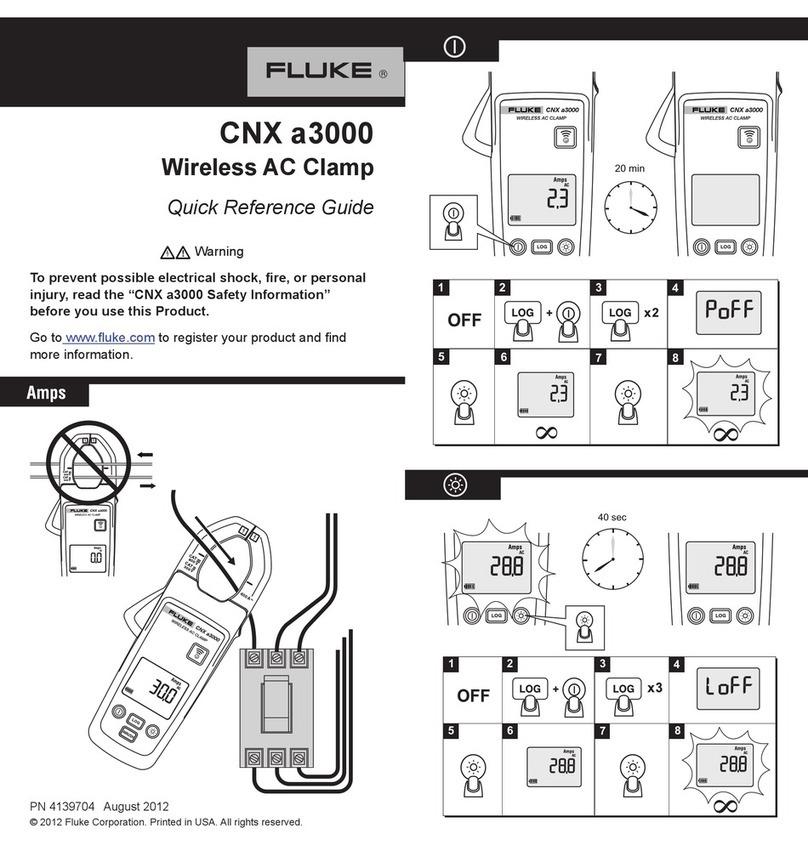
7. Motor detached from drive train?
Answer NO unless:
a. The driven component is physi-
cally disconnected from the motor
- or -
b. You want to test only the motor and
not any attached components. (If a
or b is true, answerYES).
Detached Motor
8. Motor Close Coupled?
Answer NO unless:
a. The motor shaft is driving the
driven component directly
- and -
b. The only bearings are on the motor
shaft (for example, when the motor
is bolted directly to a fan, a pump,
or a compressor)
Then, answer YES.
Motor Close Coupled
Also called “direct mount” or
“direct drive,” a motor is “
close-coupled” if:
•There are no bearings on
the driven unit.
•There is only one shaft
running at one speed
9. Coupling between motor and next
component?
Flexible Coupling
If there is flexible
material between the
flanges of the coupling,
answer YES.
Rigid Coupling
Otherwise, if the
coupling is rigid and
the flanges are bolted
together with no
flexible material, or no
coupling, answer NO.
Next component: Press Enter on the
center of the Dial, rotate the Dial, and
select the driven unit.
If the driven unit is a gearbox,
go to step 11. Otherwise,
go to step 12.
Flexible or Rigid Coupling
Regardless of coupling type:
•There are bearings on
both the motor and the
driven shafts
•There are two shafts, both
running at the same speed
Flexible Coupling
Rigid Coupling
If in doubt, select
Flexible Coupling.
Measurement locations
Motor
Flexible coupling
Shaft
Gearbox
Fan
Belt drive Bearing
Create A New Machine Setup Answers And Diagrams
1. Push New Machine on the startup
screen. Or push SETUP.
Use the Dial to select and enter
characters.
2. Enter a machine name:
Enter a descriptive name for the ma-
chine, for example, B5 Supply Fan 3.
A maximum of 15 characters is
allowed.
Machine Setup Questions
1. Select motor type: AC DC
2. AC motor with VFD: Yes No
Select a variable frequency drive
(“Yes”) or a constant speed motor
(“No”).
