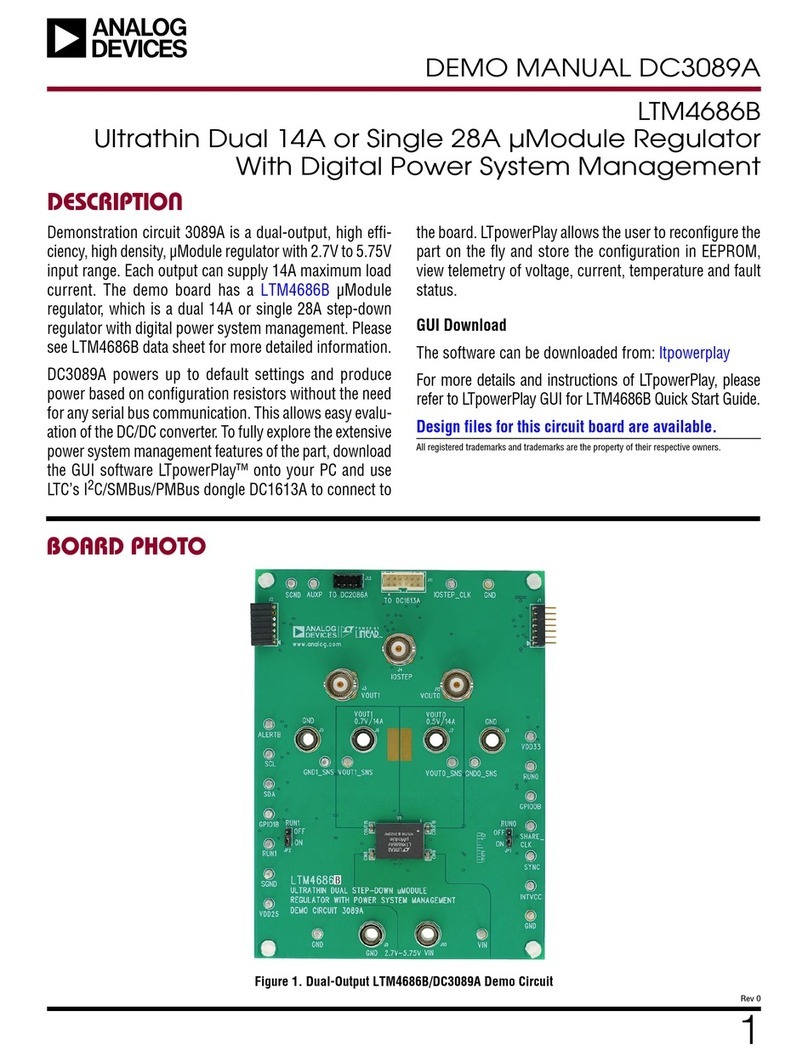
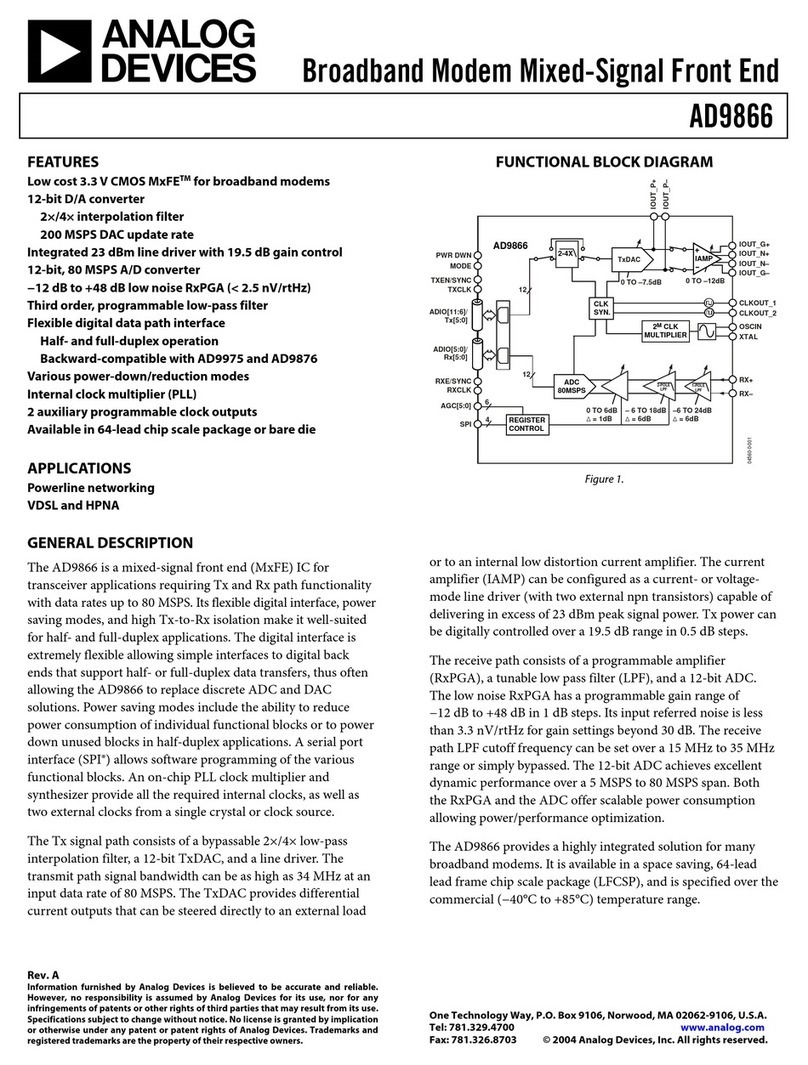
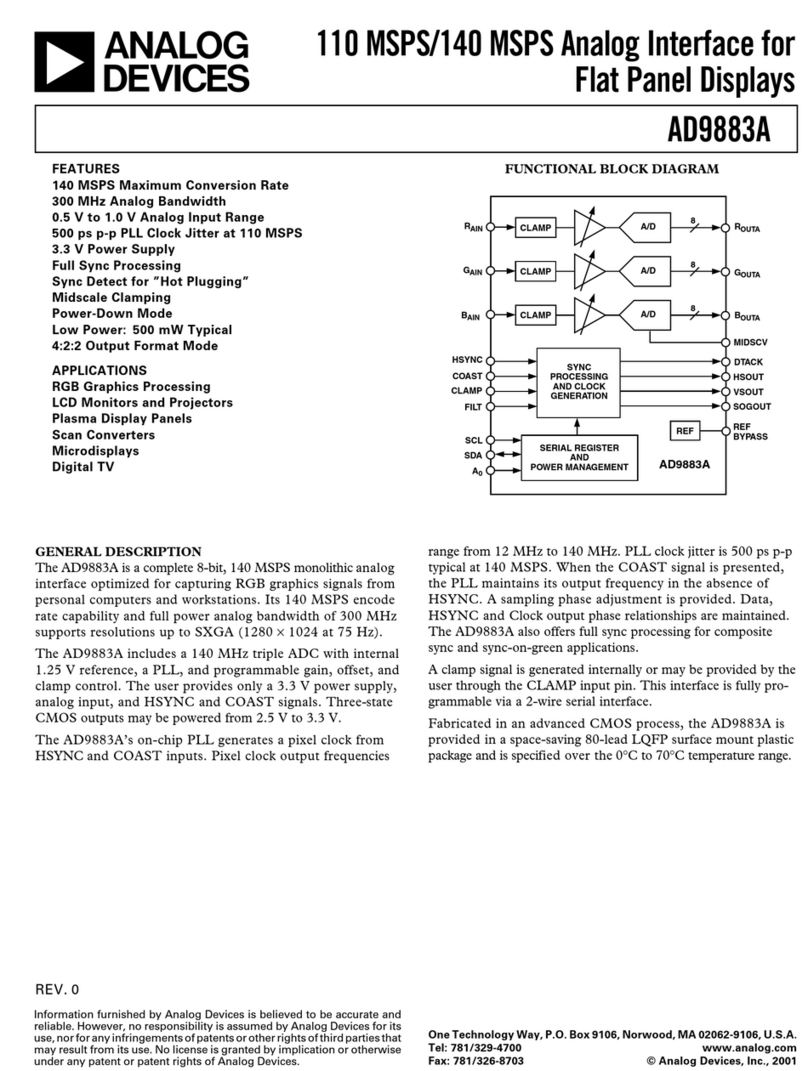
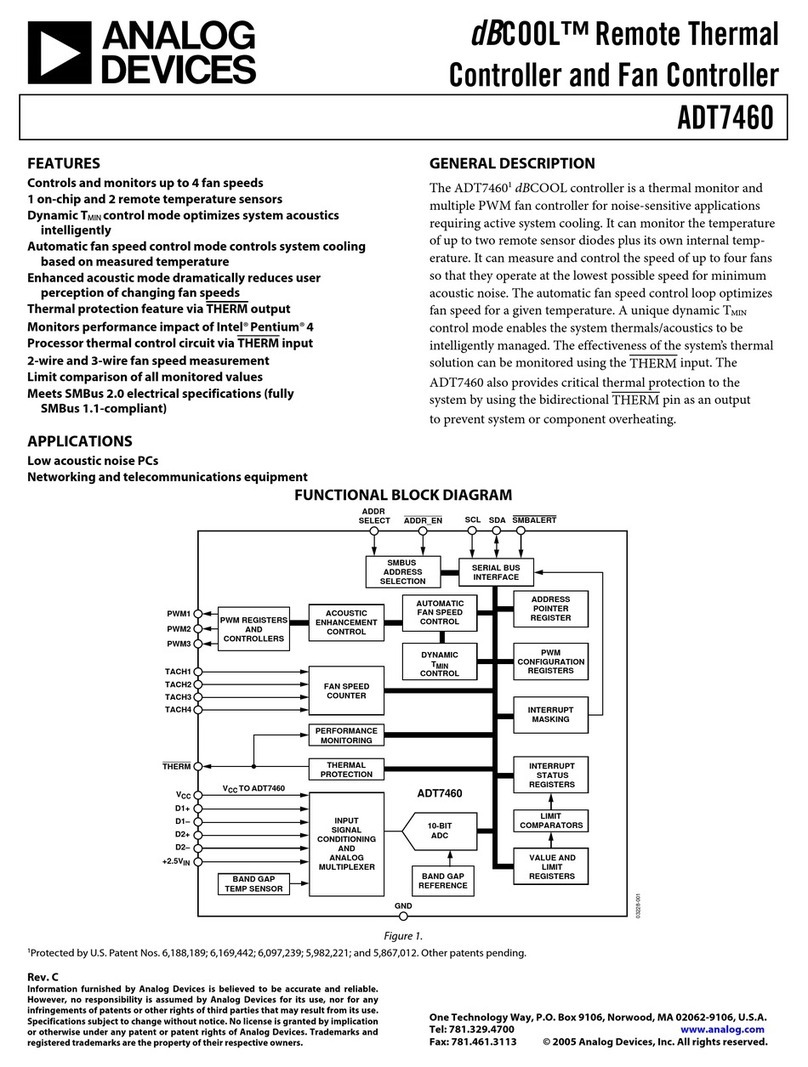
LTM4700
2
Rev. B
For more information www.analog.com
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features..................................................... 1
Applications ................................................ 1
Typical Application ........................................ 1
Description.................................................. 1
Absolute Maximum Ratings.............................. 4
Order Information.......................................... 4
Pin Configuration .......................................... 4
Electrical Characteristics ................................. 5
Typical Performance Characteristics .................. 12
Pin Functions .............................................. 15
Simplified Block Diagram ............................... 19
Decoupling Requirements............................... 19
Functional Diagram ...................................... 20
Test Circuits ............................................... 21
Operation................................................... 22
Power Module Introduction ...................................22
Power Module Overview, Major Features................22
EEPROM with ECC .................................................23
Power-Up and Initialization .................................... 24
Soft-Start ...............................................................25
Time-Based Sequencing ........................................25
Voltage-Based Sequencing ....................................25
Shutdown ..............................................................26
