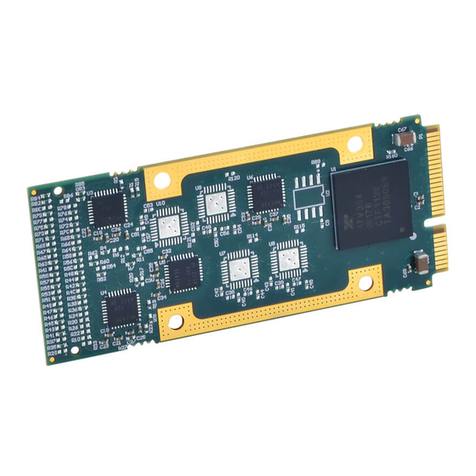
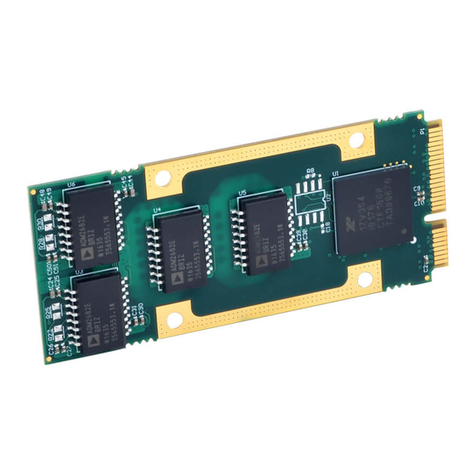
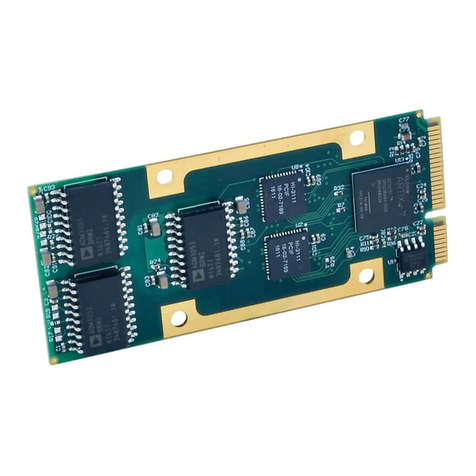
Method 1 –Calibration Using The Built-In Browser Interface:
1. Make sure the base output range is currently selected. This is 4-20mA
for 972EN models, or 0-10V for 973EN models. You can go back and
use the Test Page controls to change the output range as required.
2. Bring up the browser interface and select the Calibration Page.
3. Select an output channel, then select Zero.
4. Click the “Set Output” button and an “ideal” zero count will be written to
the DAC. The output will go to approximately zero.
At this point, you will lose control of the output and must complete the
procedure, or simply click “restart calibration” to start over. If you picked
the wrong output channel, or the wrong endpoint, click “restart
calibration” to start over.
5. With a meter connected to measure the output signal, measure the
actual output level and enter this value into the edit box labeled “DVM
Reading”. Then click the “Calibrate” button to complete calibration of the
zero endpoint.
6. Next select Span (for best results, always calibrate zero before span).
7. Click the “Set Output” button and an “ideal” full-scale count (20000) will
be written to the DAC. The output will go to approximately full-scale.
At this point, you will again lose control of the output and must complete
the procedure, or simply click “restart calibration” to start over. If you
picked the wrong output channel, or wrong endpoint, click “restart
calibration” to start over.
8. With a meter connected to measure the output signal, measure the
actual output and enter this value into the edit box labeled “DVM
Reading”. Then click the “Calibrate” button to complete calibration of the
full-scale endpoint.
9. Repeat steps 3-8 for the other output channels to be calibrated.
Method 2 - Calibration Via The Modbus TCP/IP Interface:
1. Write to the appropriate Output Range Register to select the output base
range for each channel to be calibrated. Select 4-20mA for 972EN
models, or 0-10V for 973EN models.
2. Write 24106 (5E2AH) into the Calibration Access Register to remove
write protection from the calibration registers.
3. Write the zero calibration % value to the output to be calibrated and
adjust this value as necessary to precisely reproduce the Cal LOW
(zero) signal (see table of prior page). Allow the output to settle a few
seconds.
4. Write a 16-bit value to the Zero Calibration Register with a set bit in the
bit position that corresponds to the channel number to be calibrated (one
channel at a time). If you were calibrating the zero of channel 5, you
would write 0x0010 to the Zero Calibration Register. The module will
replace calibration coefficients immediately, no reset needed.
5. Write the full-scale calibration signal % value to the output to be
calibrated and allow the output to settle about 10 seconds.
6. Write a 16-bit value to the Span Calibration Register with a set bit in the
bit position that corresponds to the channel number of the channel to be
calibrated (one channel at a time). For example, if you wanted to
calibrate the span of channel 0, write 0x0001 to the “Span Cal Register”.
Note that the calibration of the output sub-ranges are automatically
interpolated based on the calibration of the base range just completed.