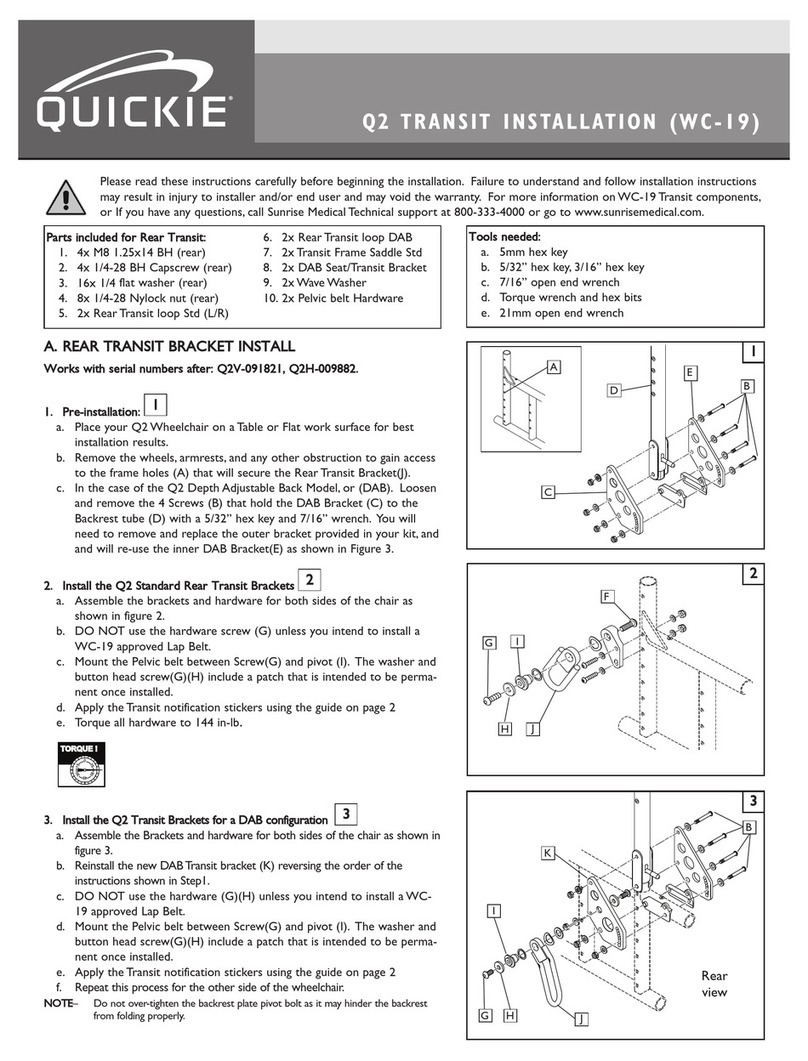
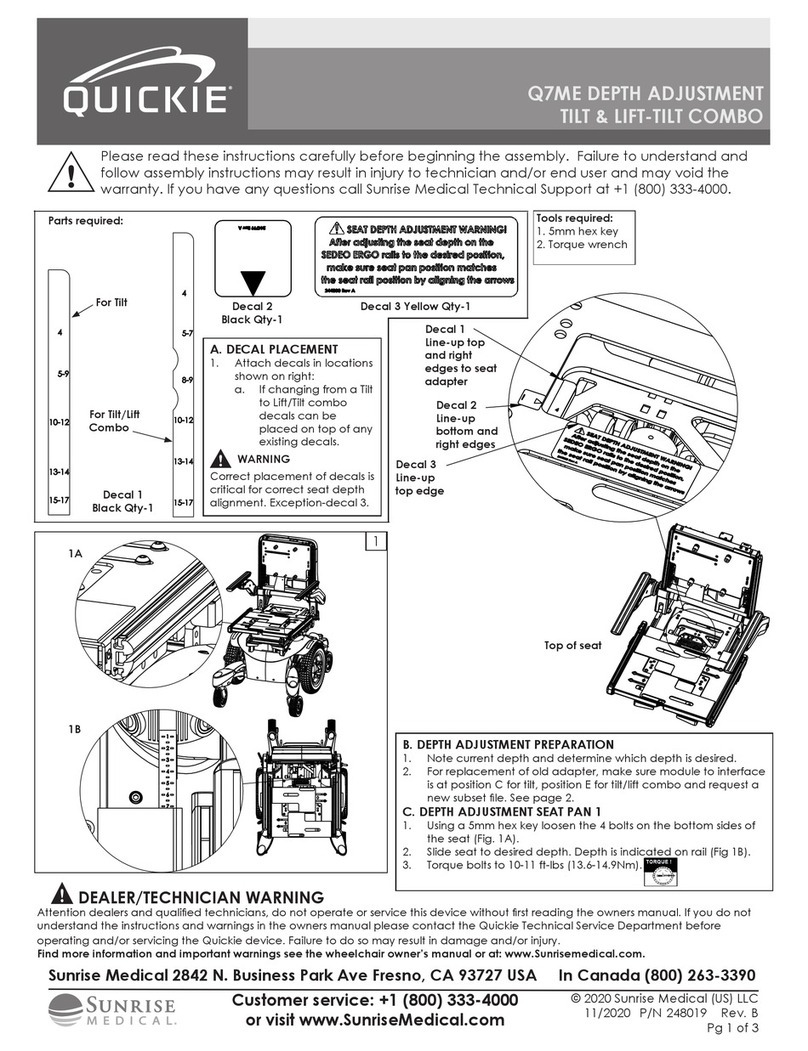
Contraindicaons
WARNING!
