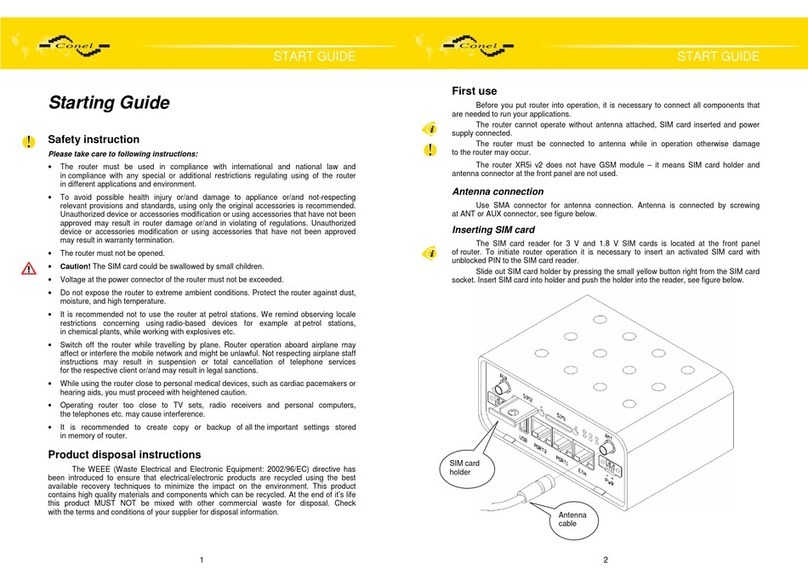
DESCRIPTION
6
2. Description of the router
2.1. Introduction
The UMTS router is a compact electronic device based on the UMTS module which
enables data transfers using UMTS/HSDPA/HSUPA/EDGE/GPRS/GSM technologies.
Primarily, the router expands the capabilities of the UMTS module by the option
of connecting more PC’s by means of the built-in Ethernet interface. In addition, the firmware
of the router provides automatic establishment and maintenance of UMTS/HSDPA/
HSUPA/EDGE/GPRS/GSM PPP connection. By means of the integration of a DHCP server it
provides the user with simple installation and Internet access.
In addition, the router is equipped with a two USB 1.1 Host interfaces which is designed
only for connection to a USB device.
By customer request it is possible to equip the router with the XPORT module
and extend the function of the UMTS router about RS232, RS485/RS422, M-BUS or CNT (I/O
module).
The UMTS router has two versions. The first version is basic UR5i and the second
version is UR5i SL in the aluminum box.
Examples of Possible Applications
•mobile office
•fleet management
•security system
•telematic
•telemetric
•remote monitoring
•vending and dispatcher machines
2.2. UMTS technology
For radio terrestrial part UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication System), which is
marked as UTRA (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access), is warranted 155 MHz band in frequency
band about the 2 GHz. It are bands 1900–1980 MHz, 2010–2025 MHz and 2110–2170 MHz.
The UMTS system is based on code division of carried channels – use the access
method WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access). WCDMA exploit direct spread
spectrum DS (Direct Spread). For transmission the UMTS network exploits two duplex
techniques – transmission modes FDD (Frequency Division Duplex), which is based
on separate frequency channels (i.e. uplink and downlink uses different channels) and TDD
(Time Division Duplex), which is based on separate time (i.e. uplink and downlink uses one
channel, in which both direction are changes in time).
UMTS network consists of three basic entities:
•Basic network CN (Core Network) – own core of network UMTS,
•network UTRAN (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network) – the radio access
network,
•users part UE (User Equipment) – entity, which allows the user to access
the UMTS network.