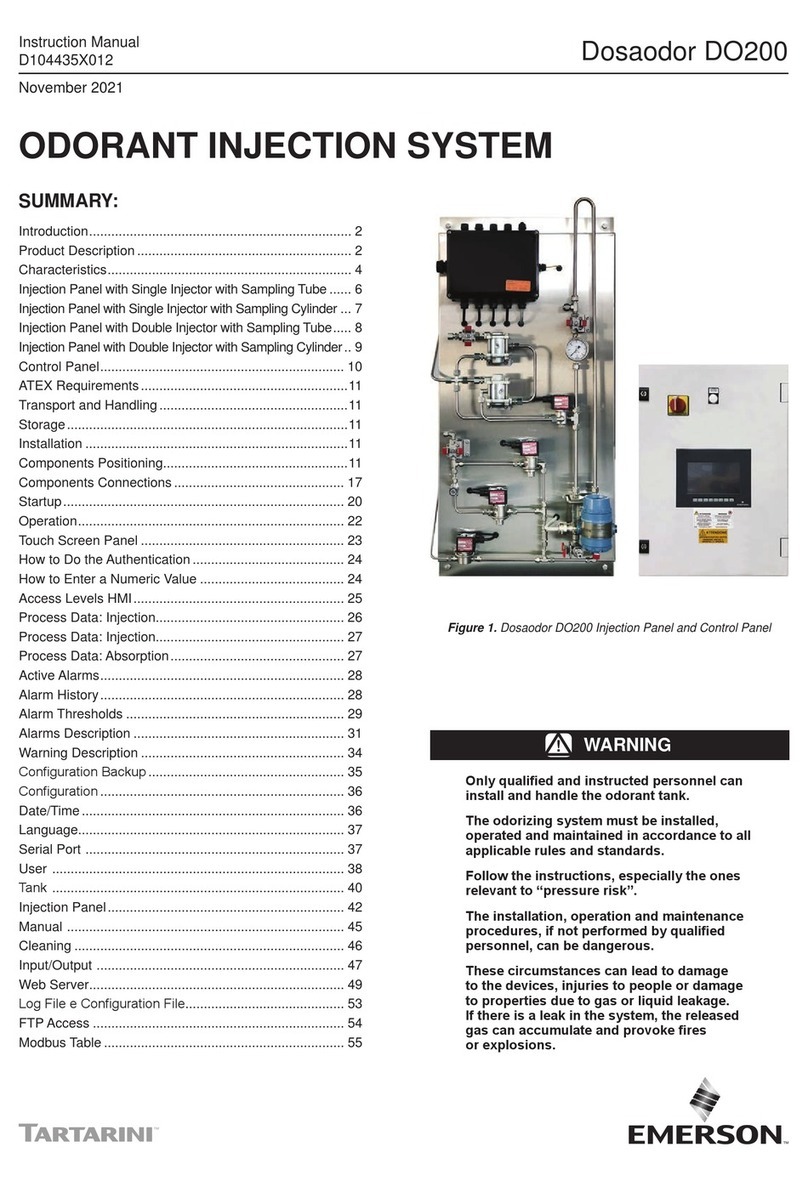
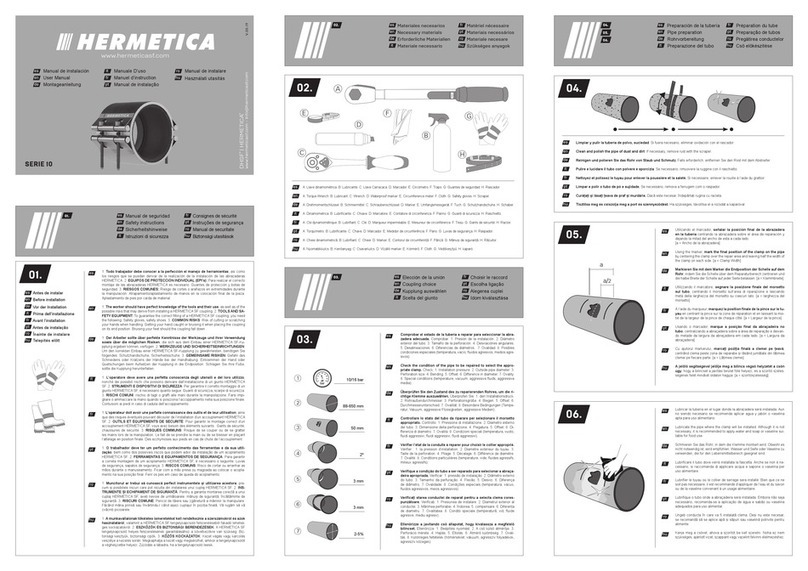
16. Open liquid odorant ll tubing valve to odorant
calibration cylinder and check for leaks.
