INDEX
Forwards Ⅰ....................................................................
Marks and arrangements used in this manual Ⅱ....................................
For safe operation Ⅲ.............................................................
1. Installation place Ⅲ.........................................................
2. Power supply Ⅴ............................................................
3. Application note Ⅴ..........................................................
History of revision Ⅵ............................................................
1. General 1.................................................................
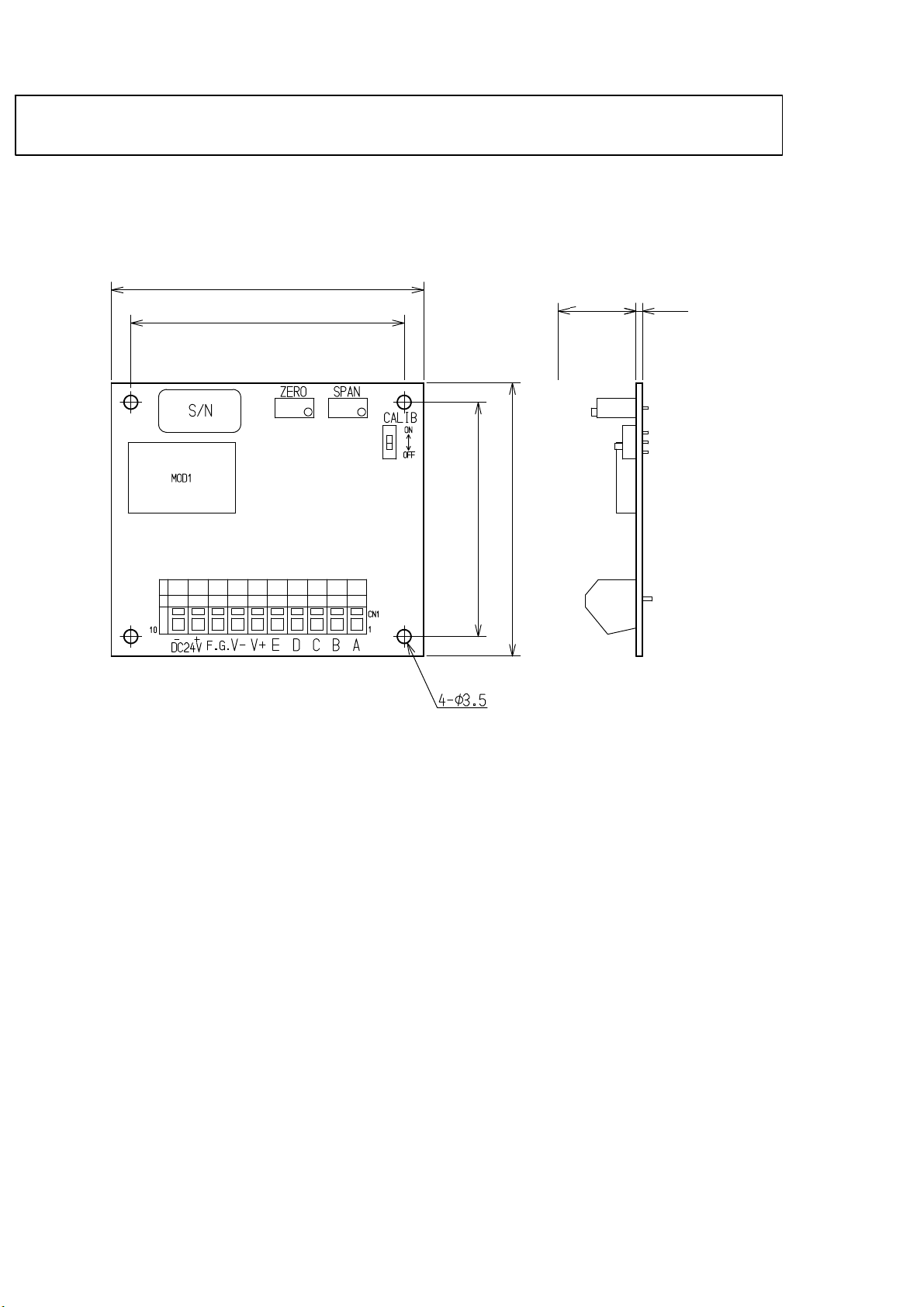
2. Name and function of each point 1..........................................
3. Connecting method 2......................................................
3−1. Layout of the terminal boards 2.........................................
3−2. Note on connection 2...................................................
3−3. Connection 3..........................................................
3−3−1. Connection with strain gage applied transducers 3...................
3−3−2. Connection of voltage output 5....................................
3−3−3. Connection with the power supply and the earth 6...................
4. Calibration procedures 7...................................................
4−1. Preparations 7........................................................
4−2. Calibration procedures 7...............................................
4−2−1. Calibration by the actual load 7....................................
4−2−2. Electronic calibration by CALIB input 8............................
4−3. Zero adjustment by mounting resistance 10................................
4−3−1. Mounting the resistance 10........................................
4−3−2. Check the initial load 11...........................................
5. Trouble shooting 13........................................................
5−1. Execute trouble shooting 14.............................................
6. Specifications 19...........................................................
6−1. Specifications 19........................................................
6−2. General specifications 19................................................
6−3. Standard specifications at the time of shipment 19.........................
6−4. Accessories 19..........................................................
7. Warranty 20................................................................
7−1. Warranty 20...........................................................
7−2. Repair 20..............................................................