Table of Contents
1. Important Notes .................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Scope ............................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Target Group .................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.3 Symbols Used ................................................................................................................................................ 1
1.4 Symbols Explanation ......................................................................................................................................1
2. Safety ................................................................................................................................................................... 2
2.1 Appropriate Usage ..........................................................................................................................................2
2.2 PE Connection and Leakage Current ............................................................................................................ 3
2.3 Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) for PV Installation .....................................................................................4
3. About Product .......................................................................................................................................................5
3.1 About S Series (G2) Inverter .......................................................................................................................... 5
3.2 Basic Features ............................................................................................................................................... 5
3.3 Terminals Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 6
3.4 Dimensions .....................................................................................................................................................6
4. Technical Data ...................................................................................................................................................... 7
4.1 DC Input ......................................................................................................................................................... 7
4.2 AC Output .......................................................................................................................................................7
4.3 Efficiency, Safety and Protection ....................................................................................................................8
4.4 General Data .................................................................................................................................................. 9
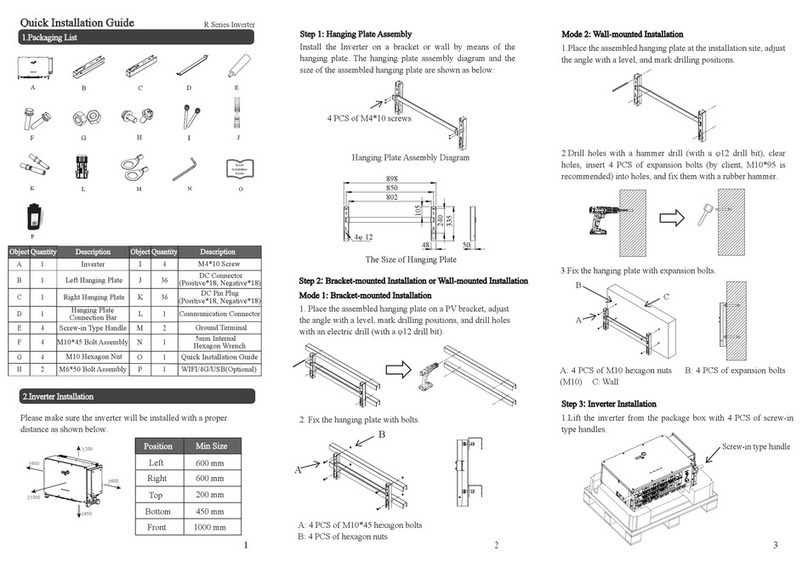
5. Installation .......................................................................................................................................................... 10
5.1 Packing List .................................................................................................................................................. 10
5.2 Preparation ...................................................................................................................................................10
5.3 Installation Space Required ..........................................................................................................................11
5.4 Tools Required ..............................................................................................................................................11
5.5 Installation Steps .......................................................................................................................................... 11
5.6 Wiring Steps ................................................................................................................................................. 12
5.7 Earth Connection ..........................................................................................................................................15
5.8 Communication Device Installation (Optional) ............................................................................................. 15
5.9 Inverter Start-Up ...........................................................................................................................................19
5.10 Inverter Switch Off ......................................................................................................................................20
6. Operation ............................................................................................................................................................20
6.1 Control Panel ................................................................................................................................................20
6.2 Function Tree ............................................................................................................................................... 21
7. Firmware Upgrading ........................................................................................................................................... 22
8. Maintenance ....................................................................................................................................................... 23
8.1 Alarm List ......................................................................................................................................................23
8.2 Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................................24
8.3 Routine Maintenance ................................................................................................................................... 25
9. Decommissioning ............................................................................................................................................... 26
9.1 Dismantling the Inverter ............................................................................................................................... 26
9.2 Packaging .....................................................................................................................................................26
9.3 Storage and Transportation ..........................................................................................................................26