HIMA HIMax X-AI 32 02 User manual

X-AI 32 02
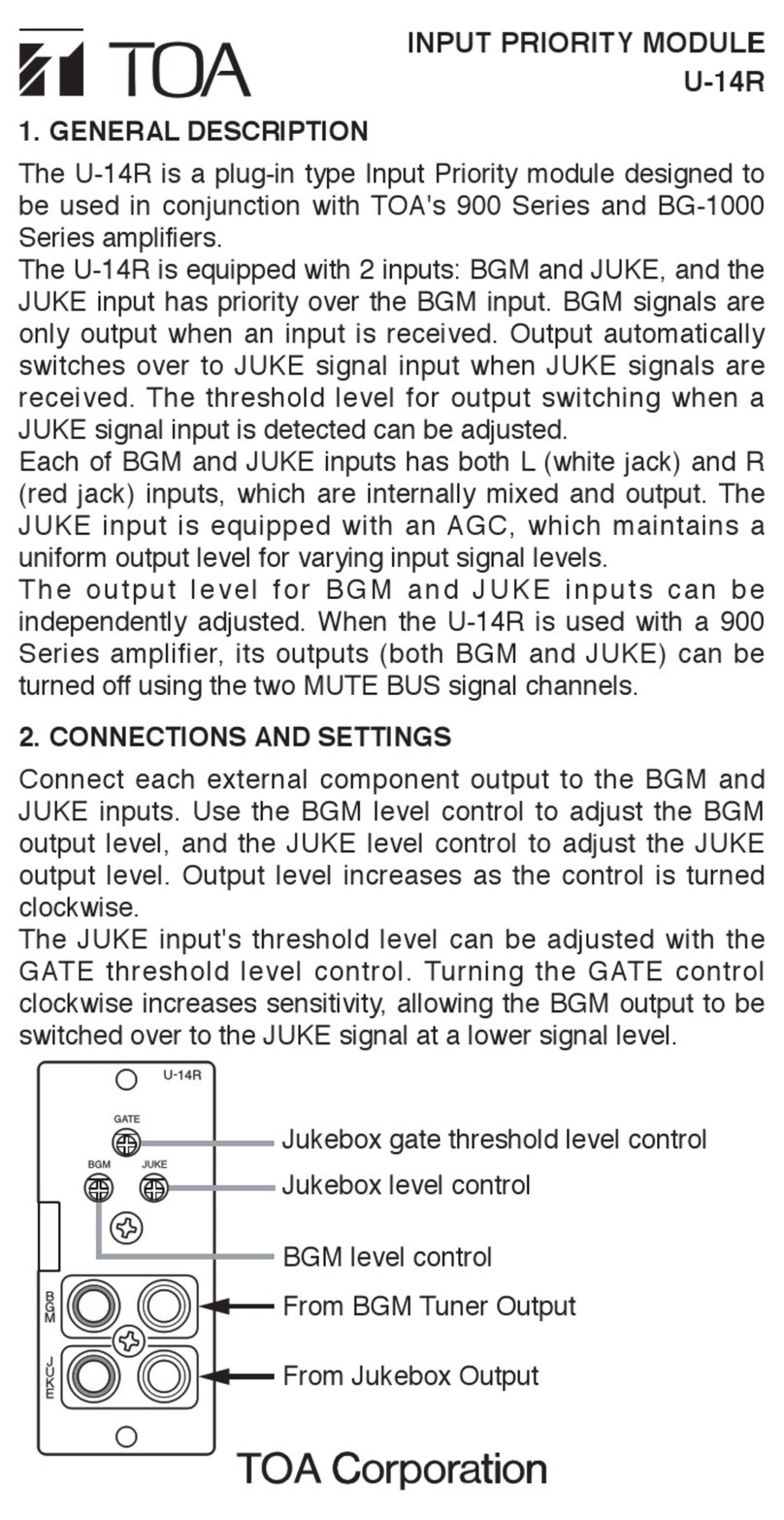
HIMax®
Analog Input Module with
Sequence of Events Recording
Manual

HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 (1117)
All HIMA products mentioned in this manual are protected by the HIMA trade-mark. Unless noted
otherwise, this also applies to other manufacturers and their respective products referred to herein.
All of the instructions and technical specifications in this manual have been written with great care and
effective quality assurance measures have been implemented to ensure their validity. For questions,
please contact HIMA directly. HIMA appreciates any suggestion on which information should be
included in the manual.
Equipment subject to change without notice. HIMA also reserves the right to modify the written material
without prior notice.
For further information, refer to the CD-ROM and our website http://www.hima.de and
http://www.hima.com.
© Copyright 2011, HIMA Paul Hildebrandt GmbH + Co KG
All rights reserved
Contact
HIMA Address
HIMA Paul Hildebrandt GmbH + Co KG
P.O. Box 1261
68777 Brühl, Germany
Phone: +49 6202 709-0
Fax: +49 6202 709-107
Type of Change
Revision
index
Revisions
technical editorial
4.00 New edition for SILworX V4 X X

X-AI 32 02 Table of Contents
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 3 of 60
Table of Contents
1Introduction ............................................................ 5
1.1 Structure and Use of this Manual......................................................................... 5
1.2 Target Audience..................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Formatting Conventions ....................................................................................... 6
1.3.1 Safety Notes ............................................................................................................ 6
1.3.2 Operating Tips ......................................................................................................... 7
2Safety...................................................................... 8
2.1 Intended Use .......................................................................................................... 8
2.1.1 Environmental Requirements................................................................................... 8
2.1.2 ESD Protective Measures........................................................................................ 8
2.2 Residual Risk ......................................................................................................... 9
2.3 Safety Precautions................................................................................................. 9
2.4 Emergency Information......................................................................................... 9
3Product Description .............................................. 10
3.1 Safety Function.................................................................................................... 10
3.1.1 Reaction in the Event of a Fault............................................................................. 10
3.2 Scope of Delivery................................................................................................. 10
3.3 Type Label ............................................................................................................ 11
3.4 Assembly.............................................................................................................. 11
3.4.1 Block Diagram........................................................................................................ 12
3.4.2 Indicators ............................................................................................................... 13
3.4.3 Module Status Indicators ....................................................................................... 14
3.4.4 System Bus Indicators ........................................................................................... 15
3.4.5 I/O Indicators.......................................................................................................... 15
3.5 Product Data......................................................................................................... 16
3.6 Connector Boards................................................................................................ 18
3.6.1 Mechanical Coding of Connector Boards .............................................................. 18
3.6.2 Coding of X-CB 008 Connector Boards ................................................................. 19
3.6.3 Pin Assignment for Connector Boards with Screw Terminals................................ 20
3.6.4 Terminal Assignment for Connector Boards with Screw Terminals....................... 21
3.6.5 Pin Assignment for Connector Boards with Cable Plug......................................... 23
3.6.6 Pin Assignment for Connector Boards with Cable Plug......................................... 24
3.6.7 Connector Board Redundancy using Two System Base Plates ............................ 25
3.6.8 Pin Assignment for X-CB 008 05 ........................................................................... 26
3.7 System Cable ....................................................................................................... 27
3.7.1 System Cable X-CA 005 ........................................................................................ 27
3.7.2 System Cable X-CA 009 ........................................................................................ 28
3.7.3 Cable Plug Coding................................................................................................. 28

