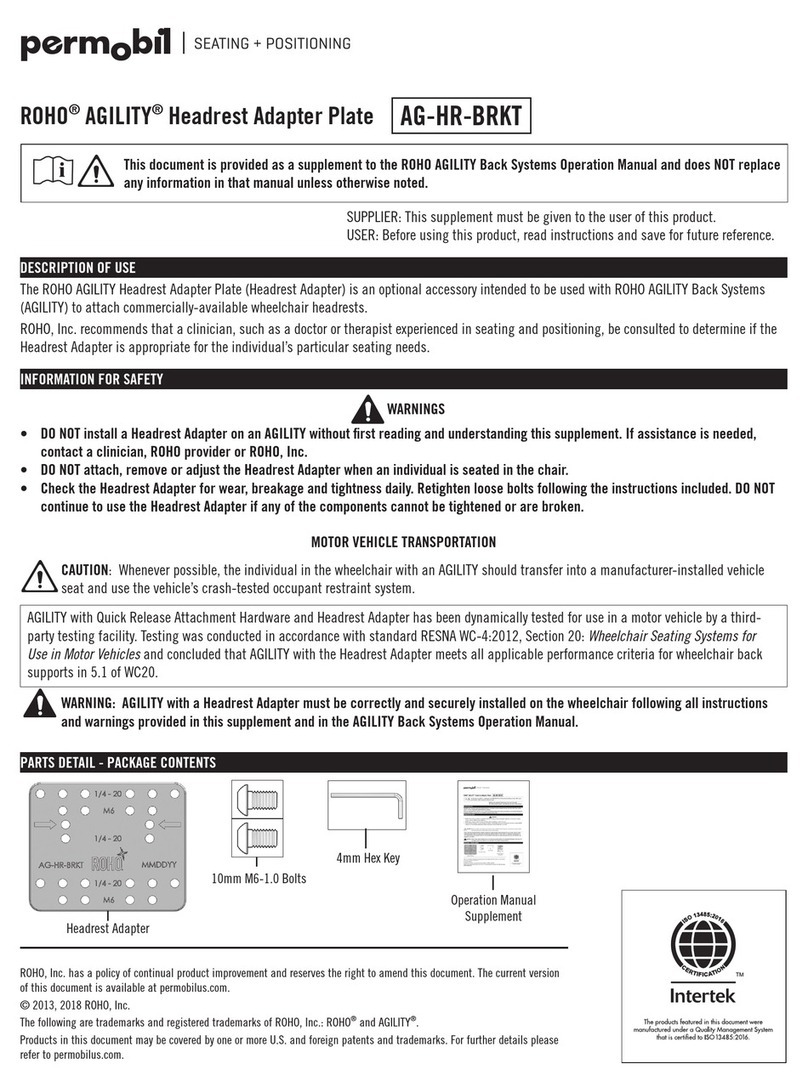
Chapter 1 Introduction 9
An ISDN connection enables you to have a conversation with someone
using one B-channel while you are connected to the Internet using the
other B-channel. The D-channel is typically used to carry network con-
trol and status information such as dialed numbers, and answer and
hang-up information. An analog connection only provides a single
channel (voice, fax, or data).
Setting Up ISDN Service
To use ISDN you must contact your local phone service provider to get
the service started. ISDN is connected through standard phone wires,
just like an ordinary analog line. The telephone wiring coming into
most homes has four wires. Each analog or ISDN line requires two
wires. If you have only one telephone line now, ISDN can usually be
installed on the remaining two wires without additional wiring. If you
have two analog lines now and you don’t plan to replace the second line
with ISDN, you will probably need to have a new ISDN line installed.
Business installations depend on the type of equipment, number of in-
stalled lines, and other factors. Your telephone company business office
can assist you in determining the best ISDN installation alternative.
Appendix D lists phone numbers for regional Bell operating companies
that offer ISDN service.
Setting Up Phone Numbers
When ordering ISDN service from your phone company you should
request two ISDN phone numbers, called Directory Numbers (DNs).
They are the numbers people will use to dial the two channels of your
ISDN TA. Typically you would use one DN for data (remote access and
fax) and the other for voice calls.
In ordering ISDN service you may get Service Profile Identifier num-
bers (SPIDs) for each DN. Usually the SPIDs are necessary in config-
uring your network connection.
You will also need to ask the phone company which switch type you
will be connected to. You need to know which switch type in order to
properly set up your ISDN connection.
This product has been tested for support of EZ-ISDN. If your local
phone company supports it, EZ-ISDN is a fast, easy way to order ISDN
service.
We have made it very simple for you to request ISDN service by using
the ISDN Service Installation Flyer included in your package. Refer to
this flyer during the process of ordering service.