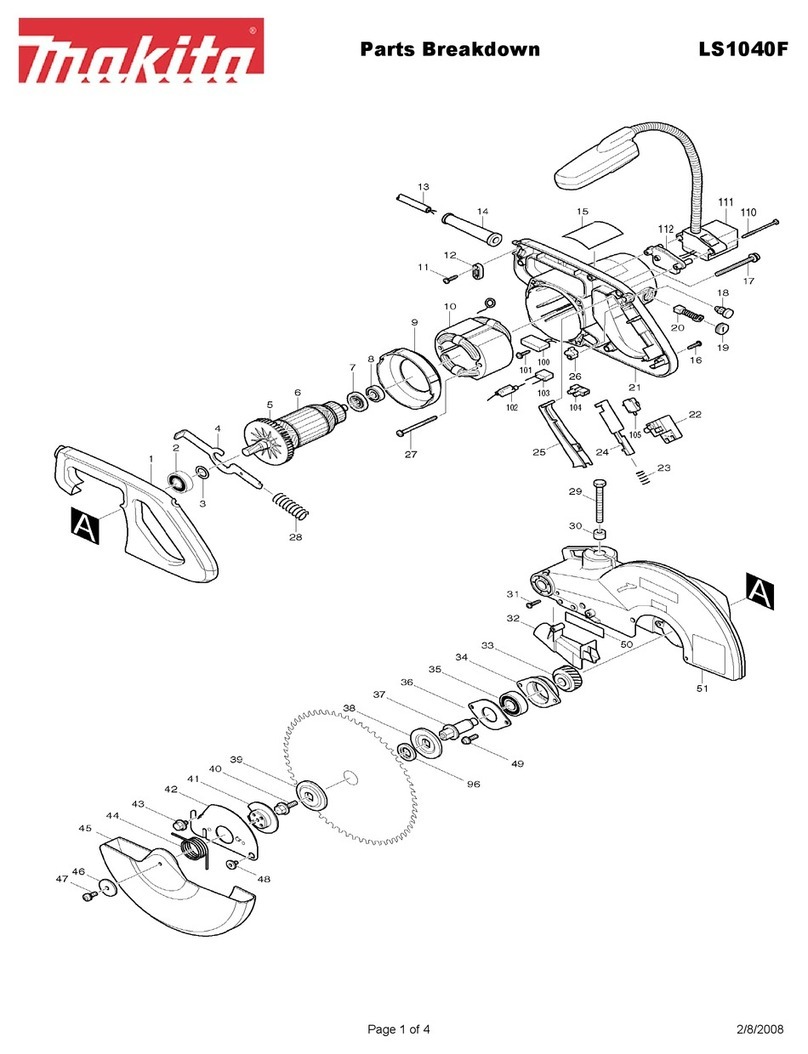
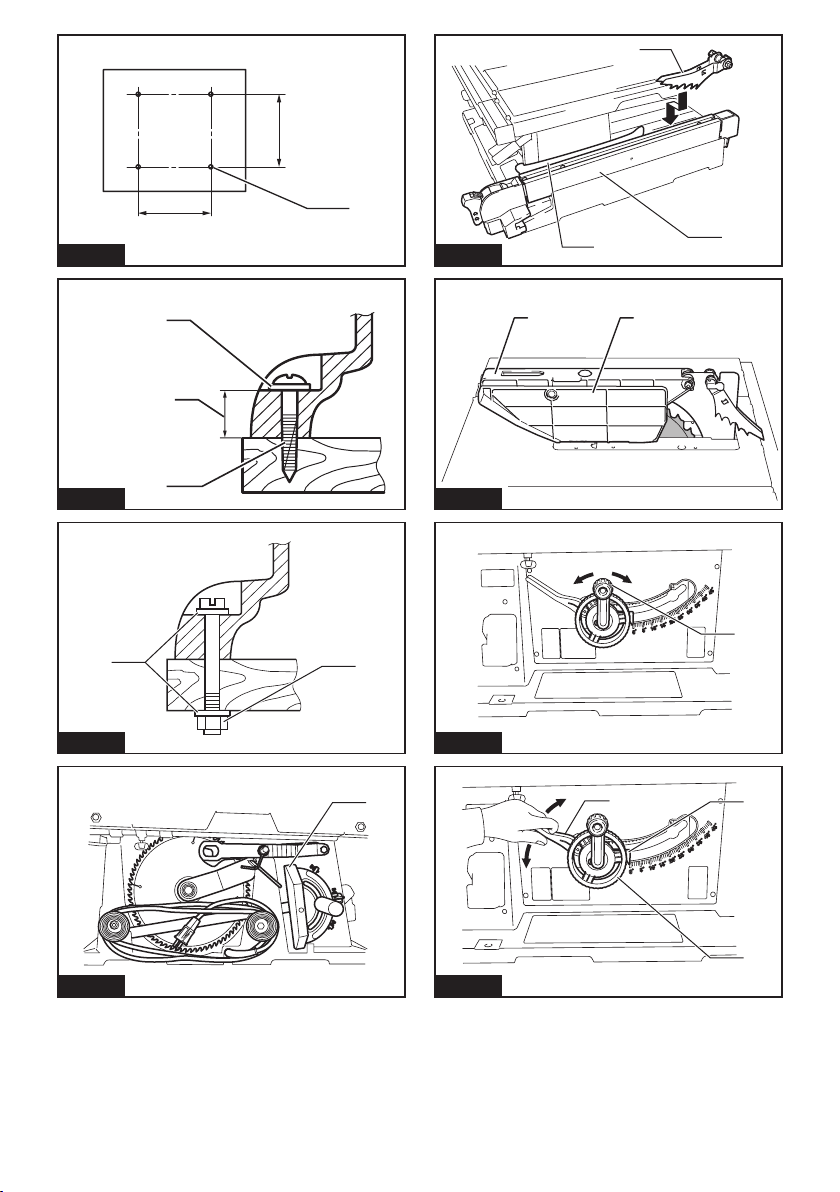
10 ENGLISH
EC Declaration of Conformity
For European countries only
The EC declaration of conformity is included as Annex A
to this instruction manual.
SAFETY WARNINGS
General power tool safety warnings
WARNING: Read all safety warnings, instruc-
tions, illustrations and specications provided