17. Do a manual rell of the odorant calibration
cylinder; check for any leaks in tubing and ttings
and correct operation of magnetic switches.
18. Do a purge of the odorant calibration cylinder (for
training and correct operation of components).
19. Rell odorant calibration cylinder.
20. Set operation mode to Manual and set ow rate
to high level (50,000 MCFH to 75,000 MCFH)
in order to push odorant through the injection
solenoids and remaining tubing down to
the pipeline.
21. Once odorant appears in sight glass, place
system in Automatic mode and continue setting up
conguration parameters.
22. Observe rst rell of odorant calibration cylinder
and recalculation of injector ow coefcient.
23. After a period of operation and allowing several
odorant calibration cylinder rells, analyze actual
injection rate against target. To conrm everything is
working correctly locate a calibration rell (at the top
of the hour) in the event log. Next, nd where there
was another rell at the top of another hour, this
may be several hours or even days later. Count the
number of rells that occurred during that time. The
volume of the odorant calibration cylinder tells you
how much odorant was measured into the pipeline
during that time. Referring to the computer, you can
add up the gas ow during that same period since
AGA calculations are summarized for each hour at
the top of the hour. Now you can divide the volume
of odorant you calculated by the gas ow volume for
the same period and verify the injection rate.
Injection System Conguration Schemes
The Type DOSAODOR-D product works using the
differential pressure that is present in regulating
station. For non-differential applications (no regulating
stations involved) please refer to appropriate solutions
and related documentation.
Installation schematic depends on the application and
needs of the customer. In the following pages, good
practices and best practices will be described.
Just to give an idea about different congurations and
installation options (see Figures 4 and 5), the following
are the most common:
1. Additional odorant ow control valve may be used
on odorant liquid line when odorant storage tank
is maintained at P2 + ∆P. ∆P = 8.7 to 21.7 psi /
0.60 to 1.5 bar. CV for built-in control valve
(position 23, Figures 12, 13): CV= 0.11. Odorant
calibration cylinder rell time should be contained
in the 45 to 120 seconds. If these constraints
cannot be satised tuning the built-in ow control
valve, an additional ow control valve must be
used according to working conditions, to obtain
the required rell time. Swagelok ow control
(metering) valves are recommended: M and
31 Series.
2. Optional 3-way valve for pressurizing odorant
storage tank to P2 + ∆P. ∆P = 8.7 to 21.7 psi / 0.60
to 1.5 bar when tank is maintained at P2. When
the 3-way valve is not energized then the storage
tank is maintained at (oats with) P2. When it is
energized for a liquid rell of the odorant calibration
cylinder then the pressure begins going up towards
P2 + ∆P bar until the rell is completed.
3. Optional 3-way valve for maintaining odorant
storage tank at P2. This is commonly used with
option 2. Refer to Figure 5.
4. Option for odorant storage tank relief to P2. If
P2 pressure (refer to Figures 4 and 5) is highly
variable or there is excess buildup of pressure
in the storage tank due to temperature changes
and at the same option 2 is not used, then a
simple pressure relief valve may be needed to
relieve excess pressure from the storage tank into
P2 stream.
5. Option for odorant calibration cylinder relief to P2.
If the pressures in P2 are highly variable, like what
may occur in a straight line pipe with no regulator
station, then the pressure in the odorant calibration
cylinder may be raised to a value that is too high
for the system to work properly during operations.
To resolve this issue a relief valve may be installed
across the 3-way valve on the pneumatic panel, to
vent excess pressure from the odorant calibration
cylinder into the downstream pipeline.
6. Options for utilizing odorant storage tank as a
bypass or absorption system. This functionality may
be activated by the Type Dosaodor-D system when
disabled or in fault.
9
Type Dosaodor-D