2
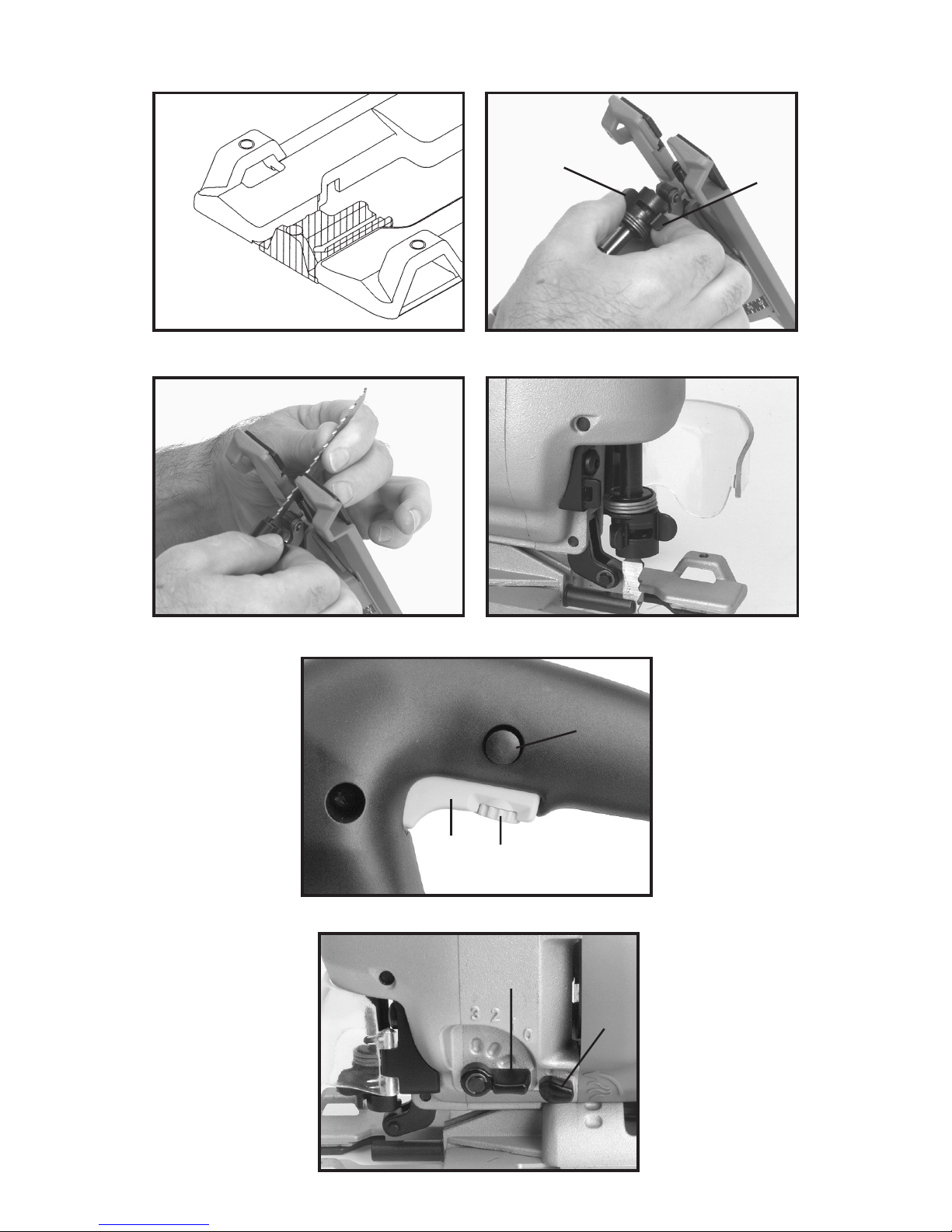
5. Während die Sägeblatthalterung in der geöffneten Stellung gehalten wird, den Hebel (A) soweit wie
möglich nach vorn bringen (siehe Abb. 2 und Abb. 3) und in dieser Stellung halten.
HINWEIS: Die Schritte 4 und 5 sollten in einer einzigen Bewegung ausgeführt werden.
6. Die Sägeblattzahnung in Schnittrichtung richten, das Sägeblatt durch die Sägeblattführung in die
Sägeblatthalterung bis zum Anschlag einstecken, dann die beiden Hebel loslassen. Siehe Abb. 4.
7. Das Sägeblatt unter leichtem Zug einrasten lassen. Das Sägeblatt ist sachgemäß eingesetzt, wenn die
beiden Hebel so ausgerichtet sind, wie in Abb. 4 gezeigt wird.