with this power tool. Failure to follow all instructions
listed below may result in electric shock, re and/or
serious injury.
Save all warnings and instruc-
tions for future reference.
The term "power tool" in the warnings refers to your
mains-operated (corded) power tool or battery-operated
(cordless) power tool.
Safety instructions for table saws
Guarding related warnings
1. Keep guards in place. Guards must be in work-
ing order and be properly mounted. A guard
that is loose, damaged, or is not functioning cor-
rectly must be repaired or replaced.
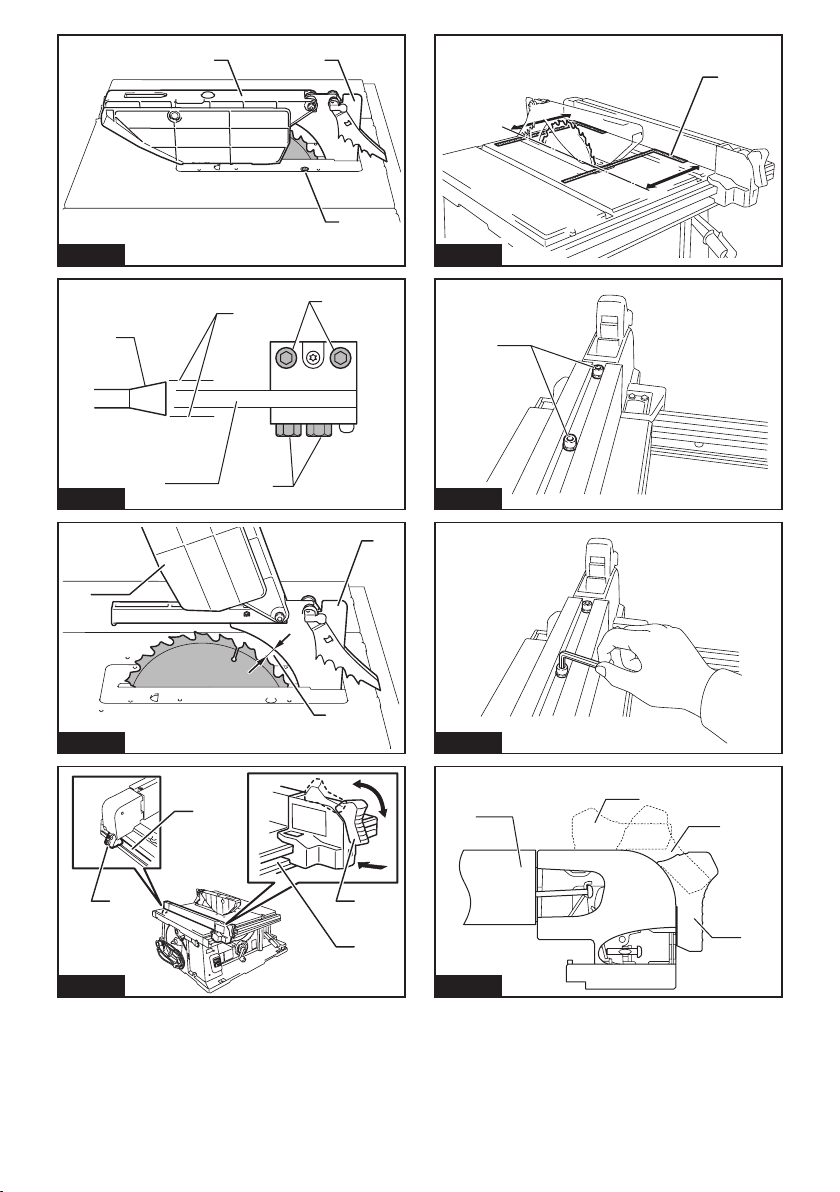
2. Make sure the saw blade is not contacting the
guard, riving knife or the workpiece before the
switch is turned on. Inadvertent contact of these
items with the saw blade could cause a hazardous