Table of Contents X-AI 32 02
Page 4 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
4Start-up................................................................. 29
4.1 Mounting ...............................................................................................................29
4.1.1 Wiring Inputs Not in Use.........................................................................................29
4.2 Mounting and Removing the Module..................................................................30
4.2.1 Mounting a Connector Board .................................................................................30
4.2.2 Mounting and Removing the Module......................................................................32
4.3 Sequence of Events Recording (SOE)................................................................34
4.4 Configuring the Module in SILworX....................................................................35
4.4.1 Tab: Module ...........................................................................................................36
4.4.2 Tab: I/O Submodule AI32_02.................................................................................37
4.4.3 Tab: I/O Submodule AI32_02: Channels................................................................ 38
4.4.4 Submodule Status [DWORD] ................................................................................. 40
4.4.5 Diagnostic Status [DWORD]...................................................................................41
4.5 Connection Variants.............................................................................................42
4.5.1 Input Wiring ............................................................................................................42
4.5.2 Wiring Transmitters via Field Termination Assembly .............................................45
4.5.3 Redundant Connection via Two Base Plates ......................................................... 46
4.5.4 Ex-Protection with Zener Barriers...........................................................................47
4.5.5 EX-Protection with Power Supply Isolator.............................................................. 47
4.5.6 Characteristics of HART Communication...............................................................48
5Operation .............................................................. 49
5.1 Handling................................................................................................................49
5.2 Diagnosis ..............................................................................................................49
6Maintenance.......................................................... 50
6.1 Maintenance Measures........................................................................................50
6.1.1 Loading the Operating System...............................................................................50
6.1.2 Proof Test...............................................................................................................50
7Decommissioning.................................................. 51
8Transport .............................................................. 52
9Disposal................................................................ 53
Appendix............................................................... 55
Glossary................................................................................................................55
Index of Figures....................................................................................................56
Index......................................................................................................................58

X-AI 32 02 1 Introduction
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 5 of 60
1 Introduction
The present manual describes the technical characteristics of the module and its use. It
provides information on how to install, start up and configure the module in SILworX.
1.1 Structure and Use of this Manual
The content of this manual is part of the hardware description of the HIMax programmable
electronic system.
This manual is organized in the following main chapters:
Introduction
Safety
Product Description
Start-up
Operation
Maintenance
Decommissioning
Transport
Disposal
Additionally, the following documents must be taken into account:
Name Content Document no.
HIMax
System manual
Hardware description of the
HIMax system
HI 801 001 E
HIMax
Safety manual
Safety functions of the HIMax
system
HI 801 003 E
HIMax
Communication manual
Description of communication
and protocols
HI 801 101 E
SILworX Online Help
(OLH)
Instructions on how to use
SILworX
-
First Steps Introduction to SILworX HI 801 103 E
Table 1: Additional Relevant Manuals
The latest manuals can be downloaded from the HIMA website at www.hima.com. The
revision index on the footer can be used to compare the current version of existing manuals
with the Internet edition.
1.2 Target Audience
This document addresses system planners, configuration engineers, programmers of
automation devices and personnel authorized to implement, operate and maintain the
devices and systems. Specialized knowledge of safety-related automation systems is
required.

1 Introduction X-AI 32 02
Page 6 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
1.3 Formatting Conventions
To ensure improved readability and comprehensibility, the following fonts are used in this
document:
Bold: To highlight important parts
Names of buttons, menu functions and tabs that can be clicked and
used in SILworX.
Italics: System parameter and variables
Courier Literal user inputs
RUN Operating state are designated by capitals
Chapter 1.2.3 Cross references are hyperlinks even though they are not
particularly marked. When the cursor hovers over a hyperlink, it
changes its shape. Click the hyperlink to jump to the corresponding
position.
Safety notes and operating tips are particularly marked.
1.3.1 Safety Notes
The safety notes are represented as described below.
These notes must absolutely be observed to reduce the risk to a minimum. The content is
structured as follows:
Signal word: danger, warning, caution, notice
Type and source of danger
Consequences arising from the danger
Danger prevention
The signal words have the following meanings:
Danger indicates hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury.
Warning indicates hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
Warning indicates hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or
modest injury.
Notice indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in property
damage.
NOTICE
Type and source of damage!
Damage prevention
SIGNAL WORD
Type and source of danger!
Consequences arising from the danger
Danger prevention

X-AI 32 02 1 Introduction
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 7 of 60
1.3.2 Operating Tips
Additional information is structured as presented in the following example:
iThe text corresponding to the additional information is located here.
Useful tips and tricks appear as follows:
TIP The tip text is located here.

