Table of Contents
5
4.2.6. Network Configuration............................................................................................................35
Figure 4-3: EtherNet / IP Module Features................................................................................................38
Table 4-2: Ethernet Status Indicators.........................................................................................................38
Figure 4-4: PROFIBUS Module Features..................................................................................................39
Table 4-3: PROFIBUS Status Indicators ...................................................................................................39
4.3. Startup......................................................................................................................................... 40
4.3.1. Pre-Power Checks ...................................................................................................................40
4.3.2. Startup Procedure and Checks.................................................................................................41
4.4. Operational Adjustments............................................................................................................41
5. MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING...............................................................................43
5.1. Periodic Testing..........................................................................................................................43
5.2. Maintenance Items......................................................................................................................43
5.3. Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................... 43
5.3.1. Green Control power light not illuminated..............................................................................43
5.3.2. Amber DC bus light not on......................................................................................................44
5.3.3. Blown DC bus fuse..................................................................................................................44
5.3.4. Fan runs constantly..................................................................................................................44
5.3.5. Fan doesn’t run ........................................................................................................................44
5.3.6. Status contact won’t close .......................................................................................................45
5.3.7. Module over-temp, or module seems too hot..........................................................................45
5.3.8. Drive trips on Overvoltage......................................................................................................46
5.3.9. Braking light flickers...............................................................................................................46
5.3.10. Red Braking light stays on all the time....................................................................................47
5.3.11. Master unit appears to function properly, but slave units do not seem to follow the master...47
5.3.12. EtherNet/IP Link Sensed light does not turn on......................................................................47
5.3.13. EtherNet/IP Module Status LED is solid red, flashing red, or flashing green.........................47
