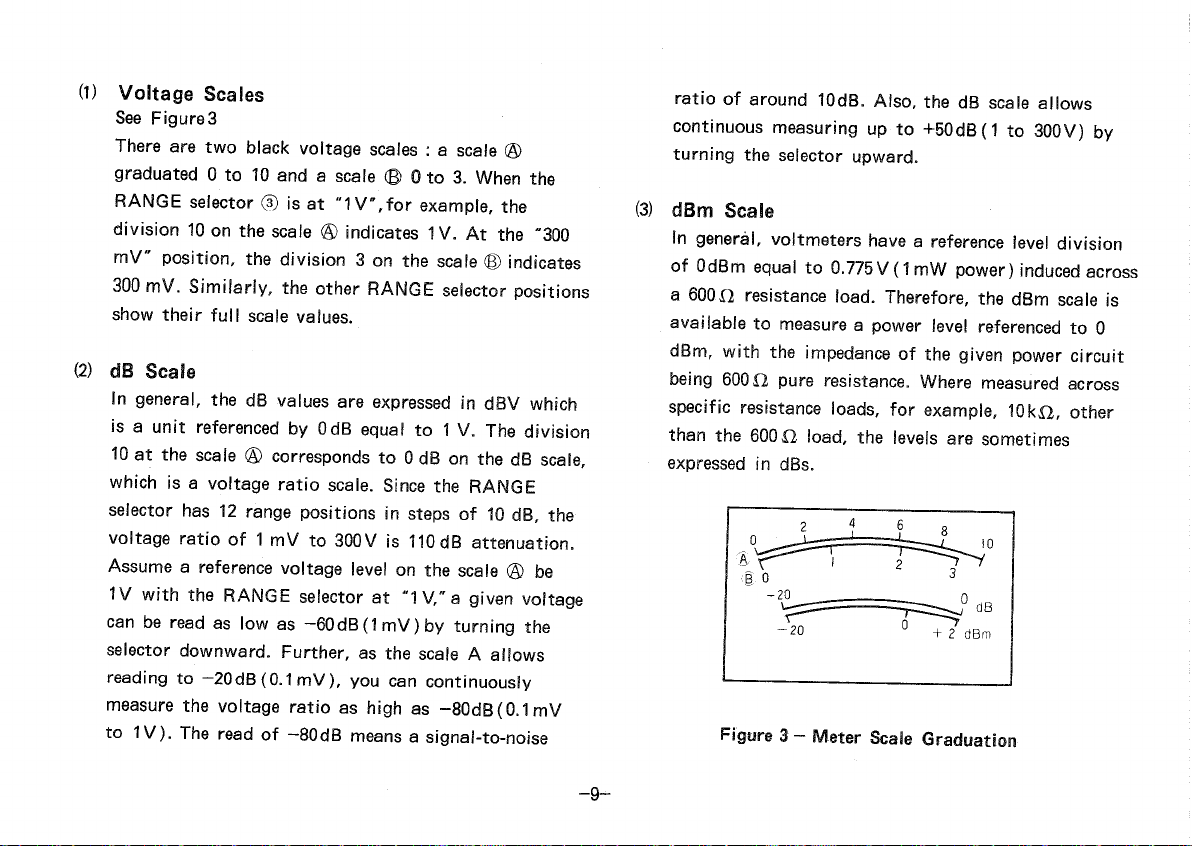
(1)
Voltage
Scales
See
Figures
There
aretwoblackvoltage
scales
: a
scale
®
graduated0 to10anda
scale
© 0 to3.Whenthe
RANGE
selector® isat"1V,forexample,the
division10onthe
scale
® indicates1V.Atthe"300
mV"position,thedivision3 onthe
scale
® indicates
300
mV.Similarly,theother
RANGE
selectorpositions
showtheir
full
scale
values.
(2)
dB
Scale
Ingeneral,thedBvaluesareexpressedindBVwhich
is
a
unit
referencedbyOdBequalto1 V.Thedivision
10
atthe
scale
® correspondsto0 dBonthedB
scale,
whichisa voltage
ratio
scale.
Sincethe
RANGE
selectorhas12rangepositionsinstepsof10dB,the
voltage
ratio
of1 mVto300Vis110dBattenuation.
Assume
a referencevoltagelevelonthe
scale
® be
1V
with
the
RANGE
selectorat"1V,"a givenvoltage
can
bereadaslowas-60dB(1mV)by
turning
the
selectordownward.Further,asthe
scale
A allows
readingto—20dB(0.1mV),youcancontinuously
measure
thevoltage
ratio
as
high
as-80dB(0.1mV
to1V).Thereadof-80dBmeansa signal-to-noise
ratio
ofaround10dB.Also,thedB
scale
allows
continuousmeasuringupto+50dB(1to300V)by
turning
theselectorupward.
(3)
dBm
Scale
Ingeneral,voltmetershavea referenceleveldivision
ofOdBmequalto0.775V(1mWpower)inducedacross
a
800Oresistanceload.Therefore,thedBm
scale
is
available
tomeasurea powerlevelreferencedto0
dBm,
with
theimpedanceofthegivenpowercircuit
being60012pureresistance.Wheremeasuredacross
specific
resistanceloads,forexample,10kO,other
thanthe600Oload,thelevelsaresometimes
expressed
indBs.
Figure
3 - Meter
Scale
Graduation
™9-