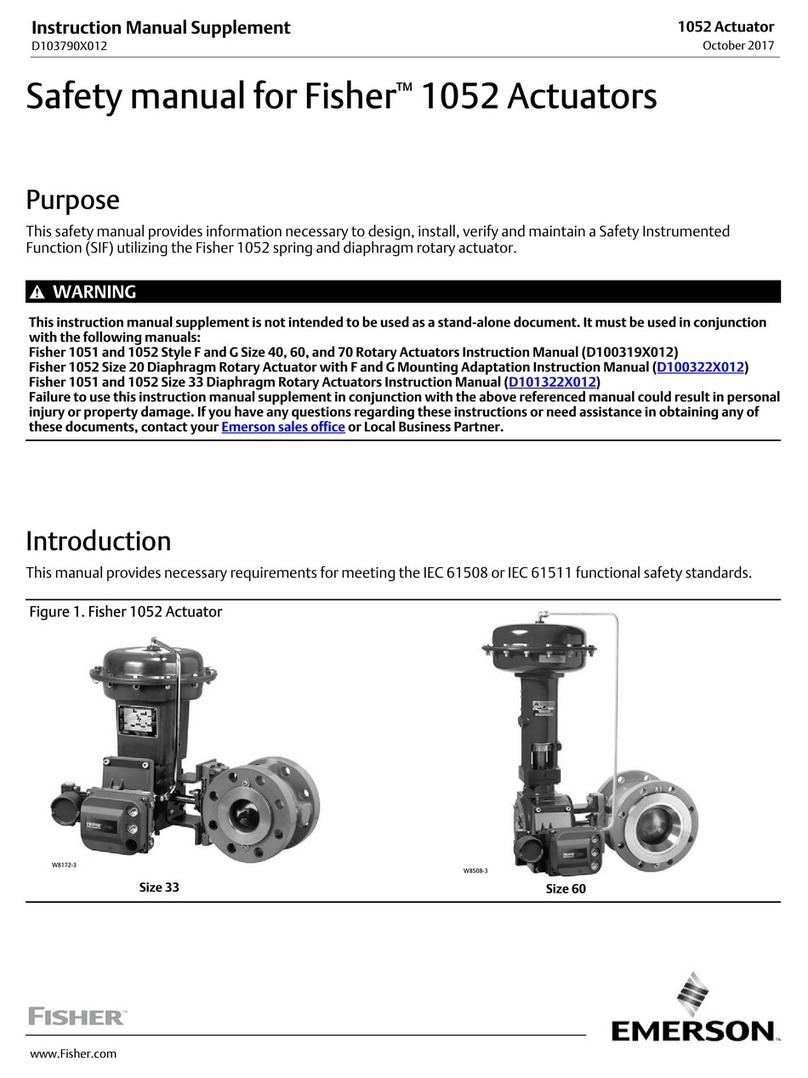
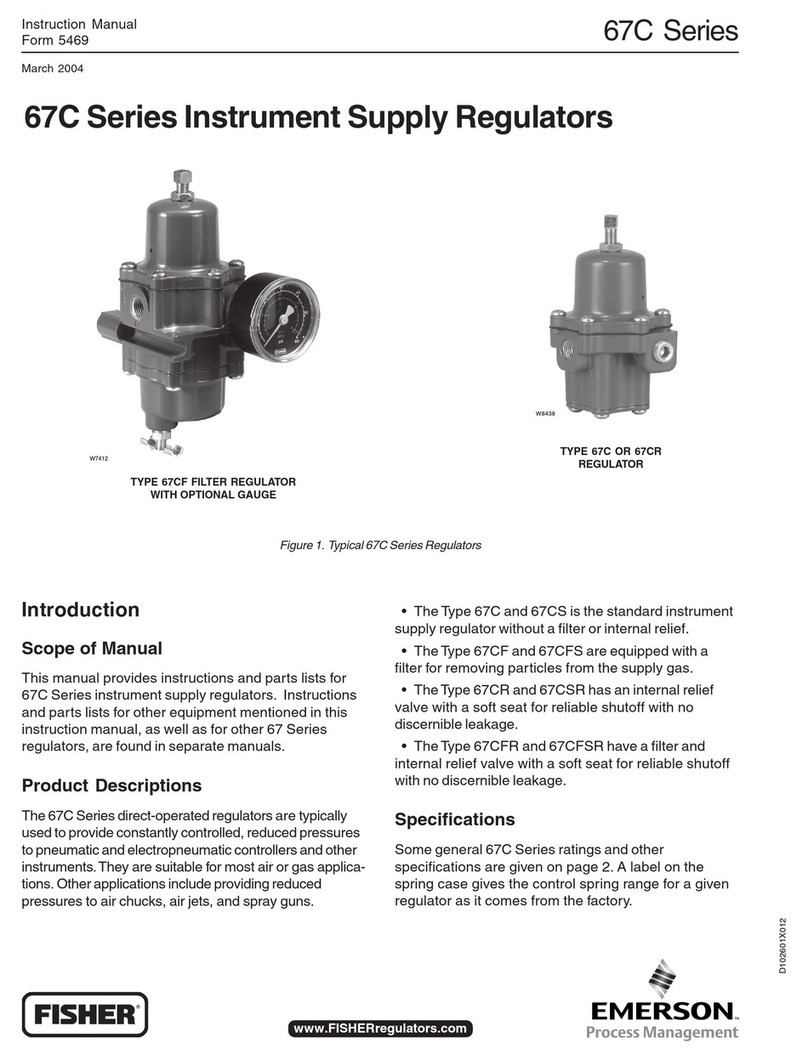
1305 Series
4
Overpressure Protection
1305 Series regulators have outlet pressure ratings
that are lower than the inlet pressure ratings. Some
type of overpressure protection (such as relief valve) is
necessary if the actual inlet pressure can exceed the
outlet pressure rating.
Maximum pressure ratings are stamped on the
nameplate. Maximum emergency outlet
(casing) pressures are 250 psig (17,2 bar) for
Type 1305C regulator and 550 psig (37,9 bar) for
Type 1305D regulator.
Overpressuring any portion of this
equipment may cause personal injury,
damage to regulator parts, or leaks
in the regulator due to bursting of
pressure-containing parts or explosion
of accumulated gas.
To avoid overpressure, provide an
appropriate overpressure protection
device to ensure that the pressure
limitations will not be exceeded.
The regulator should be inspected for
damage after any overpressure condition.
Adjustments
The regulator can be adjusted within the setting limits
stamped on the nameplate. Loosen the locknut
(key 20, Figure 4). To increase the outlet pressure
setting, turn the adjusting screw (key 19, Figure 4)
clockwise. Turn the adjusting screw counterclockwise
to decrease the outlet pressure setting.
If a different setting range is desired, choose an
appropriate spring from the parts list and substitute
it for the spring that is in the regulator. Be sure to
indicate the change on the nameplate.
Maintenance
!
WARNING
To avoid personal injury or equipment
damage from sudden release of pressure
or uncontrolled gas, do not attempt any
maintenance or disassembly without
rst isolating the regulator from system
pressure. Cautiously release all internal
