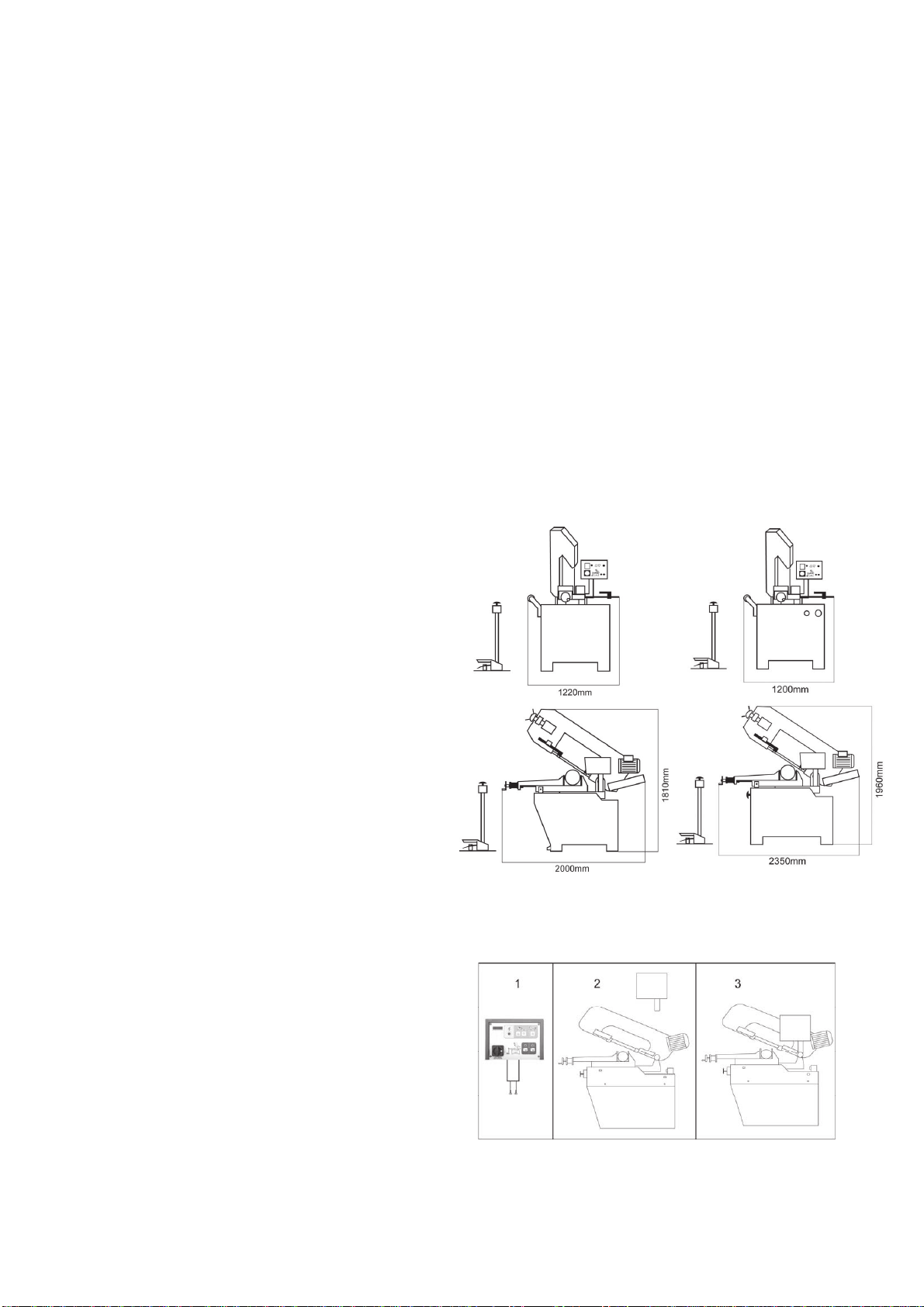
5. Indicator light 15 indicates the hydraulic motor
has overloaded.
highest position and then using the first method,
select hand operation on selector (E) and press
cycle start switch (F) to start operation. Using the
second method, Select footpad operation on
selector (E) and step on start footpad (J) to start
operation.
6. Indicator light 11 indicates the speed is not
properly selected.
-If the saw bow up/down switches are out of order
then indicator lights 2 and 3 will blink at the same
time.- In general, start cuts by slightly turning hydraulic
flow regulation switch (A1)counter-clockwise from 2
to 3 to control the saw arm descent rate. If the
arm descends too quickly, turn hydraulic flow
regulation switch (A1) clockwise all the way back to
stop its descent - When cutting different material
use the hydraulic flow regulation switch (A1)to
control saw arm’s rate of descent.
