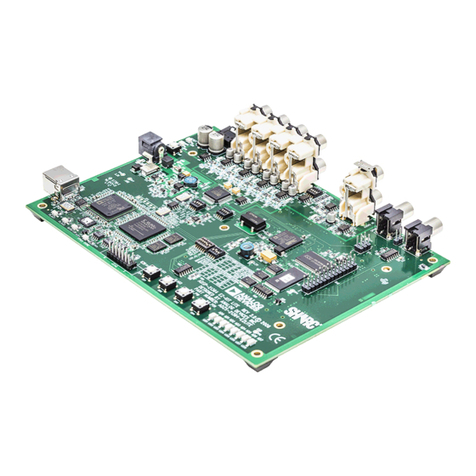
Analog Devices EZ-KIT Lite ADSP-21364 User manual
Analog Devices
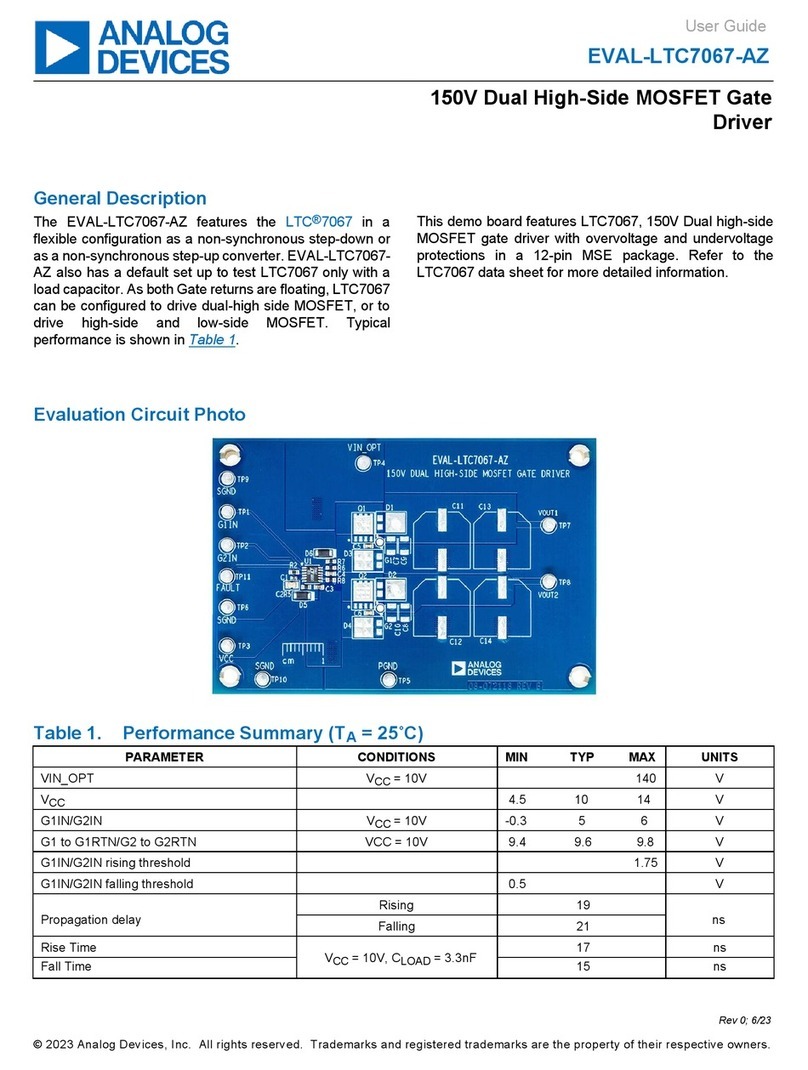
Analog Devices EVAL-LTC7067-AZ User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices ADSP-BF53x Blackfin Service manual
Analog Devices