8. Den in Abb. 12 gezeigten vorderen Schutzbügel A schließen.
HERAUSNEHMEN DES SÄGEBLATTES
1. Den in Abb. 12 gezeigten vorderen Schutzbügel A öffnen.
2. Den Spannreißschutz-Fußeinsatz abnehmen, wenn er schon eingebaut ist.
3. Die Schalttaste leicht drücken, bis der Schaft des Sägeblattes sich langsam bewegt. Den Motor
ausschalten, wenn der Schaft des Sägeblattes die untere Position seines Hubes erreicht oder sich der
unteren Position seines Hubes nähert, wie in Abb. 6 gezeigt wird.
VORSICHT: DEN NETZSTECKER DER STICHSÄGE AUS DEM NETZANSCHLUSS ZIEHEN!
4. Zum Öffnen der Sägeblatthalterung den in Abb. 2 gezeigten beweglichen Hebel (B) in Richtung des in
Abb. 2 gezeigten unbeweglichen Hebel (A) soweit wie möglich drehen.
5. Den Sägeblattschaft nach vorn bringen, bis das Sägeblatt von der Sägeblattführung frei ist.
6. Die Sägeblattspitze anfassen und in Richtung des Hebels der Sägeblatthalterung bzw. nach der rechten
Seite der Stichsäge bringen. Dann das Sägeblatt aus der Halterung herausziehen.
7. Den in Abb. 12 gezeigten vorderen Schutzbügel A schließen.
INBETRIEBNAHME
EINSCHALTEN UND AUSSCHALTEN DER STICHSÄGE
Darauf achten, daß die Spannung der Stromquelle mit der auf dem Typenschild der Stichsäge angezeigten
Spannung übereinstimmt sowie daß die Schalttaste in “AUS”-Position ist. Den Netzstecker der Stichsäge
in die Steckdose einstecken.
1. Zum Einschalten des Motors die in Abb. 5 gezeigte Schalttaste (A) drücken. Zum Ausschalten des
Motors die Schalttaste loslassen.
2. Arretierknopf – Mit dem in Abb. 5 gezeigten Arretierknopf (B) ist es möglich, die Stichsäge laufen zu
lassen, ohne daß die Schalttaste in “EIN”-Position gehalten werden muß. Zur Betätigung der
Dauereinschaltung die Schalttaste soweit wie möglich drücken, dann auf den Arretierknopf drücken und
die Schalttaste loslassen.
Zum AUFHEBEN der Dauereinschaltung die Schalttaste drücken. Dadurch springt der Arretierknopf wieder
raus. Dann die Schalttaste wieder loslassen.
STUFENLOSE HUBZAHL
Diese Stichsäge ist mit einer stufenlosen Hubzahlregulierung ausgestattet, die eine Hubzahl zwischen 500
und 3,100 Hub pro Minute ermöglicht. Die Hubzahl wird durch Drehen des in Abb. 5 gezeigten
Stellknopfes (C) eingestellt. Die Hubzahl kann sowohl beim laufenden als auch beim stillstehenden Motor
eingestellt werden.
Eine höhere Hubzahl wird bei hoher Schnittleistung eingestellt, wenn das Aussehen der Oberfläche und die
Genauigkeit des Schnittes nicht so kritisch sind. Eine kleinere Hubzahl wird beim Schneiden von
empfindlichen Materialien eingestellt, wenn die Genauigkeit des Schnittes und das Aussehen der
Oberfläche kritisch sind.
PENDELUNG DES SÄGEBLATTES
Durch Drehen des in Abb. 6 gezeigten Stellknopfes (A) kann die Pendelung des Sägeblattes nach Wunsch
eingestellt werden. Zur Wahl stehen vier Pendelhubstufen, die mit den Zahlen “0” bis “3” gekennzeichnet
sind. Die Zahl “0” bedeutet keine Pendelung und die Zahl “3” bedeutet maximale Pendelung. Die
Pendelung kann sowohl beim laufenden als auch beim stillstehenden Motor eingestellt werden. Der in Abb.
6 gezeigte Stellknopf (A) wird soweit gedreht, bis er die Arretierung im Gehäuse erreicht, die der Zahl am
Gehäuse entspricht. Gezeigt wird der Stellknopf in der Stellung “0”. Die vertikale Stellung des Stellknopfes
würde der Stellung “3” entsprechen. Beim Metallschneiden sollte die Pendelhubstufe “0” verwendet
werden.