A wheelchair with Standing funcon can only be used upon
prescripon by a doctor.
Here are the most common contraindicaon for the use of a
wheelchair with Standing funcon:
• Reduced bone density: Should the bones already be very
weak it is not recommended to stand. This could lead to
fractures. In this case consult your doctor for a bone density
measurement.
• Poor circulaon: For heart or circulatory diseases standing
should only occur under medical supervision (cardio
training). Please consult a doctor in this case.
• Severe mobility limitaons or severe contractures.
Benets Of A Daily Standing
The use of any stand-up device should be done only under the
prescripon and supervision of a medical professional.
At the outset, it is recommended that your introducon to
regular standing be closely monitored by your Physical or
Occupaonal Therapist.
It has been documented that the regular and cyclical acvity of
going from the seated to the standing posion may oer many
benets to those that are no longer able to stand on their
own. The benets are two fold:
1) there is the ability to once again funcon in daily acvies
that necessitate standing (reaching le cabinets and
equipment in the workplace, accessing cupboards/stoves/
shelving at home, as well as the ability to interact eye to eye);
and,
2) the potenal of physical benets that result from repeated
standing (these benets may include improved; range of
moon, bone density, circulaon, bowel and bladder funcon,
etc.).
WARNING!
Elevaon to standing posion:
• Elevaon to standing posion and operaon in standing
posion must only be done on a at surface. When the
chair is in elevated posion, never reach out from the chair,
due the higher pping risk.
• The operaon of the Stand Up funcon (and other pre-
dened seang posions) will cause mulple actuators to
operate simultaneously.
• If the seang system operates unintenonally or erracally
immediately switch o the system with the On/O buon.
CAUTION!
Posioning Belt:
Quickie posioning belts are designed to posion the user only
and will not protect you in an accident. You may even receive
further injury from the belts.
3.3 Indicaons And Contraindicaons
Indicaons And Contraindicaon For The Use Of Stand-Up
Wheelchairs.
These indicaons and contraindicaons are based on general
observaons. The condions for regular standing training
varies from person to person and should be individually
agreed with a doctor or therapist.
Only a doctor or therapist can decide which method and safe
standing training can be achieved with the Quickie wheelchair.
Indicaons
The Quickie Q700-Up M/F wheelchair with Standing funcon
is specically developed for people who have lost to their
ability to stand (e.g. paraplegia, mulple sclerosis, cerebral
palsy etc.). Standing is used for therapy and prophylaxis of:
• Osteoporosis: Without regular standing / vercal stress of
the bones, bone density can steadily decrease. This leads to
the risk of bone fractures and other complicaons.
• Decubitus prophylaxis: Whilst standing the pressure on the
ischial tuberosity is reduced to a minimum.
• Skeletal misalignments / back pain: Whilst seated the
spinal column is naturally elongated (kyphosis/hunchback).
Standing facilitates a natural spinal posion and therefore
beer upper body stability. This prevents the risk of a
scoliosis.
• Muscular atrophy: Without regular leg movement, the
risk of muscle shortening increases (muscular atrophy)
and consequently contractures may develop. Regular,
self-standing training help as movement therapy, thereby
avoiding contractures and prevenng possible associated
pains and expensive operaons.
• Tonus regulaon of spascity: Frequent standing helps
to reduce spascity and facilitates seat movement and
posioning in the wheelchair or bed. This supports a
peaceful sleep.
• Deeper respiraon: Straightening the upper body through
standing decreases the pressure of the abdominal cavity on
the lungs. This improves and deepens respiraon, facilitates
breathing and can also help reduce the risk of pneumonia.
• Gastrointesnal complicaons: As with breathing, standing
also reduces the pressure on the digesve system. This
facilitates digeson (intesnal peristalsis) and helps with the
improvement of bowl and bladder funcons.