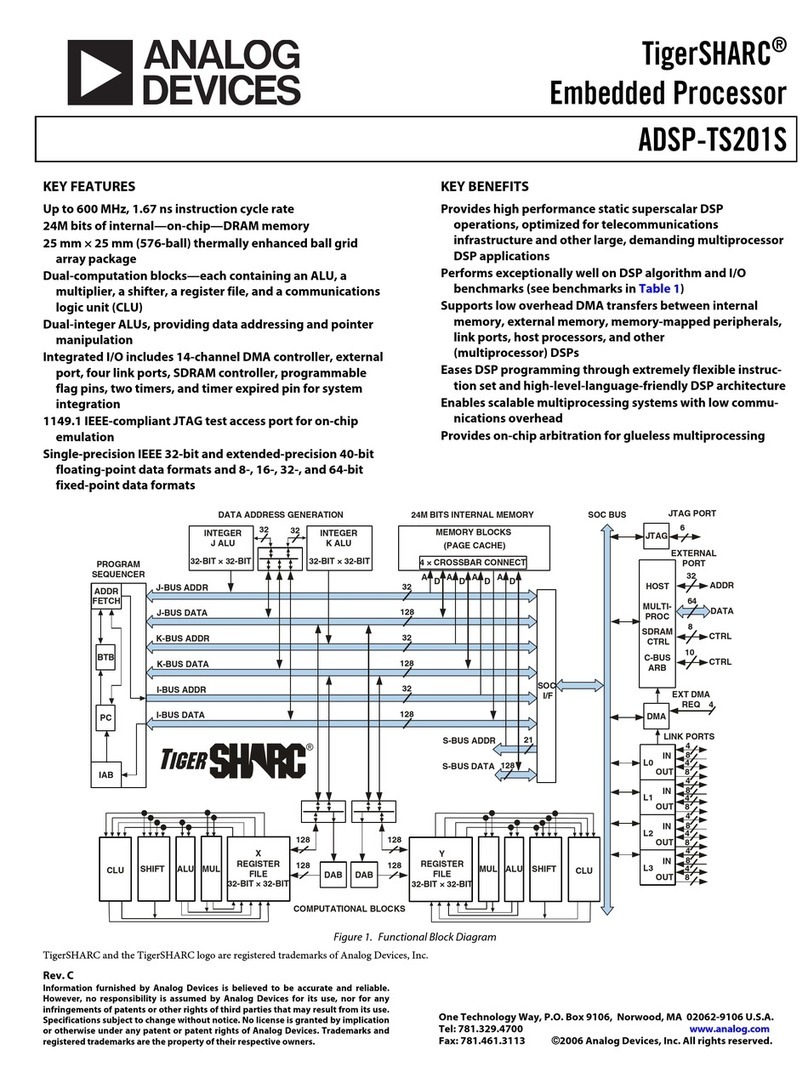
Analog Devices TigerSHARC ADSP-TS201S User manual
Analog Devices
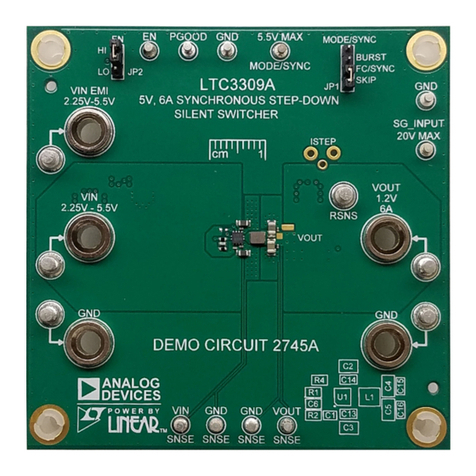
Analog Devices DC2745A Quick setup guide
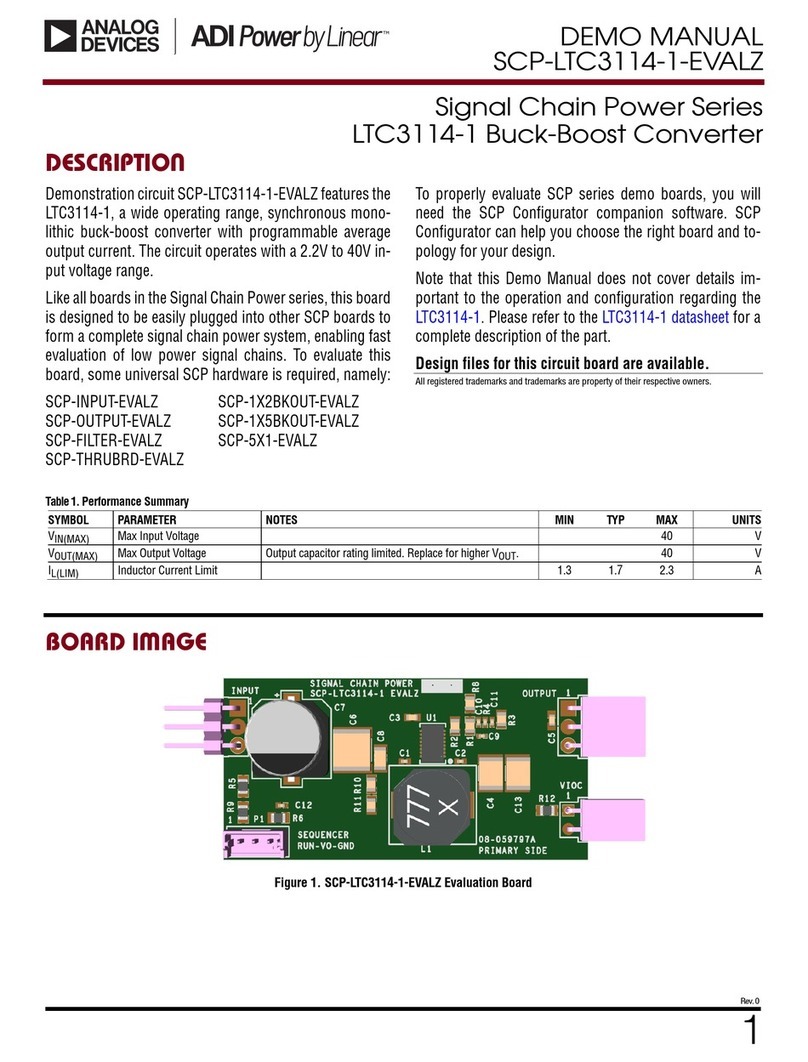
Analog Devices
Analog Devices Linear LTC3114-1 Quick setup guide

