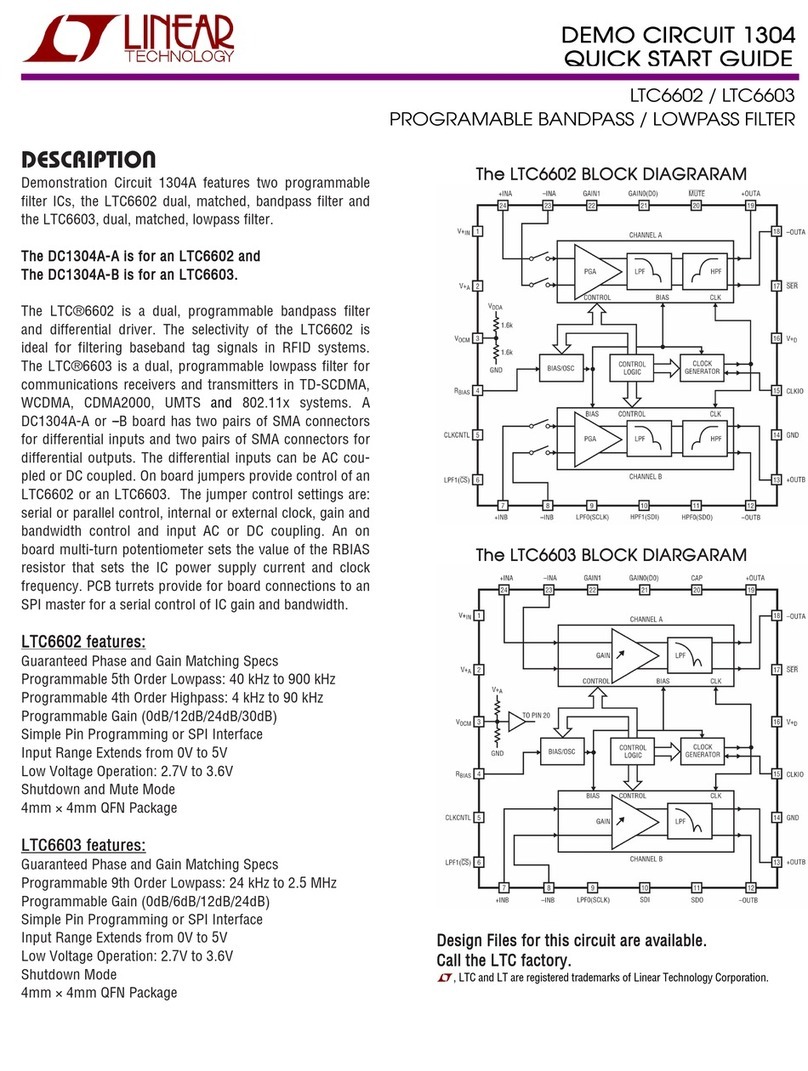
3AN1248.1
May 30, 2006
Removing the “RXBIAS-VCC” (15) jumper, and connecting a
power supply between the “RXBIAS” banana jack and GND
now sets the Rx differential input voltage, via “A1”, and
varying this supply switches the Rx output state. For
example, with the RXBIAS supply = 0V (VID =0V)the
output is high, and increasing RXBIAS to at least +200mV
(VID = -200mV) switches RA low.
To disable the Rx output via the active high RXEN pin,
ensure that the “RXEN1” (10) jumper is in the “VH” position,
and move jumper “(RXEN)” (11) to the “LOW” position. To
disable the Rx output via the active low RXEN pin, ensure
that the “(RXEN)” jumper is in the “LOW” position, and move
jumper “RXEN1” to the “VH” position.
Return the “RXEN1” and “(RXEN)” jumpers to the “VH”
position, remove the “RXBIAS” power supply and jumpers
“J10” and “B1”, and reinstall the “RXBIAS-VCC” jumper.
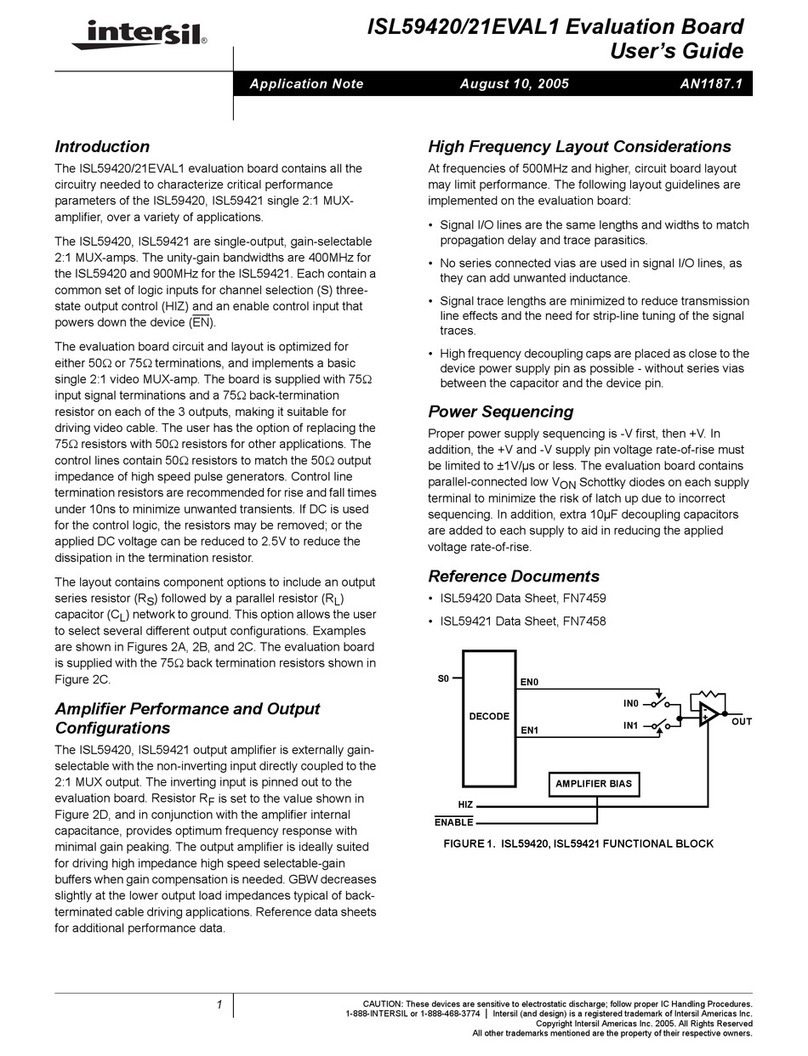
Driver Tests
Tx DC output levels are independent of Tx speed setting. In
the default configuration, the driver input, DY, is low, so the
Tx noninverting output, Z1, is low, while the inverting output,
Y1, is high. To switch the output states, simply move the
“DZ1/DE1 (DY) (14) jumper to the “VH” position. In either
state, note the exceptionally large differential voltage (VOD)
of ≈3.5V. To evaluate the double terminated VOD (≈3.3V),
install resistors R7 and R9, and configure the board for
“external loopback”, as described previously (i.e., install
jumpers (5) and (6)).
To disable the Tx output via the active high DEN pin, move
the “(DEN)” (8) jumper from the “VH” to the “LOW” position.
When finished, return the “DZ1/DE1 (DY)” and “(DEN)”
jumpers to the “LOW” and “VH” positions respectively, and
remove the “external loopback” jumpers.
Internal Loopback
To configure the ISL41387 for internal loopback mode,
simply move the “(ON)” (12) jumper to the “LOW” position,
while ensuring that the “(DEN)” (8) and “(RXEN)” (11)
jumpers are set to “VH”. Note that ICC increases by ≈1.4mA,
due to the enabling of the loopback receivers. RA is now low
due to the Tx outputs internally driving the Rx. You can
repeat the previous Rx switching tests to confirm that the
external Rx input pins now have no affect on RA.
The internal loopback receivers are not RS-485/422
compliant, so internal loopback can’t be used to create a
half duplex transceiver.
Low Power SHDN
With the “(ON)” (12) jumper still in the “LOW” position, move
the “(DEN)” (8) and “(RXEN)” (11) jumpers to the “LOW”
position, while ensuring that the “RXEN1” (10) jumper is set
