10
Ringback These parameters control the ringback tone you
will hear when you make a call over VoIP. The
parameter format is F1, F2, Tn, Tf, Tn, Tf.
Call Waiting These parameters control the call waiting tone
you will hear when someone tries to call you
while you are already on a call over VoIP. The
parameter format is F1, F2, Tn, Tf, Tn, Tf.
Alert These parameters control the alert tone that will
prompt you to enter a number while you are
configuring a supplementary feature such as
call forwarding. The parameter format is F1, F2,
Tn, Tf, Tn, Tf.
Congestion These parameters control the tone you will hear
if a VoIP call fails for a reason other than a busy
number. The parameter format is F1, F2, Tn, Tf,
Tn, Tf.
Recall Not applicable.
Stutter Dialtone These parameters control the tone you hear
when unconditional call forwarding is enabled.
The parameter format is F1, F2, Td, Tn, Tf.
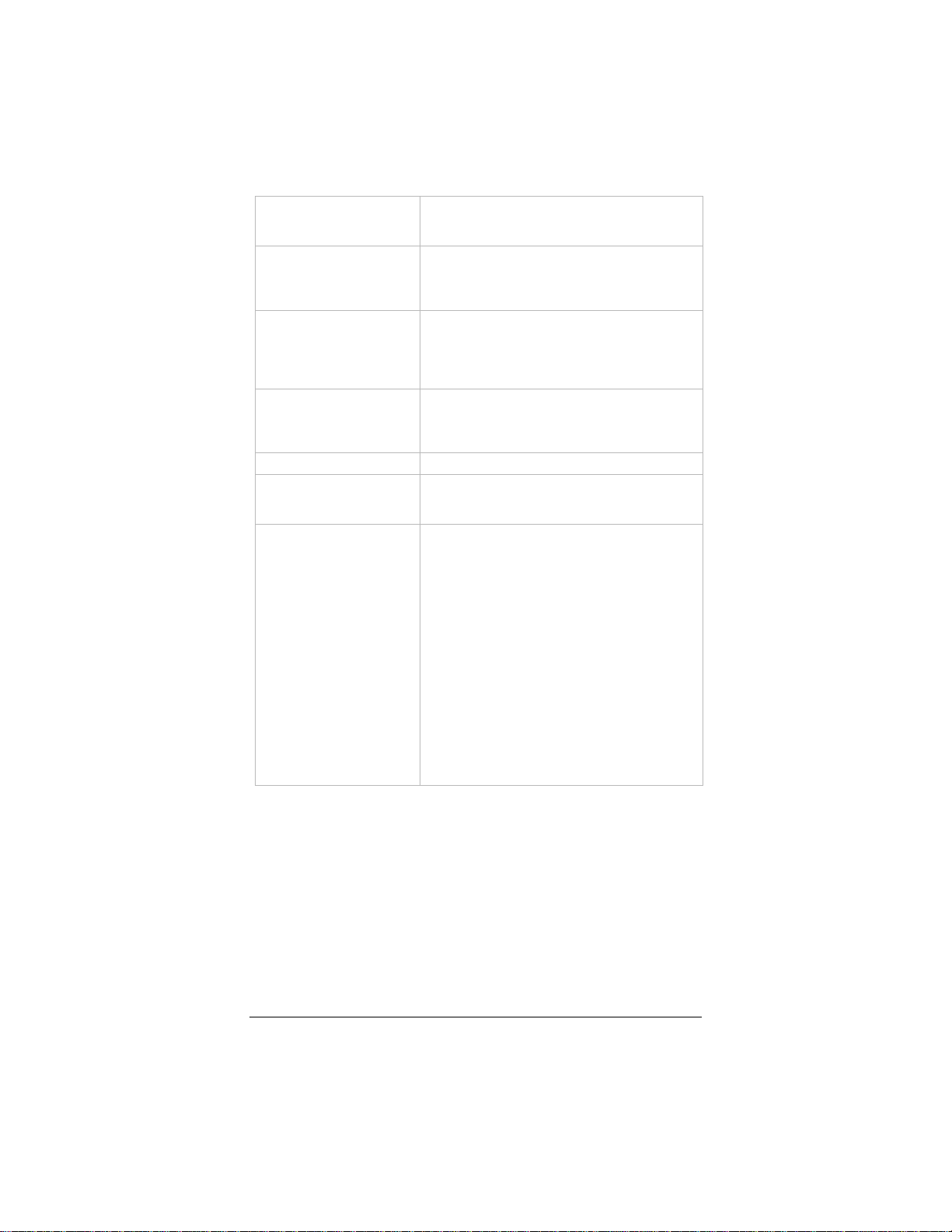
Action DISPLAY_CURR(ent)_COUNTRY_DETAILS is
the default.
To save changes to a new country, select
ADD_NEW_COUNTRY, click Save Changes
and then Write Settings to Flash and Reboot.
After reboot, the new country will appear on the
Working Country list and on the Select Ring &
Tone by Country/Region list on the Voice
over IP page.
To save changes to a country already on the
Working Country list, select EDIT_SEL(ected)_
COUNTRY, click Save Changes and then
Write Settings to Flash and Reboot.
To delete a country from the Working Country
list, select the country from the list, select
DELETE_SEL(ected)_COUNTRY, click Save
Changes and then Write Settings to Flash
and Reboot.
Note: If you know that the values you want are a close match to
those of another country, you can save time by doing the following:
•From the Voice over IP page, select that country and then
reboot your X5v or V3.
•Click New Country. Now you have to change only those
values that don’t match yours.
Be aware that it is not a requirement that the ring and tone settings
match those of any one particular country. You can set up any
tones that you like. The main reason to match certain tones to your