2 Safety X-AI 32 02
Page 8 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
2 Safety
All safety information, notes and instructions specified in this manual must be strictly
observed. The product may only be used if all guidelines and safety instructions are
adhered to.
This product is operated in accordance with SELV or PELV. No imminent danger results
from the module itself. The use in Ex-Zone is permitted if additional measures are taken.
2.1 Intended Use
HIMax components are designed for assembling safety-related controller systems.
When using the components in the HIMax system, comply with the following general
requirements
2.1.1 Environmental Requirements
Requirement type Range of values
Protection class Protection class III in accordance with IEC/EN 61131-2
Ambient temperature 0...+60 °C
Storage temperature -40...+85 °C
Pollution Pollution degree II in accordance with IEC/EN 61131-2
Altitude < 2000 m
Housing Standard: IP20
Supply voltage 24 VDC
Table 2: Environmental Requirements
Exposing the HIMax system to environmental conditions other than those specified in this
manual can cause the HIMax system to malfunction.
2.1.2 ESD Protective Measures
Only personnel with knowledge of ESD protective measures may modify or extend the
system or replace modules.
NOTE
Device damage due to electrostatic discharge!
When performing the work, make sure that the working area is free of static and
wear an ESD wrist strap.
If not used, ensure that the device is protected from electrostatic discharge, e.g.,
by storing it in its packaging.

X-AI 32 02 2 Safety
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 9 of 60
2.2 Residual Risk
No imminent danger results from a HIMax module itself.
Residual risk may result from:
Faults in the engineering
Faults in the user program
Faults in the wiring
2.3 Safety Precautions
Observe all local safety requirements and use the protective equipment required on site.
2.4 Emergency Information
A HIMax controller is a part of the safety equipment of a system. If the controller fails, the
system adopts the safe state.
In case of emergency, no action that may prevent the HIMax systems from operating safely
is permitted.

3 Product Description X-AI 32 02
Page 10 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
3 Product Description
The X-AI 32 02 analog input module is intended for use in the programmable electronic
system (PES) HIMax.
The module can be inserted in any of the base plate slots with the exception of the slots
reserved for system bus modules. For more information, refer to the System Manual
(HI 801 001 E).
The module is used to evaluate up to 32 analog input signals.
The module is suitable for sequence of events recording (SOE). Events are recorded within
a module cycle of 2 ms, refer to Chapter 4.3 for more information.
The module has been certified by the TÜV for safety-related applications up to SIL 3
(IEC 61508, IEC 61511 and IEC 62061), Cat. 4 (EN 954-1) and PL e (EN ISO 13849-1).
Refer to the HIMax Safety Manual (HI 801 003 E) for more information on the standards
used to test and certify the modules and the HIMax system.
3.1 Safety Function
The module measures the current of the connected devices with safety-related accuracy,
providing the transmitter supply with a guaranteed minimum voltage.
The safety function is performed in accordance with SIL 3.
3.1.1 Reaction in the Event of a Fault
If a fault occurs, the module adopts the safe state and the assigned input variables transmit
the initial value to the user program.
The initial values must be set to 0 to ensure that the input variables transmit the value 0 to
the user program if a fault occurs. If the raw value is evaluated instead of the process
value, the user must program the monitoring function and the value in the event of faults
from within the user program.
The module activates the Error LED on the front plate.
3.2 Scope of Delivery
The module must be installed on a suitable connector board to be able to operate. If a FTA
is used, a system cable is required to connect the connector board to the FTA. Connector
boards, system cables and FTAs are not included within the scope of delivery.
The connector boards are described in Chapter 3.6, the system cables are described in
Chapter 3.7. The FTAs are described in own manuals.

X-AI 32 02 3 Product Description
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 11 of 60
3.3 Type Label
The type label specifies the following important details:
Product name
Mark of conformity
Bar code (2D or 1D code)
Part number (Part-No.)
Hardware revision index (HW Rev.)
Software revision index (SW Rev.)
Operating voltage (Power)
Ex specifications (if applicable)
Production year (Prod-Year:)
Figure 1: Sample Type Label
3.4 Assembly
The module has 32 analog current inputs (0/4...20 mA), each input is measured and
functionally tested using two internal measuring facilities. A short-circuit-proof transmitter
supply is assigned to each input.
The 32 analog inputs can be used to evaluate the values measured for the transmitters,
safety transmitters or wired contacts. Two-wire or three-wire transmitters with a maximum
supply current of 30 mA can be connected to the input module.
The functional units are electrically isolated to ensure that the input signals are non-
reactive.
The safety-related 1oo2 processor system for the I/O module controls and monitors the I/O
level. The data and states of the I/O module are made available to the processor modules
via the redundant system bus. The system bus has a redundant structure for reasons of
availability. Redundancy is only ensured if both system bus modules are inserted in the
base plates and configured in SILworX.
The module is equipped with LEDs to indicate the status of the digital inputs, see Chapter
3.4.2.