to “VH”. This setting places the ISL41387 into shutdown
(SHDN), which disables the Tx and Rx outputs, and places
the IC in its lowest power mode. Note that ICC drops to less
than 5µA.
Return jumpers “(ON)”, “(DEN)”, and “(RXEN)” to the “VH”
position.
Basic RS-485 AC Evaluation
Remember that there aren’t any differential term resistors,
so if they are desired they must be added at positions R7 -
for the Tx - and R9 for the Rx.
Receiver Tests
Before starting, ensure that the jumpers are back in the
default positions. Note that the RS-485 Rx operates at high
speed, regardless of the Tx speed selection.
Add jumper “B1” (4) to connect that input to GND, and add
jumper “A1” (1) to engage the 50Ωterm. Connect a
generator to the “A1” BNC, and set it for a -1.5V to +1.5V
swing. Monitoring test points “TP6” (input), and “RB1 (RA)”
(output) with a scope allows the Rx prop delays and skews
to be measured. If desired, you can load the Rx output with a
1kΩresistor by adding jumper “J6” (not numbered), located
below test point “RB1 (RA)”. This resistor terminates to the
“VLOAD” banana jack (upper left hand corner), allowing the
resistor to be terminated to GND by shorting “VLOAD” to
GND, or terminated to any voltage by connecting “VLOAD”
to an external supply.
You can also measure the Rx enable/disable time to/from a
low output state via the active high RXEN pin. From the
previous jumper configuration, leave the “B1” and “J6”
jumpers installed, remove the “A1” jumper, and install the A1
Rx bias jumper, “J10” (2). Connect the “VLOAD” jack to VCC,
switch the “(RXEN)” (11) jumper to the low position to
engage the 50Ωterm, set the generator to swing from 0V to
3V, and move the generator to the “NC (RXEN)” BNC.
Monitoring test points “TP12” (input), and “RB1 (RA)”
(output) with a scope allows the Rx enable and disable times
to be measured. To evaluate the Rx enable/disable time
to/from a high output state, simply remove “J10”, and
connect “VLOAD” to GND.
To evaluate the Rx enable/disable times using the active low
RXEN pin, repeat the previous test but leave the “(RXEN)”
jumper in the “LOW” position, move the “RXEN1” (10)
jumper to the “LOW” position to connect the 50Ωterm, and
connect the generator to the “RXEN1” BNC.
Tx Speed Selection
Before performing any Tx switching tests, ensure that the
jumpers are in their default positions, and then configure the
“DZ/(SLEW)” (13) and “SPB” (9) jumpers for the desired Tx
speed setting. Table 1 details the jumper settings for each of
the speed options.
Application Note 1248