5.3.14. EtherNet/IP Network Status LED is solid red.........................................................................47
5.3.15. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Offline light is red.................................................................................48
5.3.16. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Diagnostics light is blinking .................................................................48
5.3.17. Attached Drive Will Not Precharge.........................................................................................48
5.4. Technical Help –Before You Call .............................................................................................48
6. ENGINEERING DATA................................................................................................................49
6.1. Ratings Charts.............................................................................................................................49
Table 6-1: Module Ratings: 230 –240 VAC Drives (375 VDC Setpoint) ................................................49
Table 6-2: Module Ratings: 380 –415 VAC Drives (620 VDC Setpoint) ................................................50
Table 6-3: Module Ratings: 460 –480 VAC Drives (750 VDC Setpoint) ................................................51
Table 6-4: Module Ratings: 575 –600 VAC Drives (940 VDC Setpoint) ................................................52
Table 6-5: Module Ratings: 690VAC Drives (1090 VDC Setpoint).........................................................53
6.2. Watt loss..................................................................................................................................... 53
Table 6-6: Watt Loss .................................................................................................................................53
6.3. UL 508A Short Circuit Current Rating ...................................................................................... 53
6.4. Fuse/Circuit Breaker Sizing and Rating .....................................................................................53
6.5. DC Bus Link Length Limits....................................................................................................... 54
Table 6-7: Maximum Inductance for DC Link Cable................................................................................54
Figure 6-1: DC Link ..................................................................................................................................54
6.6. Resistor Link Length Limits.......................................................................................................54
6.7. Dimensions and Mechanical Drawings ...................................................................................... 55
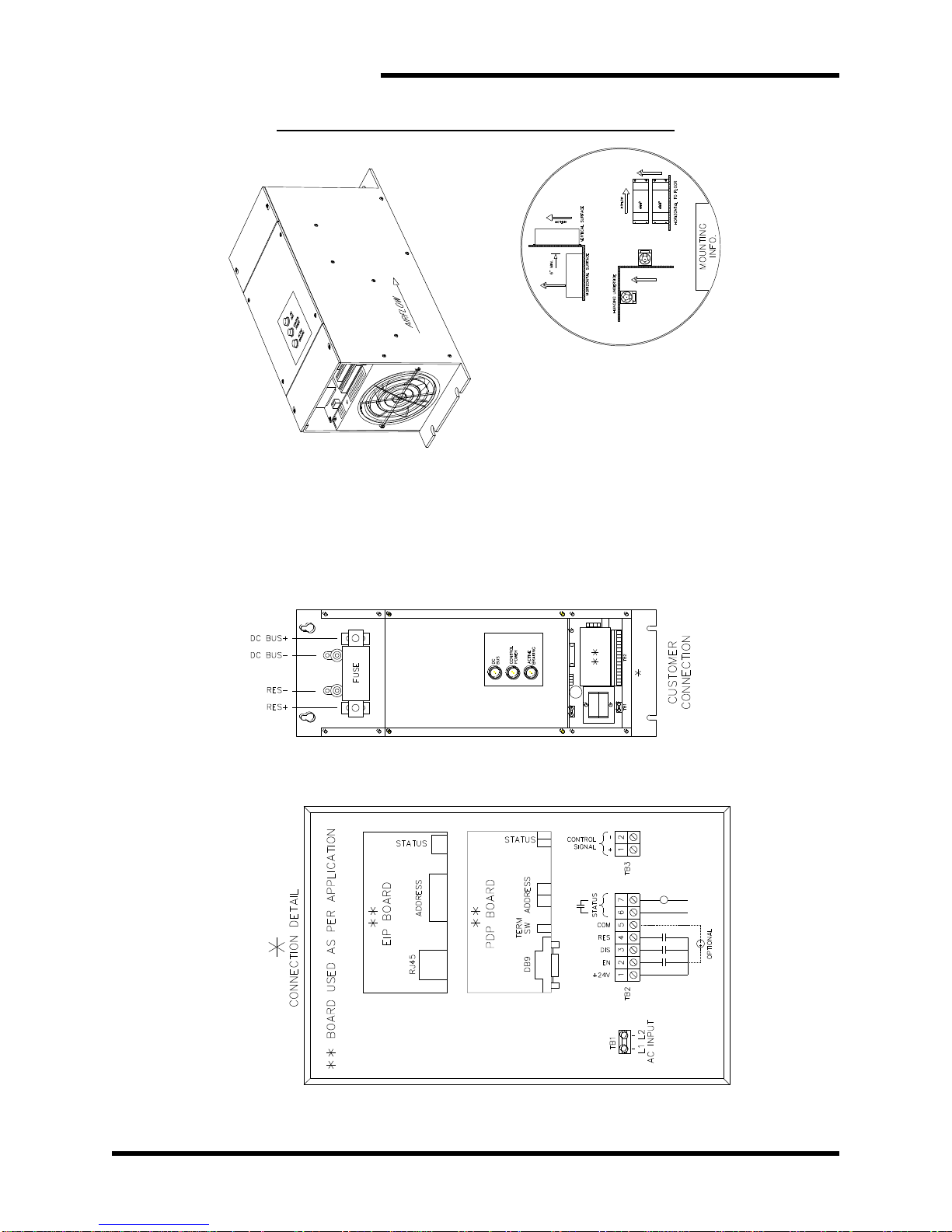
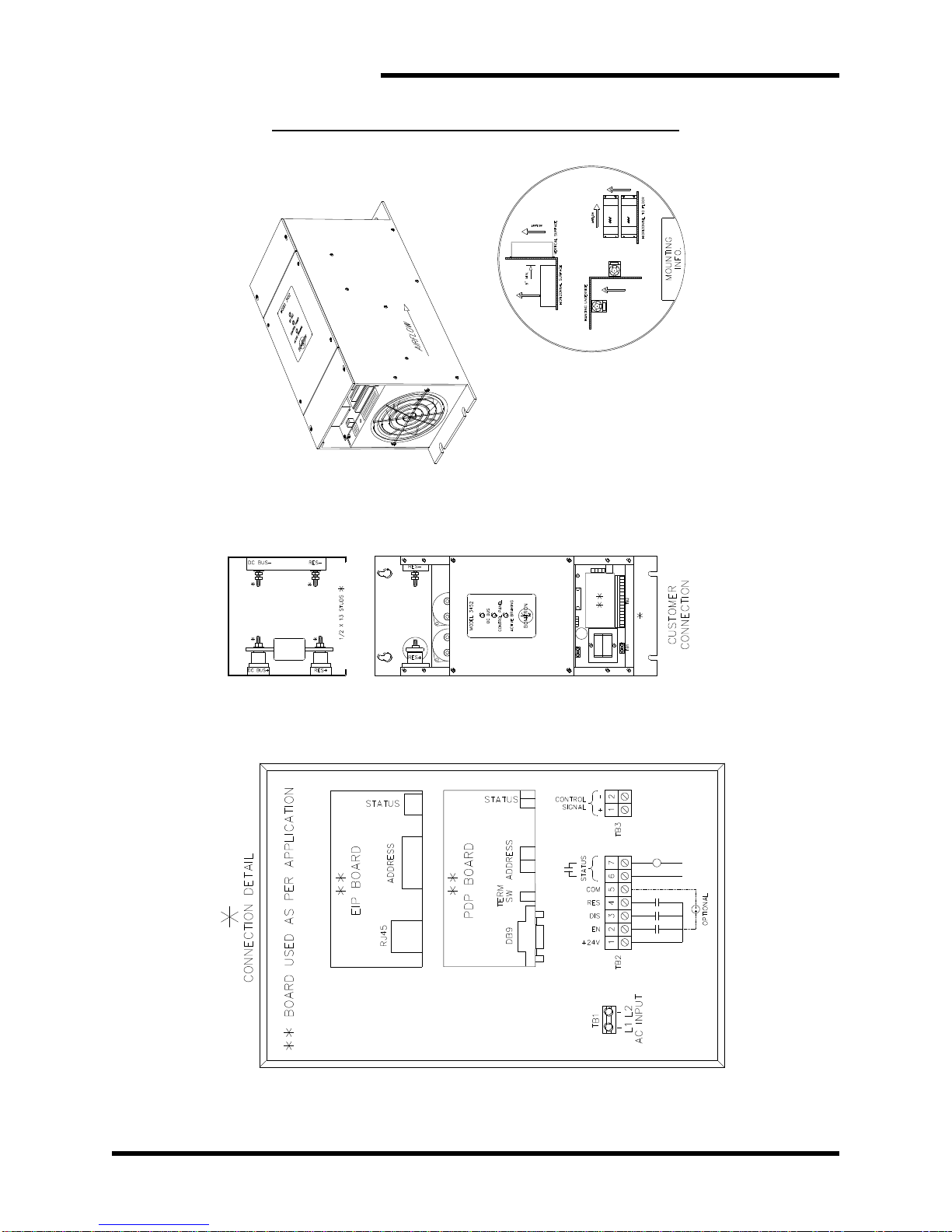
Figure 6-2: M3452 K6 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing.................................................................55
Figure 6-3: M3452 K9 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing.................................................................56
Figure 6-4: M3452 K10 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing...............................................................57
Figure 6-5: M3452 M14 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing ..............................................................58
Figure 6-6: M3452 T10 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing ...............................................................59