3 Product Description X-AI 32 02
Page 12 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
3.4.1 Block Diagram
The following block diagram illustrates the structure of the module.
Field Side: Transmitter and Wired Contacts
External Transmitter Supply
Interface
Safety-Related Processor System
System Busses
Figure 2: Block Diagram

X-AI 32 02 3 Product Description
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 13 of 60
3.4.2 Indicators
The following figure shows the LED indicators for the module.
Figure 3: Indicators

3 Product Description X-AI 32 02
Page 14 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
The LEDs indicate the operating state of the module.
The LEDs on the module are divided into three groups:
Module status indicators (Run, Error, Stop, Init)
System bus indicators (A, B)
I/O indicators (AI 1...32, Field)
When the supply voltage is switched on, a LED test is performed and all LEDs briefly flash
simultaneously.
Definition of Blinking Frequencies
The following table defines the blinking frequencies of the LEDs:
Name Blinking Frequencies
Blinking1 Long (approx. 600 ms) on, long (approx. 600 ms) off
Blinking2 Short (approx. 200 ms) on, short (approx. 200 ms) off, short (approx. 200
ms) on, long (approx. 600 ms) off
Blinking-x Ethernet communication: Flashing in sync with data transfer
Table 3: Blinking Frequencies of LEDs
3.4.3 Module Status Indicators
These LEDs are located on the front plate, on the upper part of the module.
LED Color Status Description
On Module in RUN, normal operation
Blinking1 Module state:
STOP/OS_DOWNLOAD or
OPERATE (only with processor modules)
Run Green
Off Module not in RUN,
observe the other status LEDs
On/Blinking1 Internal module faults detected by self-tests, e.g.,
hardware, software or voltage supply.
Fault while loading the operating system
Error Red
Off Normal operation
On Module state:
STOP / VALID CONFIGURATION
Blinking1 Module state:
STOP / INVALID CONFIGURATION or
STOP / OS_DOWNLOAD
Stop Yellow
Off Module not in STOP, observe the other status LEDs
On Module state: INIT, observe the other status LEDs
Blinking1 Module state: LOCKED, observe to the other status
LEDs
Init Yellow
Off Module state: neither INIT nor LOCKED, observe
the other status LEDs
Table 4: Module Status Indicators

X-AI 32 02 3 Product Description
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 15 of 60
3.4.4 System Bus Indicators
The system bus LEDs are labeled Sys Bus.
LED Color Status Description
On Physical and logical connection to the system bus
module in slot 1.
Green
Blinking1 No physical connection to the system bus module in
slot 1.
A
Yellow Blinking1
The physical connection to the system bus module
in slot 1 has been established.
No connection to a (redundant) processor module
running in system operation.
On Physical and logical connection to the system bus
module in slot 2.
Green
Blinking1 No physical connection to the system bus module in
slot 2.
B
Yellow Blinking1
The physical connection to the system bus module
in slot 2 has been established.
No connection to a (redundant) processor module
running in system operation.
A+B Off Off Neither physical nor logical connection to the
system bus modules in slot 1 and slot 2.
Table 5: System Bus Indicators
3.4.5 I/O Indicators
LED Color Status Description
On The input current is > 4 mA or greater than the HIGH
switching point (dig) configured in SILworX.
Blinking2 Channel fault (module field or hardware fault). Input
current > 20 mA
Channel
1...32
Yellow
Off The input current is < 4 mA or less than the LOW
switching point (dig) configured in SILworX.
Blinking2 Field fault on at least one channel or supply (open-circuit,
short-circuit, over-current, etc.)
Depending on the configured current thresholds.
Field Red
Off No faults on the field zone.
Table 6: I/O Indicators

