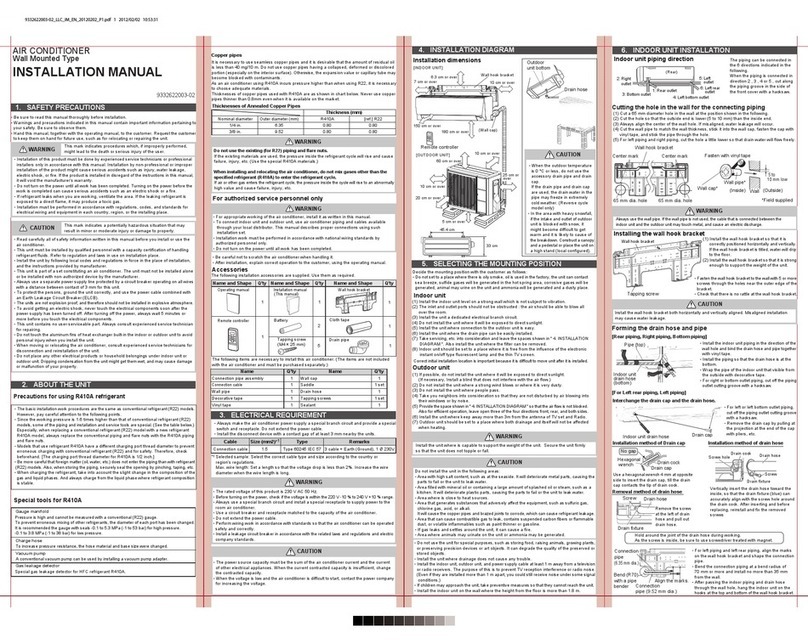
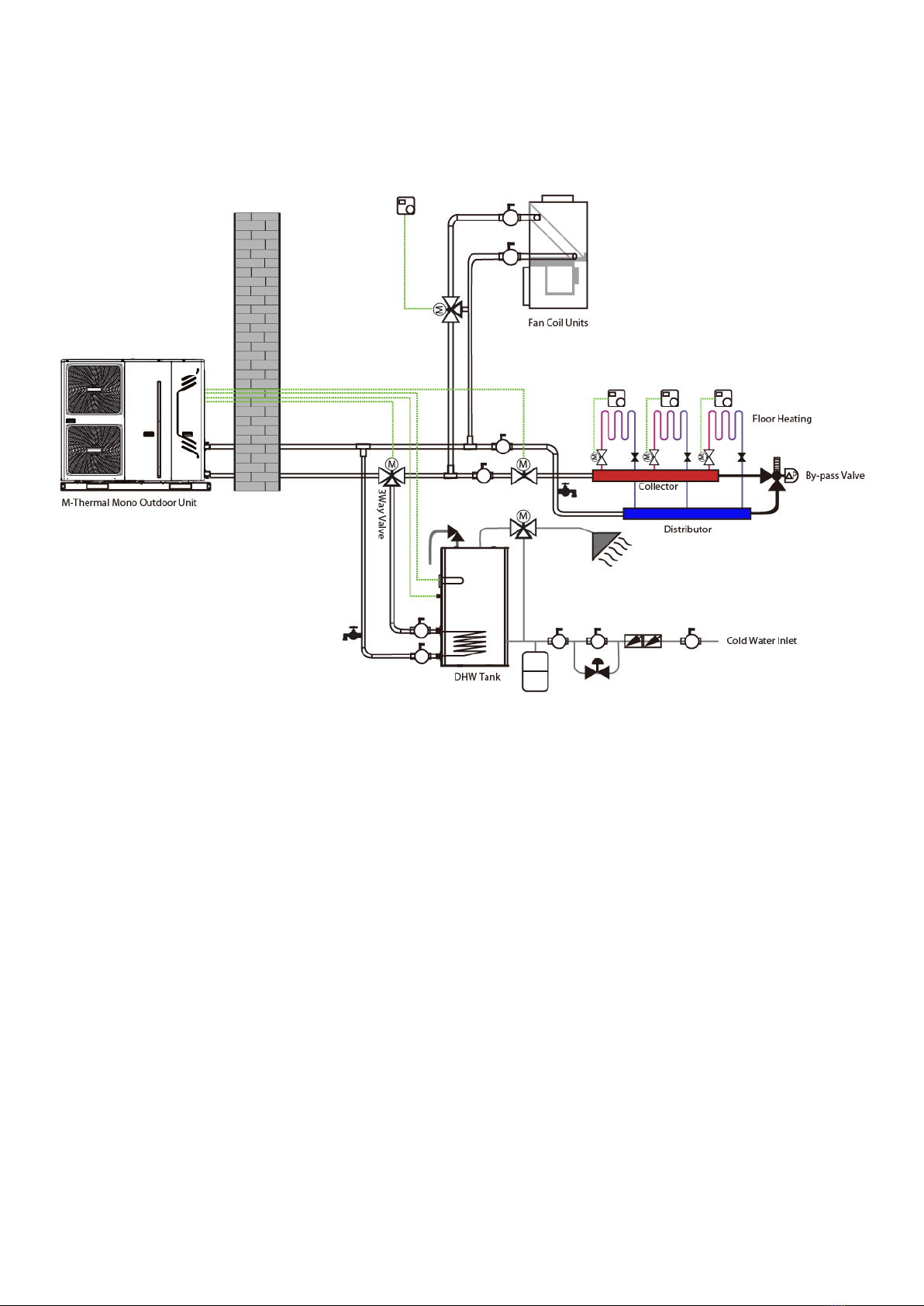
1.2 System Configurations
M-Thermal Mono can be configured to run with the electric heater either enabled or disabled and can also be used in
conjunction with an auxiliary heat source such as a boiler.