Light-Load Current Operation ................................26
Switching Frequency and Phase .............................27
PWM Loop Compensation .....................................27
Output Voltage Sensing .........................................27
INTVCC and Build-in 5V Bias Converter .................27
Output Current Sensing and Sub Milliohm
DCR Current Sensing .............................................28
Input Current Sensing ............................................28
PolyPhase Load Sharing ........................................28
External/Internal Temperature Sense .....................29
RCONFIG (Resistor Configuration) Pins .................29
Fault Detection and Handling .................................32
Status Registers and ALERT Masking ................33
Mapping Faults to FAU LT Pins ...........................35
Power Good Pins ...............................................35
CRC Protection ..................................................35
Serial Interface ......................................................35
Communication Protection ................................35
Device Addressing .................................................35
Responses to VOUT and IIN/IOUT Faults ..................36
Output Overvoltage Fault Response ..................36
Output Undervoltage Response .........................37
Peak Output Overcurrent Fault Response ..........37
Responses to Timing Faults ...................................37
Responses to VIN OV Faults ...................................37
Responses to OT/UT Faults ....................................37
Internal Overtemperature Fault Response .........37
External Overtemperature and
Undertemperature FaultResponse .................38
Responses to Input Overcurrent and Output
Undercurrent Faults ...............................................38
Responses to External Faults .................................38
Fault Logging .........................................................38
Bus Timeout Protection .........................................38
Similarity Between PMBus, SMBus and
I2C 2-Wire Interface ...............................................39
PMBus Serial Digital Interface ...............................39
Figures 7 to 24 PMBus Protocols ........................... 41
PMBus Command Summary ............................ 44
PMBus Commands ................................................44
Applications Information ................................ 50
VIN to VOUT Step-Down Ratios ...............................50
Input Capacitors ....................................................50
Output Capacitors ..................................................50
Light Load Current Operation .................................50
Switching Frequency and Phase ............................ 51
Output Current Limit Programming .......................52
Minimum On-Time Considerations .........................53
Variable Delay Time, Soft-Start and
Output Voltage Ramping ........................................53
Digital Servo Mode ................................................53
Soft Off (Sequenced Off) .......................................54
Undervoltage Lockout ............................................55
Fault Detection and Handling .................................55
Open-Drain Pins ....................................................55
Phase-Locked Loop and Frequency
Synchronization .....................................................56
Input Current Sense Amplifier ................................57