3 Product Description X-AI 32 02
Page 16 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
3.5 Product Data
General
Supply voltage 24 VDC, -15 %...+20 %, rP≤5 %, SELV, PELV
Current input min. 500 mA (without channels/transmitter supplies)
max. 1.5 A (in case of short-circuit of the transmitter
supplies)
Current input per channel min. 0 mA (without transmitter supply)
min. 30 mA (with transmitter supply)
Operating temperature 0...+60 °C
Storage temperature -40...+85 °C
Humidity max. 95 % relative humidity, non-condensing
Type of protection IP20
Dimensions (H x W x D) in mm 310 x 29.2 x 230
Weight approx. 1.4 kg
Table 7: Product Data
Figure 4: Views

X-AI 32 02 3 Product Description
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 17 of 60
Analog inputs
Number of inputs (number of
channels)
32 with common ground AI-
(electrical isolation from the system bus and the
24 VDC supply voltage).
Nominal range 0/4...20 mA
Operating range 0...22.5 mA
Digital resolution 12-bit
Shunt for current measurement 200 Ω1)
Maximum permitted current via shunt 50 mA
Withstand voltage of the input ≤10 VDC
Interference voltage suppression > 60 dB (common mode 50/60 Hz)
Refresh of measured values (in the
user program)
Cycle time of the user program
Sampling time 2 ms
Sequence of events recording cycle 2 ms
Measurement accuracy
Measurement accuracy on full
temperature range (-10 °C...70 °C)
±0.15 % of final value
Settling time to 99 % of the process
value when the input signal changes
15 ms
1) For high precision measurements see Table 11
Table 8: Specifications for the Analog inputs
Transmitter supply
Number of transmitter
supplies
32
Output voltage for
transmitter supply
26.5 VDC +0/-15 %
Output current of
transmitter supply
max.30 mA
Monitoring of
transmitter supply
Low voltage: 22.5 VDC
Overvoltage: 30 VDC
Max. number of
transmitter supplies
that may be
simultaneously short-
circuited.
12
If more than 12 supplies are closed for longer than 3 seconds, the
entire transmitter supply is switched off.
If the overload disappears within 30 seconds, the transmitter
supply is switched on again.
Maximum connectable
load
(transmitter + line)
≤750 Ωat 22.5 mA
Table 9: Product Data for the Transmitter Supply

3 Product Description X-AI 32 02
Page 18 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
3.6 Connector Boards
A connector board connects the module to the field zone. Module and connector board
form together a functional unit. Insert the connector board into the appropriate slot prior to
mounting the module.
The following connector boards are available for the module:
Connector board Description
X-CB 008 01 Connector board with screw terminals
X-CB 008 02 Redundant connector board with screw terminals
X-CB 008 03 Connector board with cable plug
X-CB 008 04 Redundant connector board with cable plug
X-CB 008 05 Redundant connector board with cable plug, redundant field
termination assembly
X-CB 008 06 Three-fold redundant connector board with screw terminals
X-CB 008 07 Three-fold redundant connector board with cable plug
Table 10: Available Connector Boards
For high precision measurements, the following connector boards must be used:
Connector board Description
X-CB 019 01 Connector board with screw terminals
X-CB 019 02 Redundant connector board with screw terminals
X-CB 019 03 Connector board with cable plug
X-CB 019 04 Redundant connector board with cable plug
Table 11: Connector Boards for High Precision Measurements
3.6.1 Mechanical Coding of Connector Boards
I/O modules and connector boards are mechanically coded starting from hardware revision
AS10 to prevent them from being equipped with improper I/O modules. Coding avoids
incorrect installation of improper I/O modules thus preventing negative effects on redundant
modules and field zone. A part from that, improper equipment has no effect on the HIMax
system since only I/O modules that are correctly configured in SILworX enter the RUN
state.
I/O modules and the corresponding connector boards have a mechanical coding in form of
wedges. The coding wedges in the female connector of the connector board match with the
male connector recesses of the I/O module plug, see Figure 5.
Coded I/O modules can only be plugged in to the corresponding connector boards.