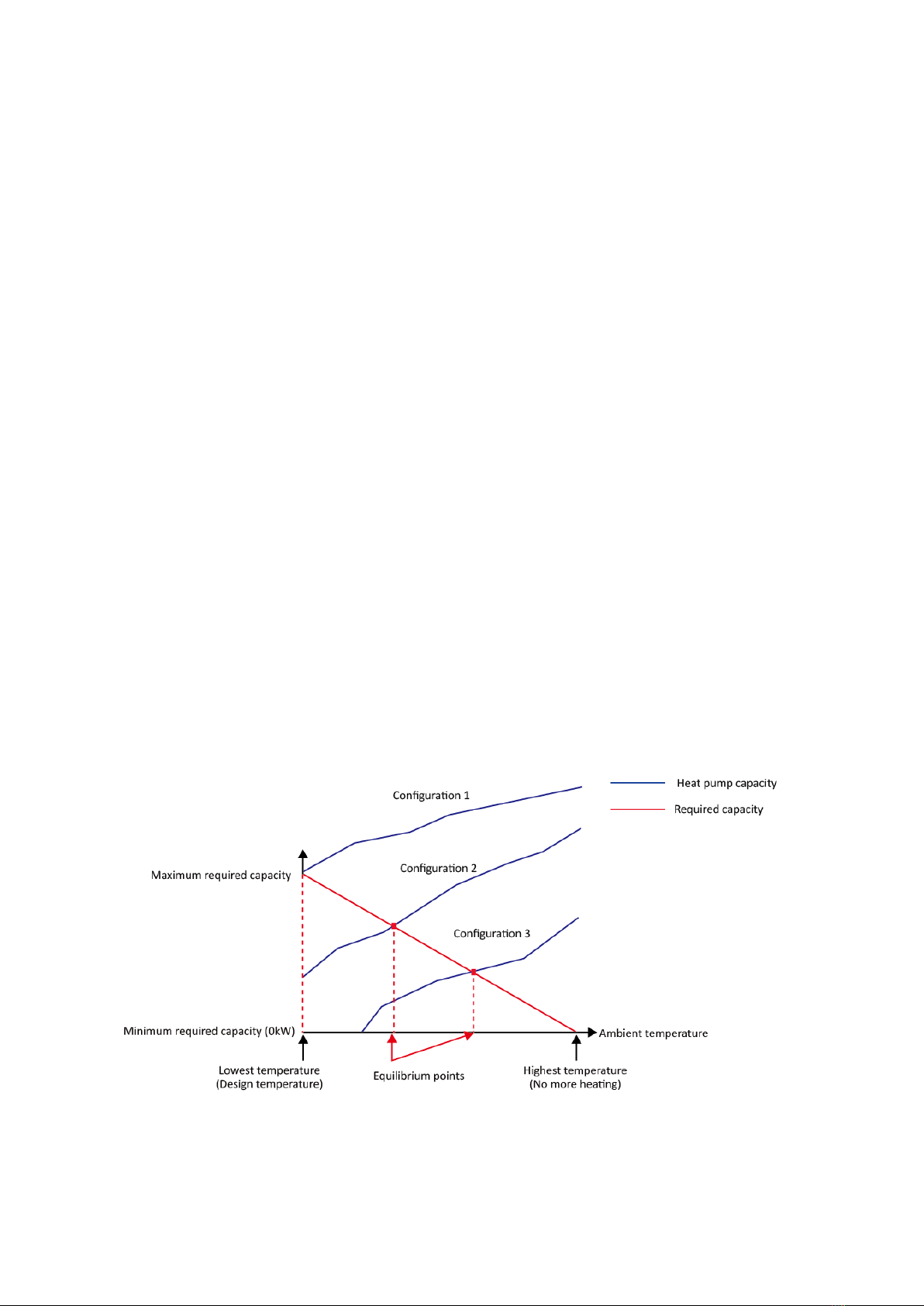
The chosen configuration affects the size of heat pump that is required. Three typical configurations are described below.
Refer to Figure 1-1.2.
Configuration 1: Heat pump only
The heat pump covers the required capacity and no extra heating capacity is necessary.
Requires selection of larger capacity heat pump and implies higher initial investment.
Ideal for new construction in projects where energy efficiency is paramount.
Configuration 2: Heat pump and backup electric heater
Heat pump covers the required capacity until the ambient temperature drops below the point at which the heat
pump is able to provide sufficient capacity. When the ambient temperature is below this equilibrium point (as shown
in Figure 1-1.2), the backup electric heater supplies the required additional heating capacity.
Best balance between initial investment and running costs, results in lowest lifecycle cost.
Ideal for new construction.
Configuration 3: Heat pump with auxiliary heat source
Heat pump covers the required capacity until the ambient temperature drops below the point at which the heat
pump is able to provide sufficient capacity. When the ambient temperature is below this equilibrium point (as shown
in Figure 1-1.2), depending on the system settings, either the auxiliary heat source supplies the required additional
heating capacity or the heat pump does not run and the auxiliary heat source covers the required capacity.
Enables selection of lower capacity heat pump.
Ideal for refurbishments and upgrades.
Figure 1-1.2: System configurations
5