pressure from the regulator before
attempting disassembly.
Parts such as the valve disk, orice, diaphragm,
and O-rings wear out even under normal conditions.
Normal wear of the valve disk and orice is
accelerated by high-pressure drops and large amounts
of impurities in the ow stream. External sources may
also cause damage to the regulator.
Inspect the regulator periodically or after any unusual
condition. Replace parts as necessary. The frequency
of inspection and replacement depends upon the
severity of service conditions or the requirements of
state and federal laws.
Instructions are given below for disassembly and
reassembly of these regulators. Figure 4 shows key
numbers for the 1305 Series regulators.
Disassembly
1. Disconnect the outlet piping.
2. Unscrew the union nut (key 8) and slide the
regulator out of the inlet adaptor (key 3).
3. The disk holder assembly (key 5) can be
unscrewed from the stem (key 6). Replace the
disk holder assembly if the seating surface is
worn or nicked.
4. Check, and replace if necessary, O-ring (key 7).
5. Loosen hex nut (key 20) and turn the adjusting
screw (key 19) counterclockwise to ease the
spring compression on the diaphragm.
6. Remove the machine screws (key 21). Lift off
the spring case (key 2), spring (key 17), and
upper spring seat (key 18).
7. Take hex nut (key 16) off of the pusher post
(key 11).
8. Lift off the diaphragm head (key 15) and
diaphragms (key 14).
9. An O-ring (key 13, not shown) is mounted on
the lever pin (key 12). Unscrew the lever pin
from the body and check the O-ring.
10. Take the bafe (key 28), pusher post assembly
(key 11), and lever assembly (key 10) out of
the body. Separate the lever from the pusher
post. Slip the bafe off of the pusher post to
check O-ring (key 30, if present).