Table of Contents
1 Overview 5
1.1 General ................................................... 5
1.1.1 Introduction ................................................ 5
1.1.2 Warranty .................................................. 5
1.1.3 RoHS .................................................... 5
1.1.4 DisposalandWEEE ............................................ 5
1.1.5 Safety Recommendations and Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1.6 ElectrostaticDischarge .......................................... 6
1.1.7 Electromagnetic Compatibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 Features................................................... 6
1.3 Deliverables ................................................ 6
1.4 Accessories................................................. 6
1.4.1 ReferenceDesign ............................................. 6
1.4.2 Mercury+PE1BaseBoard ........................................ 7
1.5 IntelToolSupport............................................. 7
2 Module Description 8
2.1 BlockDiagram............................................... 8
2.2 Module Configuration and Product Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3 Article Numbers and Article Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
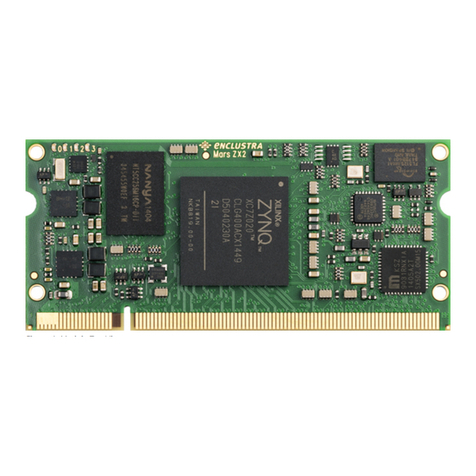
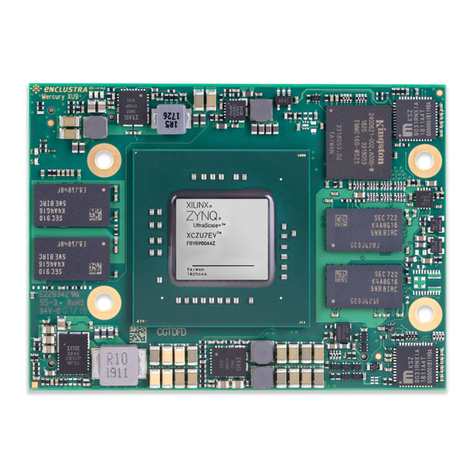
2.4 TopandBottomViews .......................................... 11
2.4.1 TopView .................................................. 11
2.4.2 BottomView................................................ 11
2.5 Top and Bottom Assembly Drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.5.1 TopAssemblyDrawing .......................................... 12
2.5.2 BottomAssemblyDrawing........................................ 12
2.6 ModuleFootprint ............................................. 13
2.7 MechanicalData.............................................. 14
2.8 ModuleConnector ............................................ 14
2.9 UserI/O................................................... 15
2.9.1 Pinout.................................................... 15
2.9.2 Dual-PurposePins............................................. 17
2.9.3 DifferentialI/Os .............................................. 18
2.9.4 I/OBanks.................................................. 18
2.9.5 VREFUsage................................................. 19
2.9.6 VCC_IOUsage ............................................... 19
2.9.7 SignalTerminations ............................................ 21
2.10 Power.................................................... 21
2.10.1 PowerGenerationOverview ....................................... 21
2.10.2 PowerEnable/PowerGood........................................ 21
2.10.3 VoltageSupplyInputs........................................... 22
2.10.4 VoltageSupplyOutputs ......................................... 22
2.10.5 PowerConsumption............................................ 23
2.10.6 HeatDissipation.............................................. 23
2.11 ClockGeneration ............................................. 24
2.12 Reset .................................................... 24
2.13 LEDs..................................................... 24
2.14 DDR2SDRAM ............................................... 25
2.14.1 DDR2SDRAMType ............................................ 25
2.14.2 SignalDescription............................................. 26
2.14.3 Termination................................................. 26
2.14.4 Parameters................................................. 26
2.15 SPIFlash .................................................. 27
2.15.1 SPIFlashType ............................................... 27
D-0000-421-002 3 / 50 Version 05, 25.07.2019