Analog Devices
Analog Devices ADSP-2181 User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices Linear ADI Power LTC3310-1 User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices Linear DC2331A-A Quick setup guide

Analog Devices
Analog Devices VisualDSP++ 5.0 User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices ADDS-218X-ICE-2.5V User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices Blackfin FPGA EZ-Extender User manual
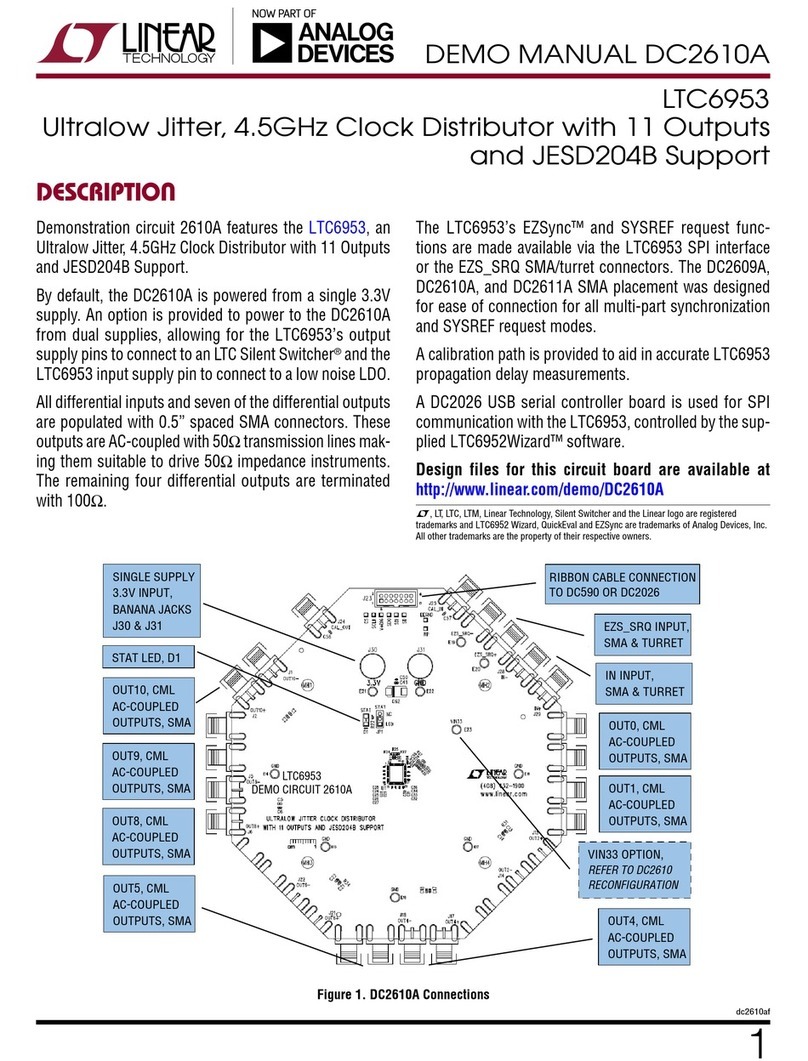
Analog Devices
Analog Devices Linear Technology LTC6953 Quick setup guide
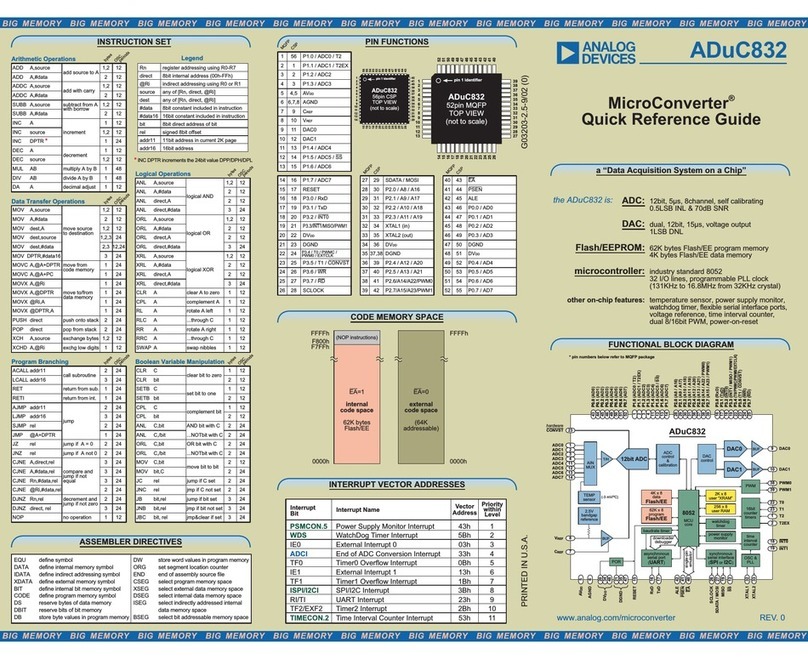
Analog Devices
Analog Devices MicroConverter ADuC832 User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices SHARC ADSP-21368 Application guide
