4 EN
thermohygrometer BC25
Information about the device
Device description
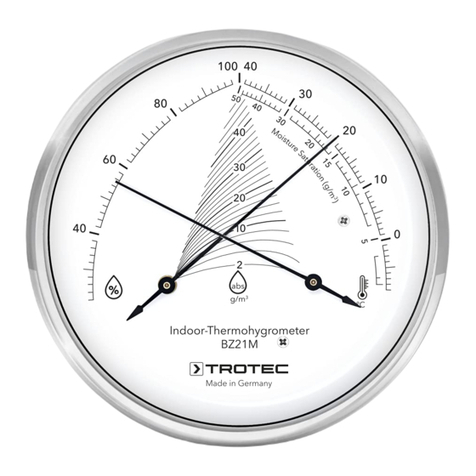
The thermohygrometer BC25 can be used to determine the air,
dew point and wet-bulb temperature as well as the humidity
level of indoor areas.
For assessing the measurements, a Max/Min function
(maximum and minimum value), an average value and a Hold
function for freezing the currently measured value are also
available.
Moreover, the heat index (HI) and apparent temperature
(WBGT index) can be determined. A configurable alarm function
issues a warning as soon as a certain value is exceeded.
When not in use, an automatic switch-off saves the battery.
Heat index
The heat index, also referred to as humidex, is an indicator
developed in the 1970s by the American Steadman. It describes
the combined effect of temperature and (high) humidity levels
on the human body.
The higher the relative humidity, the worse or slower does the
moisture (perspiration) emitted by the human body evaporate as
the ambient air can only absorb little additional moisture.
This evaporation, however, is necessary for the human
organism to be able to regulate itself in case of strong heat or
physical exertion and to keep the core body temperature on a
healthy level. If this natural cooling mechanism is slowed down,
the body can no longer discharge the generated heat properly,
which results in so-called heat stress. Overheating or heat
strokes can be among the health consequences.
Even without any physical effort, high temperatures combined
with high humidity levels (muggy heat) are therefore generally
considered as unpleasant, while high temperatures and low
humidity values are more tolerable.
Sweating and the associated cooling effect are thus vitally
important for both humans and many mammals, and are
indispensable for the physical well-being.
wet-bulb globe temperature index (WBGT index)
The wet-bulb globe temperature index is a climate index
developed by the US army as early as in the 1950s. It serves to
specify the effects of the current climate on the human body.
Unlike the heat index, the WBGT does not only incorporate the
air temperature (dry-bulb temperature) and humidity level, but
also the wind speed, the wet-bulb and radiation temperature
(globe temperature) for assessing the outdoor thermal stress.
The wet-bulb temperature (or theoretical limit of cooling) is the
lowest temperature that can be reached through direct
evaporative cooling only. It is determined by wrapping a cotton
cloth soaked with distilled water around the measuring tip or
mercury bulb of a thermometer and then exposing it to the
environment. The cooling effect achieved by the evaporated
water can thus be measured and simulated for the perspiring
human body under these conditions.
The radiation temperature, which is also taken into
consideration, is measured inside a thin-walled matt black
globe reacting to the infrared heat radiation emitted by the sun.
When calculating the WBGT in indoor areas or outdoor areas
exposed to negligible amounts of sunlight, it can be assumed
that the radiation temperature has practically no influence. In
this case, the globe temperature is assumed to be identical with
the ambient temperature.
Therefore, the WBGT index is another indicator for determining
the climate effects on the human organism. It is, however, even
more informative than the heat index since additional
parameters are included in the calculation. Established as an
international standard, it is described in ISO7243 and
DINEN27243.