condition.
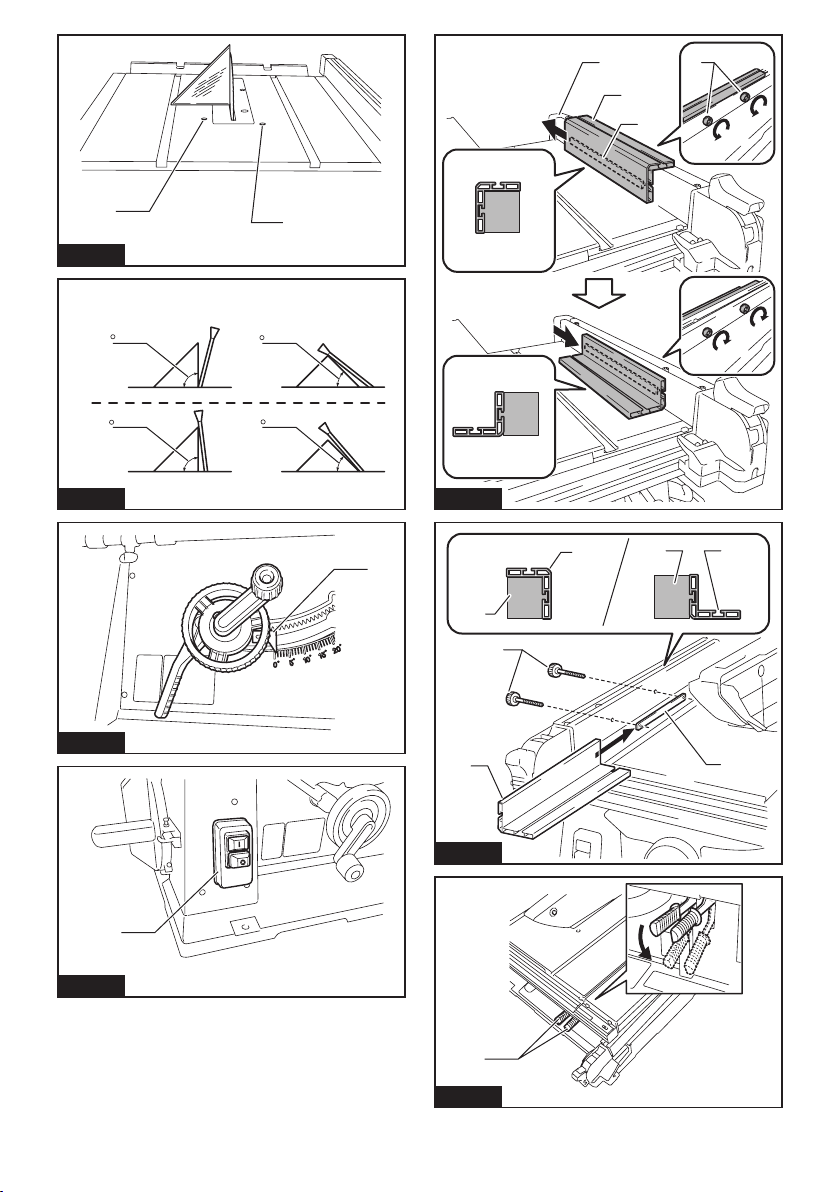
3. Adjust the riving knife as described in this
instruction manual. Incorrect spacing, position-
ing and alignment can make the riving knife inef-
fective in reducing the likelihood of kickback.
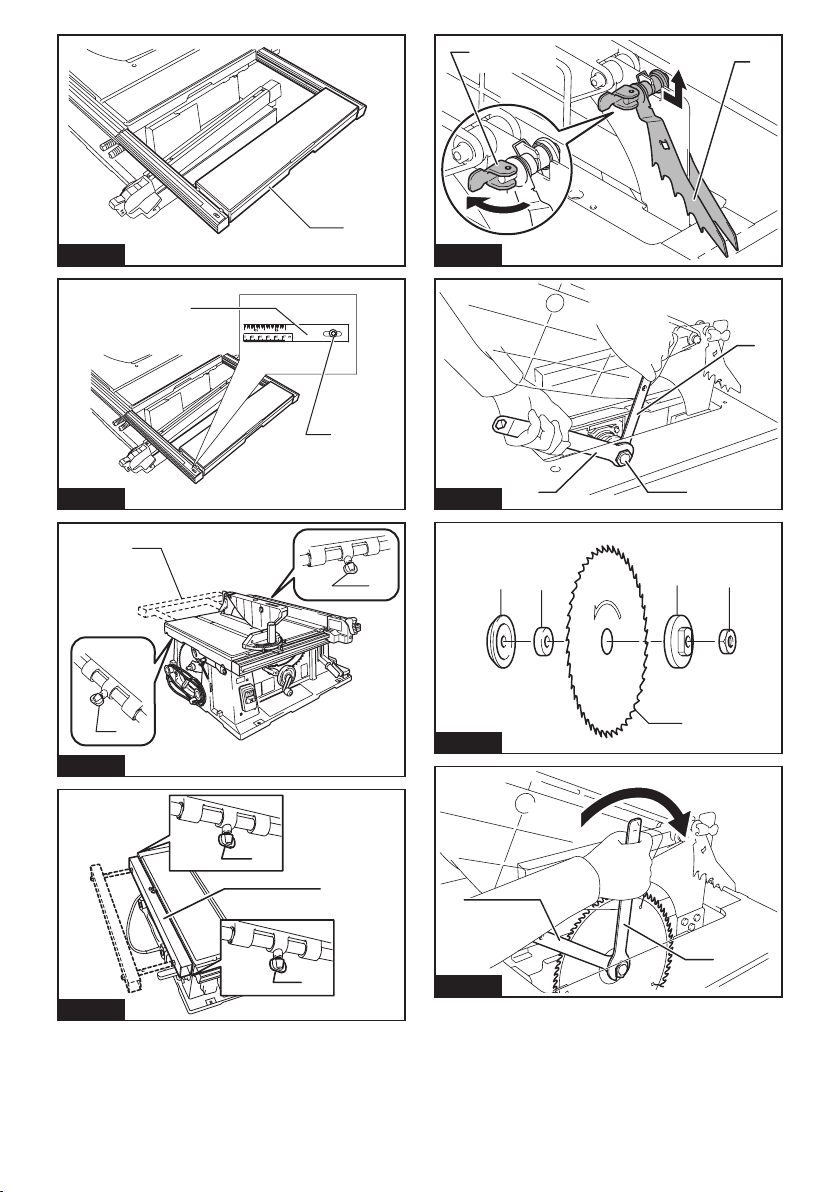
4. For the riving knife and anti-kickback pawls to
work, they must be engaged in the workpiece.