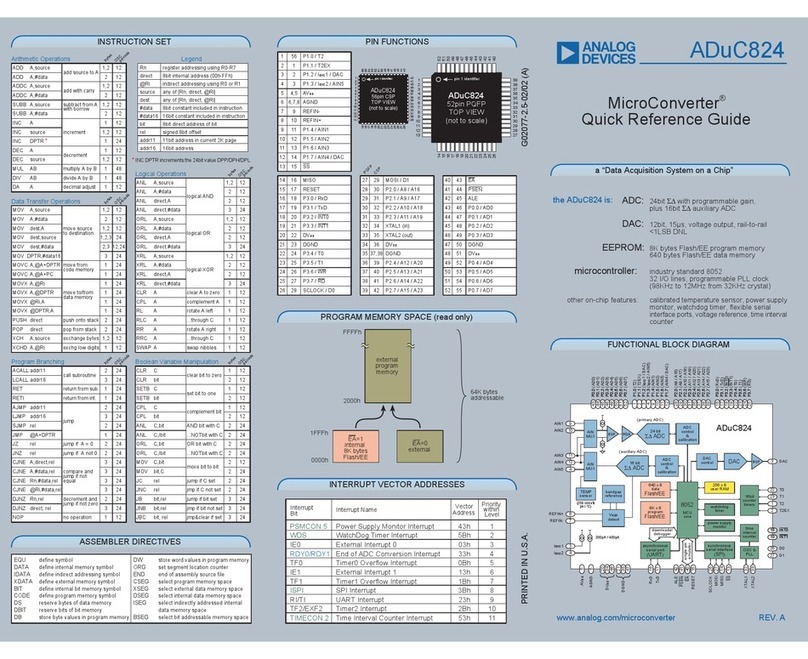
Analog Devices
Analog Devices MicroConverter ADuC824 User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices EVAL-ADuCM420QSP1Z User manual

Analog Devices
Analog Devices ADSP-2106x SHARC User manual
Analog Devices
Analog Devices ADuCM355 Quick start guide
Analog Devices
Analog Devices ADM8611 User manual
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

EMC2
EMC2 VNX Series Hardware Information Guide

Panasonic
Panasonic DV0PM20105 Operation manual

Mitsubishi Electric
Mitsubishi Electric Q81BD-J61BT11 user manual

Gigabyte
Gigabyte B660M DS3H AX DDR4 user manual

Raidon
Raidon iT2300 Quick installation guide

National Instruments
National Instruments PXI-8186 user manual

