BLADE CUTTING DIRECTION
*Note: A saw arm dropping too quickly can cause
the blade to stall on the work piece and the
machine will shut off. If so, push down on either
emergency push buttons (H or I) to immediately
stop all machine functions. 4ADVICE ON USING YOUR
BANDSAW
- During the operation cycle, the hydraulic vise will
automatically close on the work piece for a
distance up to 8mm. The hydraulic vise will then
open maximum 8mm on end of operation. Now it
is ready for the next operation. Therefore, it is not
necessary to manually lock down the vise jaws on
the work piece for every operation. Allowing a
gap of 4-5mm between jaws and the work piece
will suffice.
4.1 Recommendations and advice for using the
machine
The machine has been designed to cut metal
building materials, with different shapes and profiles,
used in workshops, turner's shops and general
mechanical structural work.
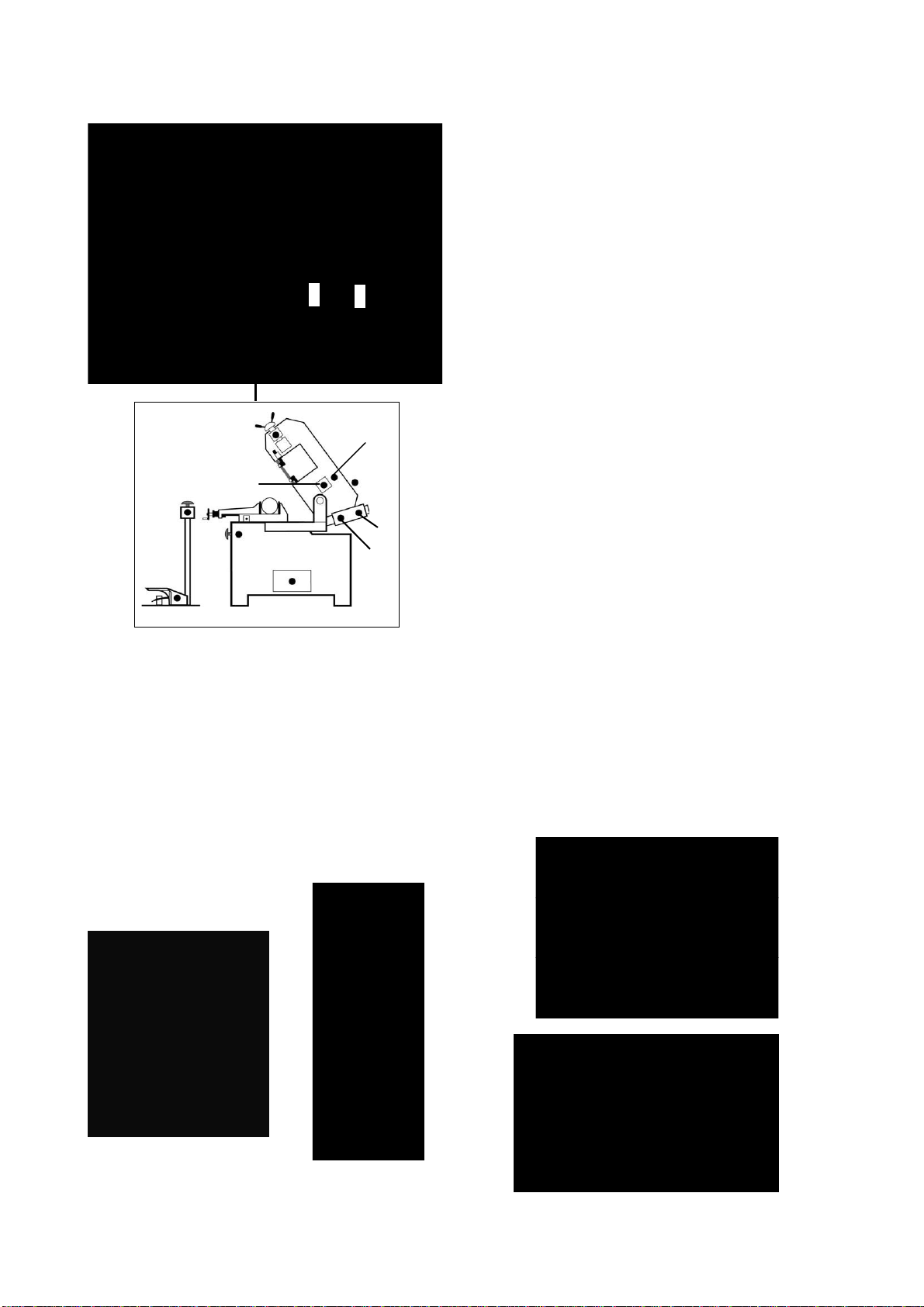
Only one operator is needed to use the machine,
that must stand as shown in the picture.
-The saw bow will return to the bow’s maximum
height upon completion of operation.
- In case of Emergency or problem during the
operation cycle, press the emergency push button
(H or I) down to shut off all functions.
-To release the emergency push button (H or I),
rotate the mushroom shaped button clock-wise.
The button will pop up and then the cutting cycle
can be restarted.
-The hydraulic start switch (G) will automatically
shut-off after 5 minutes of non-operation.
*Note: If the hydraulic start switch fails to activate,
then switch (C), (D), and (F) cannot operate.