3. Enter speed in RPM:
Enter the speed from the motor’s
nameplate or the tachometer.
4. Enter nominal hp (kw):
Enter the horsepower or kilowatts
listed on the motor’s nameplate.
Press Next Page.
5. Motor mounted: Horiz/Vert
Specify whether the motor shaft is
horizontal or vertical.
6. Motor bearing type: Roller/Journal
Choose roller or journal bearings.
Roller or Journal Bearings
Roller Bearing
Roller bearings
support a load
with round
rolling elements
Journal Bearing
Journal bearings
support a load
without round
rolling elements
If in doubt,
select Roller Bearings.
Setup Questions and Results
Answering the Setup Questions
Use the Fluke 810 User’s Manual and this guide to help answer the setup questions
required for each test.
Symbols used in this guide
10.
Coupling between motor and next
component? Answer “No.”
Next component: Belt Drive
Press Enter on the center of the Dial,
rotate the Dial, then select Belt Drive.
Input shaft speed:
Enter the motor shaft speed.
Output shaft speed:
Enter the driven unit shaft speed.
Rotation speed (optional):
Use a strobe or contact tachometer to
measure the speed of the belt.
Next component: Press Enter on
the center of the Dial, rotate the Dial,
then select driven unit.
If the next component is Gearbox,
skip to #13.
Belt driven machine
•Bearings on motor and
driven shafts
•Two shafts with
different speeds
11.
After completing the steps in #9:
Next component: Gearbox
Press Enter on the center of the Dial,
rotate the Dial, then select Gearbox.
Gearbox bearing type: Roller/
Journal
Select roller or journal bearings.
Number of speed changes: 1/2 /3
Scroll and select the number of
changes.
What is known: Shaft speeds/
Gear ratios/Gear Teeth Count
Make selection and enter either shaft
speeds, gear ratio, or gear teeth count.
Flexible coupling between gearbox
and next component? Yes/No
Select whether there is or isn’t a
coupling between the gearbox and
the coupling.
Next component that gearbox is
attached to:
Press Enter on the center of the Dial,
rotate the Dial, then select the
driven unit.
If the next component is a belt
drive, skip to #14.
Gear driven machine
•Bearings on motor, gearbox
and driven shafts
•Motor shaft, gear shafts,
driven shaft – different
speeds
If in doubt, use input and
output shaft speeds to
calculate ratio.
Always use number one in
ratio – 4.25:1 (reducer) or
1:4.25 (increaser).
12.
After completing the steps in #9:
Next component:
Press Enter on the center of the Dial,
rotate the Dial, then select Driven
unit - Pump, Fan, Compressor,
Blower, or Spindle.
Driven component (Fan) bearing
type: Roller / Journal
Select roller or journal bearings.
Driven Unit (Fan) is supported by:
Two Bearings/Overhung
“Two bearings” means the fan is sup-
ported on both sides (see diagram)
“Overhung” the fan is mounted at the
end of the shaft unsupported on one
side.
No. of fan blades [optional]:
If you are certain you know the num-
ber of blades, enter the number.
If not, leave blank.
When you are done, select Next
Page, and then select Done.
Supported or Overhung
Component
If in doubt, select spindle
for all driven units that
are not a pump, fan,
compressor, or blower.
Blower refers to a driven
with multi-stage centrifugal
wheels or lobes, not a fan
with blades (should be
setup as a fan).
Screw compressors –
select roller bearings even
if you have journals.
13.
After completing the steps in #10:
Next component: Gearbox
Press Enter on the center of the Dial,
rotate the Dial, then select Gearbox.
Then follow steps in #11 for Gearbox.
Belt and Gearbox driven
machines
14.
After completing the steps in #11:
Next component: Belt drive
Press Enter on the center of the Dial,
rotate the Dial, then select Belt drive.
Then follow steps in #10 for Belt
drive.
©2013 Fluke Corporation.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
Printed in U.S.A. 6/2013 4161309B_EN
Modification of this document is not
permitted without written permission from
Fluke Corporation.
Fluke. The Most Trusted Tools
in the World.
Supported Fan
Overhung Fan