! "# $ %
! "# $ %
Table of Contents
ITC-Series Inverter Page 3 Owner’s Manual 8/07/03
Table of Contents
1 SYSTEM FEATURES AND SPECIFICATIONS
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
7
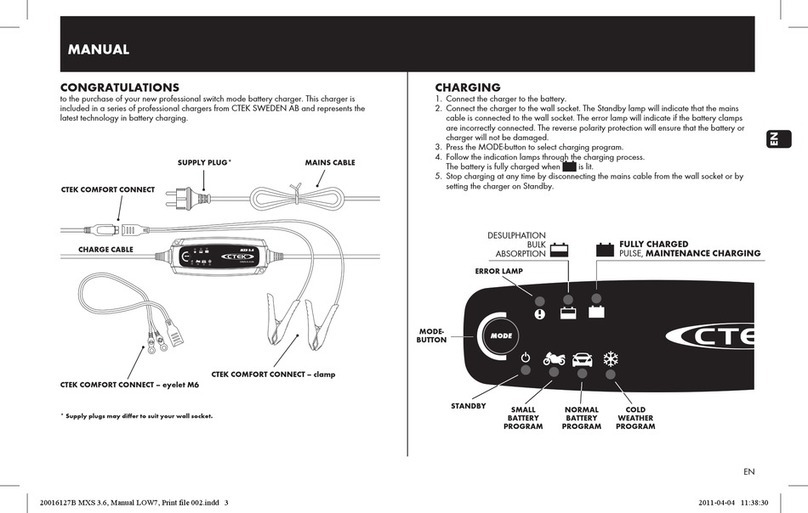
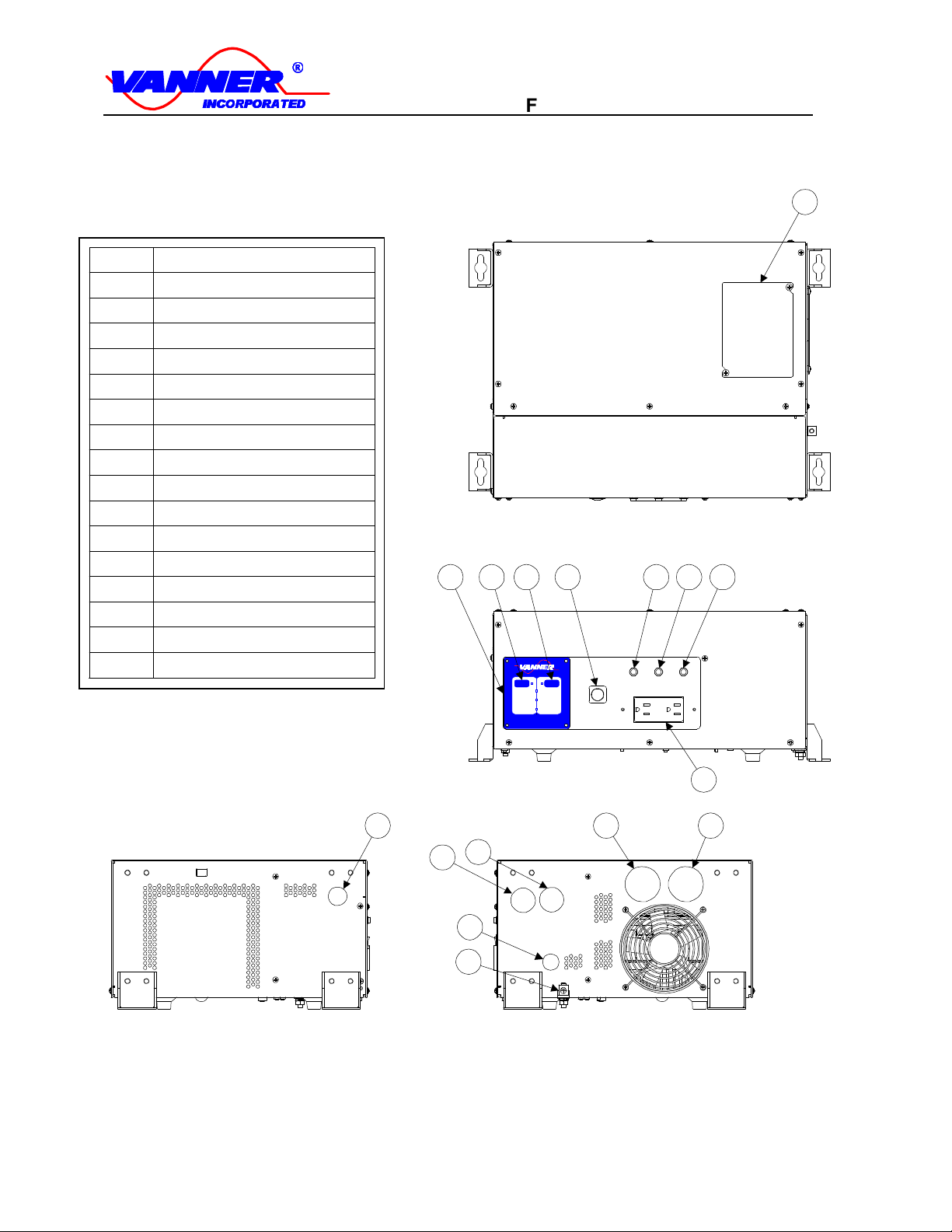
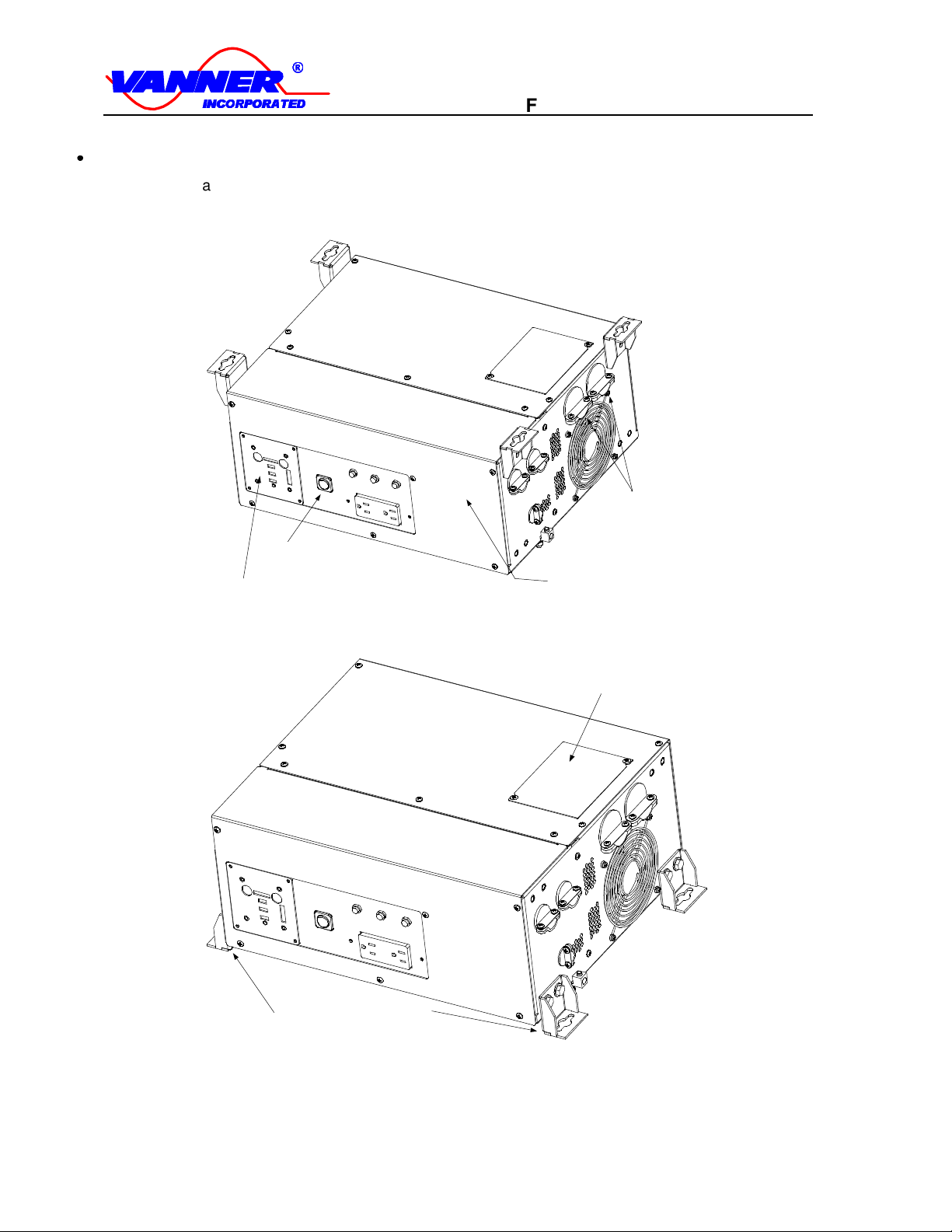
1.4 COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/LOCATION
................................
................................
................................
8
2 DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION
................................
................................
................................
.........................
................................
................................
................................
................................
............................
................................
................................
................................
................................
14
2.3 GEN START/AUTO-THROTTLE
................................
................................
................................
..........................
15
2.4 CHARGER AND APM PROGRAMMING
................................
................................
................................
16
3CUSTOMER WIRING IDENTIFICATION
................................
................................
................................
17
3.1 AC INPUT & OUTPUT WIRING
................................
................................
................................
.........................
17
3.2 DC (BATTERY) WIRING
................................
................................
................................
................................
17
3.3 FRONT PANEL CONTROL/DISPLAY OUTLET
................................
................................
................................
17
3.4 SYSTEM ON/OFF SWITCH
................................
................................
................................
................................
18
3.5 REMOTE SIGNAL CONTACTS
................................
................................
................................
.............................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
21
4.4 SYSTEM START-UP AND TESTING
................................
................................
................................
23
5 GENERAL INFORMATION SECTION
................................
................................
................................
23
5.1 GENERIC INVERTER DESCRIPTION
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
................................
24
5.3 DC POWER CONSUMPTION
................................
................................
................................
...............................
25
5.4 BATTERY TERMINOLOGY AND RATINGS
................................
................................
................................
25
5.5 SIZING THE INVERTER BATTERY
................................
................................
................................
27
5.6 BATTERY AND CHARGING SYSTEM CONSIDERATIONS
................................
................................
27
5.7 BATTERY CHARGING GUIDELINES
................................
................................
................................
28
6 MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
................................
................................
................................
29
6.1 PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
................................
................................
................................