Combined lifts
Combined lifts present special risks. This is where two or more chain blocks are used simultaneously
on the same load. Danger to persons and risk of material damage can arise through dynamic stresses
and uneven load distribution causing overload on individual blocks. Combined lifts must therefore be
supervised by a competent person with experience in this type of lift.
Daily checks
After every working day on which the chain block has been used, the following should be checked:
Is the chain block deformed or otherwise damaged? Are any parts missing?
Is any deformation or other damage visible on the suspension device (eye, shackle, bolt, trolley
etc.)?
Are the hooks intact or have any hooks opened? Are the hook latches correct and functional?
Wipe down the chain block and oil the load chain as required.
The load chain must be undamaged, i.e. no signs of wear and no deformed or otherwise
damaged links.
The load chain must not be kinked or twisted. With two-fall or multi-fall chain blocks there is a risk
of the chain twisting if the bottom hook assembly ends up looped through the chain sling –usually
during refitting or moving the chain block between work stations. See Fig 3.
The hand chain must also be in good condition.
The brake function must be intact.
In the event of faults or failures, the hoist must be repaired and carefully checked by a specialist before
reuse.
Continuous maintenance - lubrication
Oil the hook latches and bearings. Grease the pawl and ratchet and also the gear. Lubrication must be
sparingly and carefully applied so no grease gets on the brake disk. Oil the load chain for longer life.
Periodic checks
Periodic checks are normally carried out yearly to detect and remedy any faults. If required (e.g. high
frequency of use), more frequent checks may be carried out. See “Checklist for periodic checks”.
Measure hooks and chain to detect any changes in shape.
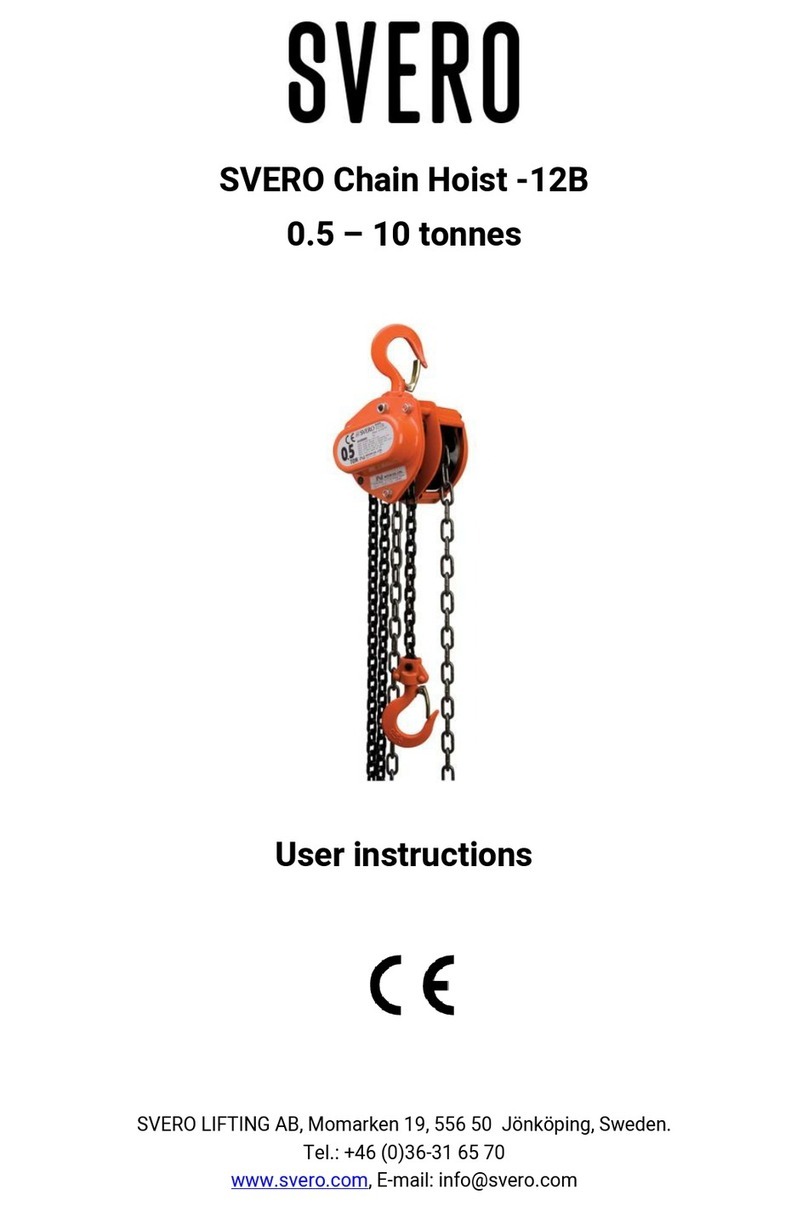
Checks on load hook (see Fig. 4 and Table 1)
Opening dimension A on the hooks is important. A hook with too large a maximum dimension has been
exposed to overloading or overheating. It therefore does not have the necessary load capacity. The
hooks may also have been exposed to long-term wear (dimension B).