X-AI 32 02 3 Product Description
HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00 Page 19 of 60
Male Connector Recess
Prepared Male Connector Recess
Coding Wedge
Guideway for Coding Wedge
Figure 5: Coding Example
Coded I/O modules can be plugged in to uncoded connector boards. Uncoded I/O modules
cannot be plugged in to coded connector boards.
3.6.2 Coding of X-CB 008 Connector Boards
a7 a13 a20 a26 c7 c13 c20 c26
X X X
Table 12: Position der Codierkeile

3 Product Description X-AI 32 02
Page 20 of 60 HI 801 055 E Rev. 4.00
3.6.3 Pin Assignment for Connector Boards with Screw Terminals
Mono Redundant Three-fold redundant
X-CB 008 01 X-CB 008 02 X-CB 008 06
X-CB 019 01 X-CB 019 02
01a
01b
01c
03a
03b
03c
05a
05b
05c
07a
07b
07c
02a
02b
02c
04a
04b
04c
06a
06b
06c
08a
08b
08c
09a
09b
09c
11a
11b
11c
13a
13b
13c
15a
15b
15c
10a
10b
10c
12a
12b
12c
14a
14b
14c
16a
16b
16c
17a
17b
17c
19a
19b
19c
21a
21b
21c
23a
23b
18a
18b
18c
20a
20b
20c
22a
22b
22c
24a
24b
24c
25a
25b
25c
27a
27b
27c
29a
29b
29c
31a
31b
31c
26a
26b
26c
28a
28b
28c
30a
30b
30c
32a
32b
32c
23c
01a
01b
01c
03a
03b
03c
05a
05b
05c
07a
07b
07c
02a
02b
02c
04a
04b
04c
06a
06b
06c
08a
08b
08c
09a
09b
09c
11a
11b
11c
13a
13b
13c
15a
15b
15c
10a
10b
10c
12a
12b
12c
14a
14b
14c
16a
16b
16c
17a
17b
17c
19a
19b
19c
21a
21b
21c
23a
23b
18a
18b
18c
20a
20b
20c
22a
22b
22c
24a
24b
24c
25a
25b
25c
27a
27b
27c
29a
29b
29c
31a
31b
31c
26a
26b
26c
28a
28b
28c
30a
30b
30c
32a
32b
32c
23c
01a
01b
01c
03a
03b
03c
05a
05b
05c
07a
07b
07c
02a
02b
02c
04a
04b
04c
06a
06b
06c
08a
08b
08c
09a
09b
09c
11a
11b
11c
13a
13b
13c
15a
15b
15c
10a
10b
10c
12a
12b
12c
14a
14b
14c
16a
16b
16c
17a
17b
17c
19a
19b
19c
21a
21b
21c
23a
23b
18a
18b
18c
20a
20b
20c
22a
22b
22c
24a
24b
24c
25a
25b
25c
27a
27b
27c
29a
29b
29c
31a
31b
31c
26a
26b
26c
28a
28b
28c
30a
30b
30c
32a
32b
32c
23c
X-CB
008 01
X-CB
008 02
X-CB
008 06
I/O Module Plug Connection to the Field Zone (Screw Terminal
Connector Block)
Figure 6: Connector Boards with Screw Terminals
Table of contents
Other HIMA Control Unit manuals

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-CI 24 01 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-MIO 7 01 User manual

HIMA
HIMA DIO 24/16 01 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-DI 32 52 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-DI 32 05 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMatrix F60 DI 32 01 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-DO 12 51 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-DI 32 51 User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-COM 01 E User manual

HIMA
HIMA HIMax X-DI 64 51 User manual
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands

Hubbell
Hubbell GAI-TRONICS XCP0020A instructions
Allen-Bradley
Allen-Bradley ArmorPoint A Series installation instructions

Jadac
Jadac THINGMAGIC M6e user guide

Azbil
Azbil Actival VY5199J Series Specifications and Instructions

Johnson Controls
Johnson Controls tyco AMD-2 manual

TLV
TLV SR-3 instruction manual