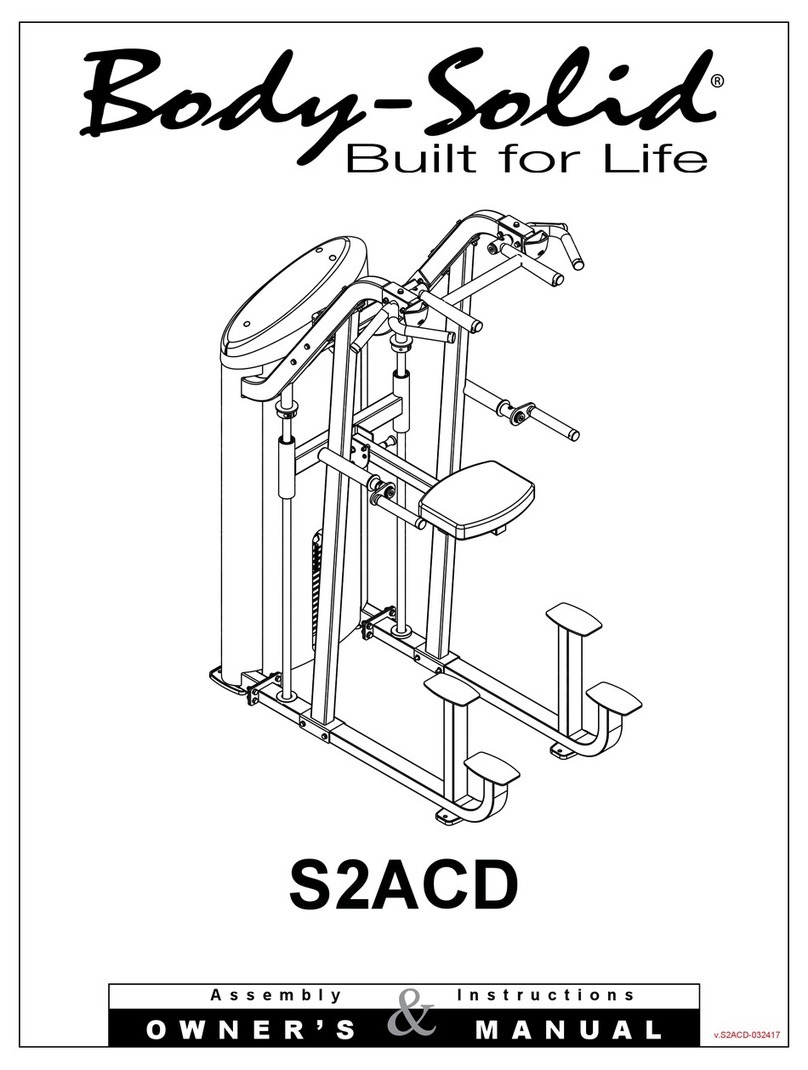
Before You Begin
Retain this Owner's Manual for future reference!
To maximize your use of the equipment please study this Owner's Manual thoroughly. Please retain this
manual for future reference or parts information.
Thank ou for purchasing the GCEC-340.
This g m is part of the Bod -Solid line of qualit
strength training machines, which let ou target spe
cific muscle groups to achieve better muscle tone
and overall bod conditioning.
Unpacking the Equipment
The GCEC-340 is carefull tested and inspected be
fore shipment. We have shipped the unit in several
pieces that require assembl . Ask for assistance dur
ing the assembl process. Carefull unpack the boxes
and la the pieces on the floor near the area where
ou plan to use the equipment.
The GCEC-340 is designed for our enjo ment. B fol
lowing these precautions and using common sense,
ou will have man safe and pleasurable hours of
healthful exercise with our Bod -Solid GCEC-340.
After assembl , ou should check all functions to en
sure correct operation. If ou experience problems,
or if an items are missing, first recheck the assembl
instructions to locate an possible errors made dur
ing assembl . If ou are unable to correct the prob
lem, call the dealer from whom ou purchased the
machine or call 1-800-556-3113 for the dealer near
est ou.
Obtaining Service
Please use this Owner's Manual to make sure that all
parts have been included in our shipment. When
ordering parts, ou must use the part number and
description from this Owner's Manual. Use onl Bod -
Solid replacement parts when servicing this unit. Fail
ure to do so will void our warrant and could result in
personal injur .
For information about product operation or service,
check out the official Bod -Solid website at www.
bod solid.com or contact an authorized Bod -Solid
dealer or a Bod -Solid factor -authorized service
compan or contact Bod -Solid customer service, M-F
8:30am-5:00pm CST, at one of the following:
*
or write to:
Toll Free: (800) 556-3113
Local: (708) 427-3555
Fax: (708) 427-3556
E-mail: service@bod solid.com
Bod -Solid, Inc.
Service Department
1900 S. Des Plaines Ave.
Forest Park, IL 60130 USA
Body-Solid continually seeks ways to improve the performance, specifications and product manuals in order to ensure that only superior products are re
leased from our factories. Please take the time to carefully read through this manual thoroughly. nstructions contained in this document are not intended
to cover all details or variations possible with Body-Solid equipment, or to cover every contingency that may be met in conjunction with installation,
operation, maintenance or troubleshooting of the equipment. Even though we have prepared this manual with extreme care, neither the publisher nor the
author can accept responsibility for any errors in, or omission from, the information given. Should additional information be required, or should situations
arise that are not covered by this manual, the matter should be directed to your local Body-Solid representative, or the Service Department at Body-Solid
nc. in Forest Park, llinois.
An Questions?
Call (800) 556-3113
5