Indicator light (7) will blink if any are pressed,
indicating that hydraulic start switch (G) has failed
to activate.
- Before starting each cutting operation, ensure that
the part is firmly clamped in the vise and that the
end is suitably supported.
-If the hand operation is selected and the footpad is
used, then the hand operation indicator light (4)
will blink. And vice versa, If the footpad operation
is selected and the hand switches are used, then
the foot operation indicator light (5) will blink.
They indicate improper selection.
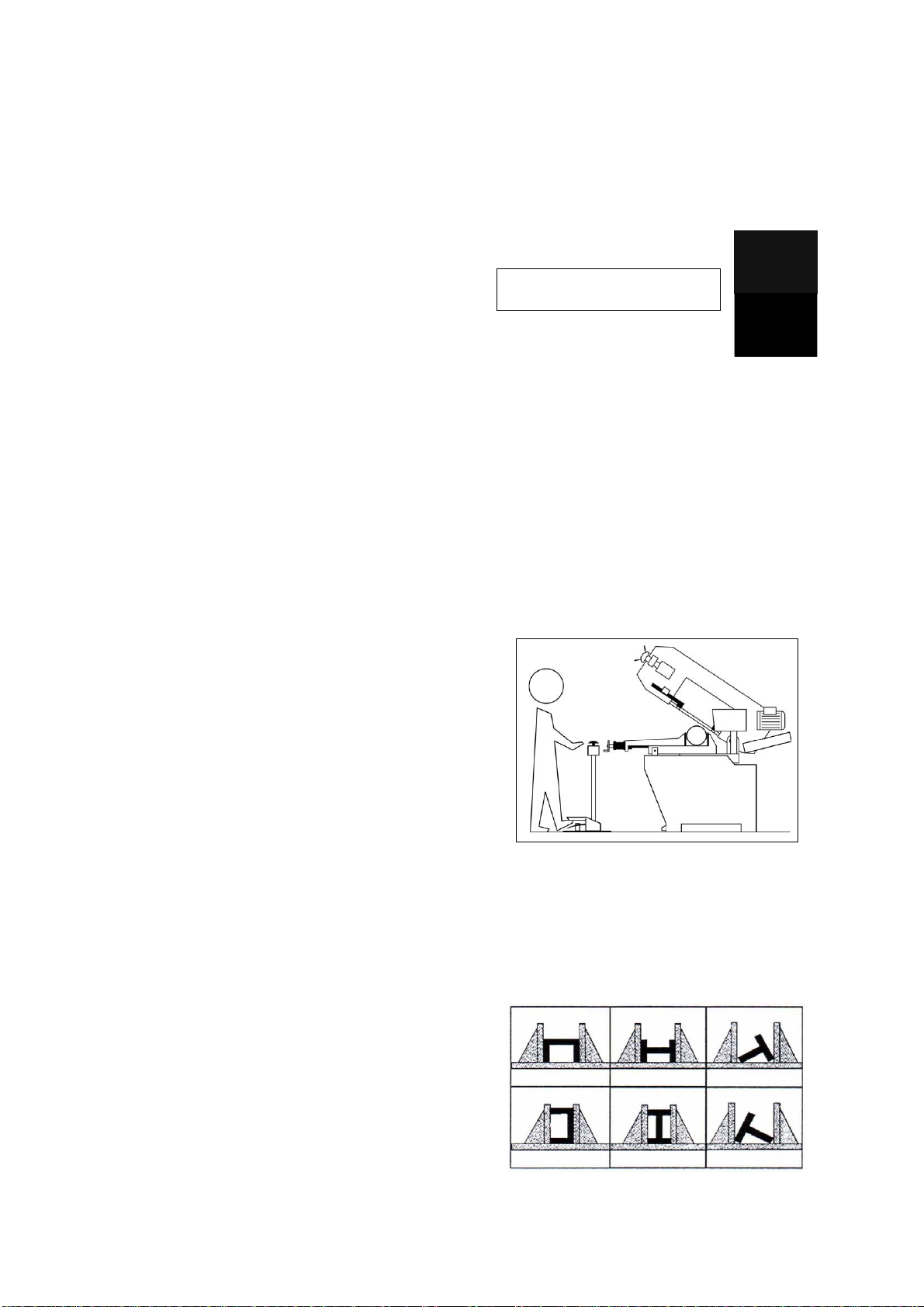
- These figures below show examples of suitable
clamping of different section bars, bearing in mind
the cutting capacities of the machine in order to
achieve a good efficiency and blade durability.
-The appropriate indicator light will blink to indicate
which part of the machine has gone out of order.
1. Indicator light 14 indicates the emergency
button is pressed. Indicator light 16 indicates
the emergency button on foot pad is pressed.
2. Indicator light 13 indicates the band saw blade
has broken.
3. Indicator light 10 indicates the blade cover is
open. - Do not use blades of a different size from those
stated in the machine specifications.
4. Indicator light 12 indicates the motor has
overloaded.
-6