The riving knife and anti-kickback pawls are inef-
fective when cutting workpieces that are too short
to be engaged with the riving knife and anti-kick-
back pawls. Under these conditions a kickback
cannot be prevented by the riving knife and anti-
kickback pawls.
5. Use the appropriate saw blade for the riving
knife. For the riving knife to function properly, the
saw blade diameter must match the appropriate
riving knife and the body of the saw blade must be
thinner than the thickness of the riving knife and
the cutting width of the saw blade must be wider
than the thickness of the riving knife.
Cutting procedures warnings
1. DANGER: Never place your ngers or
hands in the vicinity or in line with the saw
blade. A moment of inattention or a slip could
direct your hand towards the saw blade and result
in serious personal injury.
2. Feed the workpiece into the saw blade only
against the direction of rotation. Feeding the
workpiece in the same direction that the saw blade
is rotating above the table may result in the work-
piece, and your hand, being pulled into the saw
blade.
3. Never use the mitre gauge to feed the work-
piece when ripping and do not use the rip
fence as a length stop when cross cutting with
the mitre gauge. Guiding the workpiece with the
rip fence and the mitre gauge at the same time
increases the likelihood of saw blade binding and
kickback.
4. When ripping, always apply the workpiece
feeding force between the fence and the saw
blade. Use a push stick when the distance
between the fence and the saw blade is less
than 150 mm, and use a push block when this
distance is less than 50 mm. “Work helping”
devices will keep your hand at a safe distance
from the saw blade.
5. Use only the push stick provided by the manu-
facturer or constructed in accordance with the
instructions. This push stick provides sufcient
distance of the hand from the saw blade.
6. Never use a damaged or cut push stick. A
damaged push stick may break causing your hand
to slip into the saw blade.
7. Do not perform any operation “freehand”.
Always use either the rip fence or the mitre
gauge to position and guide the workpiece.
“Freehand” means using your hands to support or
guide the workpiece, in lieu of a rip fence or mitre
gauge. Freehand sawing leads to misalignment,
binding and kickback.
8. Never reach around or over a rotating saw
blade. Reaching for a workpiece may lead to
accidental contact with the moving saw blade.
9. Provide auxiliary workpiece support to the rear
and/or sides of the saw table for long and/or
wide workpieces to keep them level. A long and/
or wide workpiece has a tendency to pivot on the
table’s edge, causing loss of control, saw blade
binding and kickback.
10. Feed workpiece at an even pace. Do not bend
or twist the workpiece. If jamming occurs, turn
the tool off immediately, unplug the tool then
clear the jam. Jamming the saw blade by the
workpiece can cause kickback or stall the motor.
11. Do not remove pieces of cut-off material while
the saw is running. The material may become
trapped between the fence or inside the saw blade
guard and the saw blade pulling your ngers into
the saw blade. Turn the saw off and wait until the
saw blade stops before removing material.
12. Use an auxiliary fence in contact with the table
top when ripping workpieces less than 2 mm
thick. A thin workpiece may wedge under the rip
fence and create a kickback.
Kickback causes and related warnings
Kickback is a sudden reaction of the workpiece due to a
pinched, jammed saw blade or misaligned line of cut in
the workpiece with respect to the saw blade or when a
part of the workpiece binds between the saw blade and
the rip fence or other xed object.