X-DI 32 05 Table of Contents
HI 801 053 E Rev. 4.00 Page 3 of 56
Table of Contents
1Introduction ............................................................ 5
1.1 Structure and Use of this Manual......................................................................... 5
1.2 Target Audience..................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Formatting Conventions ....................................................................................... 6
1.3.1 Safety Notes ............................................................................................................ 6
1.3.2 Operating Tips ......................................................................................................... 7
2Safety...................................................................... 8
2.1 Intended Use .......................................................................................................... 8
2.1.1 Environmental Requirements................................................................................... 8
2.1.2 ESD Protective Measures........................................................................................ 8
2.2 Residual Risk ......................................................................................................... 9
2.3 Safety Precautions................................................................................................. 9
2.4 Emergency Information......................................................................................... 9
3Product Description .............................................. 10
3.1 Safety Function.................................................................................................... 10
3.1.1 Reaction in the Event of a Fault............................................................................. 10
3.2 Scope of Delivery................................................................................................. 10
3.3 Type Label ............................................................................................................ 11
3.4 Structure............................................................................................................... 11
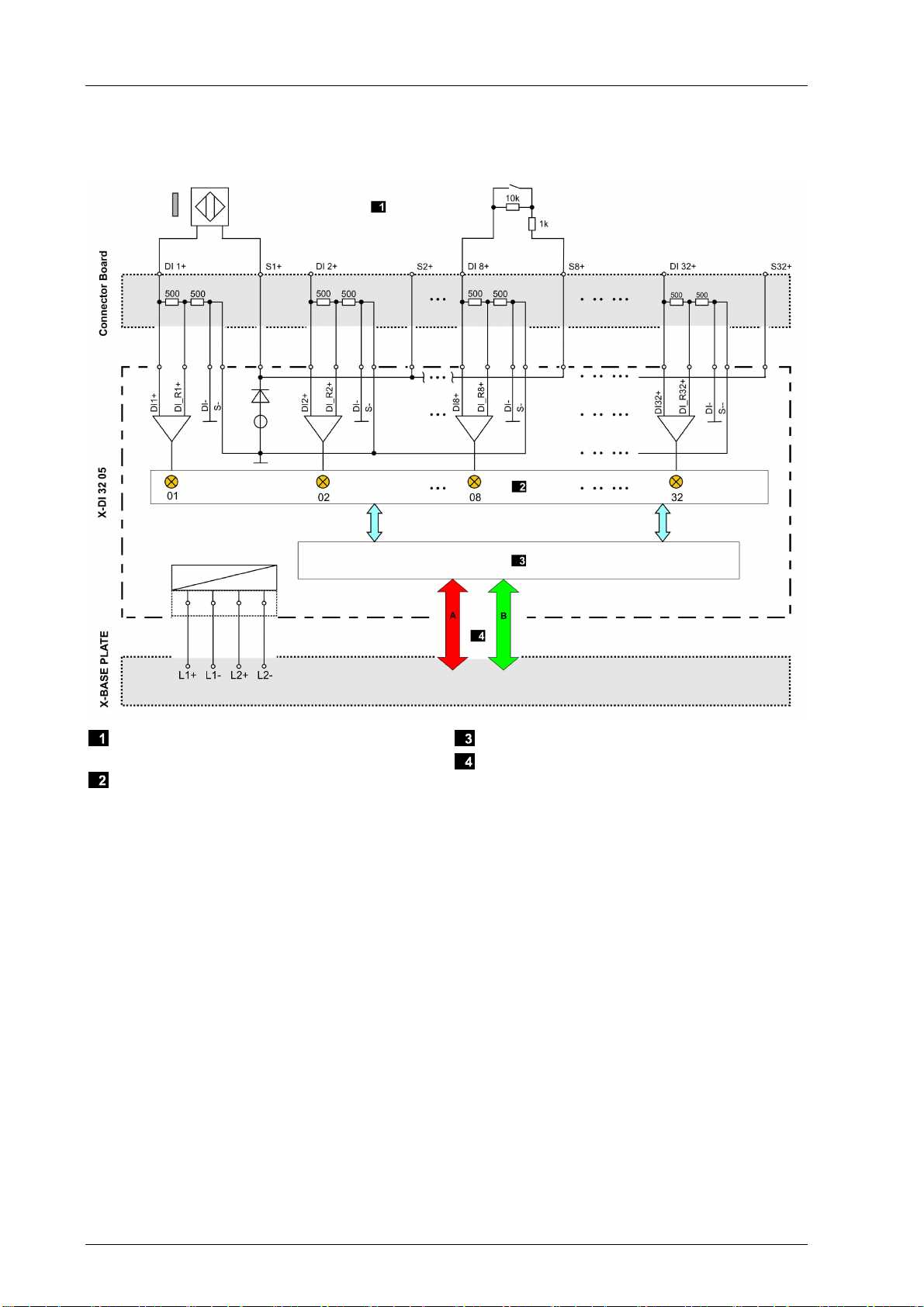
3.4.1 Block Diagram........................................................................................................ 12
3.4.2 Indicators ............................................................................................................... 13
3.4.3 Module Status Indicators ....................................................................................... 14
3.4.4 System Bus Indicators ........................................................................................... 15
3.4.5 I/O Indicators.......................................................................................................... 15
3.5 Product Data......................................................................................................... 16
3.6 Connector Boards................................................................................................ 19
3.6.1 Mechanical Coding of Connector Boards .............................................................. 19
3.6.2 Coding of X-CB 005 Connector Boards ................................................................. 20
3.6.3 Connector Boards with Screw Terminals............................................................... 21
3.6.4 Terminal Assignment for Connector Boards with Screw Terminals....................... 22
3.6.5 Connector Boards with Cable Plug ........................................................................ 24
3.6.6 Pin Assignment for Connector Boards with Cable Plug......................................... 25
3.6.7 Connector Board Redundancy using Two System Base Plates ............................ 26
3.6.8 Pin Assignment for X-CB 005 05 ........................................................................... 27
3.7 System Cable ....................................................................................................... 28
3.7.1 System Cable X-CA 002 ........................................................................................ 28
3.7.2 System Cable X-CA 009 ........................................................................................ 29
3.7.3 Cable Plug Coding................................................................................................. 29